Desert climates feature extremely low precipitation, intense heat during the day, and drastic temperature drops at night, creating harsh living conditions. These arid environments influence unique plant and animal adaptations essential for survival. Discover how desert climates shape ecosystems and affect human activities in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
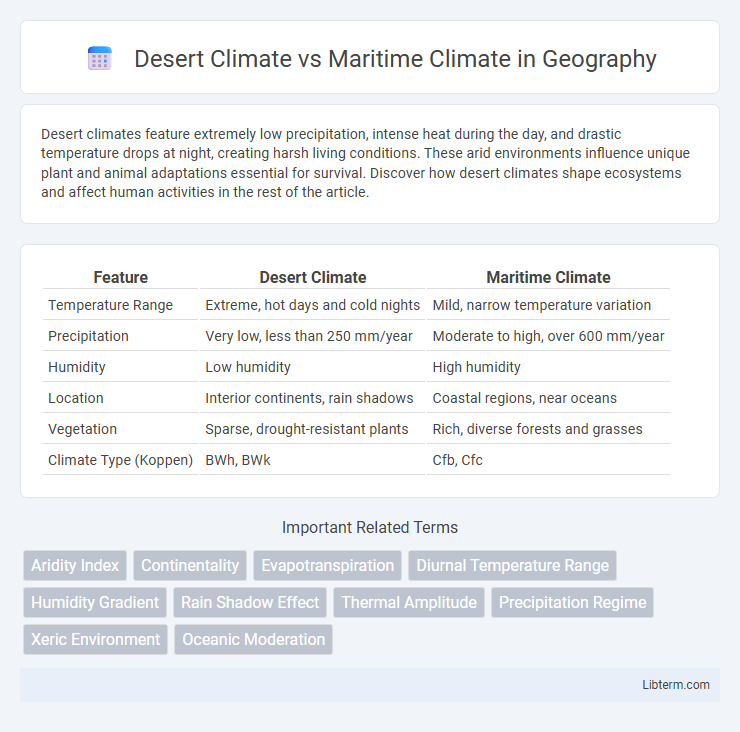
| Feature | Desert Climate | Maritime Climate |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Extreme, hot days and cold nights | Mild, narrow temperature variation |
| Precipitation | Very low, less than 250 mm/year | Moderate to high, over 600 mm/year |
| Humidity | Low humidity | High humidity |
| Location | Interior continents, rain shadows | Coastal regions, near oceans |
| Vegetation | Sparse, drought-resistant plants | Rich, diverse forests and grasses |
| Climate Type (Koppen) | BWh, BWk | Cfb, Cfc |
Introduction to Desert and Maritime Climates
Desert climates are characterized by extremely low precipitation, high temperature variations, and sparse vegetation, often found in regions such as the Sahara and Arabian deserts. Maritime climates experience moderate temperatures and higher humidity due to their proximity to oceans, typical in coastal areas like the Pacific Northwest and Western Europe. The stark contrast in moisture availability and temperature stability defines the unique ecological and weather patterns of each climate type.
Geographic Distribution: Where These Climates Occur
Desert climates predominantly occur in the subtropical regions around 20deg to 30deg latitude, such as the Sahara Desert in Northern Africa and the Arabian Peninsula, characterized by limited precipitation and extreme temperature variations. Maritime climates are found along western coasts between 40deg and 60deg latitudes, including areas like the Pacific Northwest in North America and Western Europe, influenced by proximity to large bodies of water that moderate temperatures. These distinct geographic distributions result from differing atmospheric circulation patterns and the presence or absence of oceanic influence.
Key Characteristics of Desert Climates
Desert climates exhibit extremely low precipitation, often less than 250 millimeters annually, coupled with high temperature fluctuations between day and night. These arid regions experience intense solar radiation, minimal humidity, and sparse vegetation adapted to drought conditions. The significant diurnal temperature variation and scarce rainfall define the harsh environment typical of desert climates, contrasting sharply with the moderating influence of maritime climates.
Key Characteristics of Maritime Climates
Maritime climates are characterized by mild temperatures, high humidity, and abundant precipitation due to their proximity to large bodies of water, which moderate temperature extremes. These regions experience cooler summers and warmer winters compared to desert climates, where temperature fluctuations are more extreme. The consistent moisture and stable temperatures in maritime climates support lush vegetation and diverse ecosystems unlike the arid, sparse landscapes found in deserts.
Temperature Variations: Extremes vs. Moderation
Desert climates experience extreme temperature variations with scorching daytime heat often exceeding 40degC (104degF) and rapid nighttime drops that can fall to near freezing due to low humidity and clear skies. Maritime climates maintain moderate temperatures throughout the year, rarely reaching extremes, because large bodies of water regulate heat by absorbing warmth during the day and releasing it at night. The ocean's high specific heat capacity creates a stable thermal environment, resulting in milder summers and winters compared to the sharp fluctuations found in desert regions.
Precipitation Patterns and Water Availability
Desert climates experience extremely low precipitation, often less than 250 millimeters per year, resulting in scarce water availability and arid conditions. Maritime climates, influenced by proximity to oceans, receive abundant and evenly distributed rainfall throughout the year, supporting diverse ecosystems and reliable freshwater resources. These contrasting precipitation patterns directly impact soil moisture levels, vegetation cover, and the sustainability of water-dependent human activities in each climate zone.
Effects on Local Flora and Fauna
Desert climates, characterized by extreme temperature fluctuations and minimal precipitation, limit local flora to drought-resistant species like cacti and succulents, while fauna includes nocturnal animals adapted to conserve water. Maritime climates exhibit moderate temperatures and high humidity, supporting diverse plant life such as temperate forests and lush vegetation, which in turn sustains a wide variety of birds, mammals, and insects adapted to moist environments. These climatic conditions directly influence the biodiversity, survival strategies, and distribution of species in their respective ecosystems.
Human Adaptations and Settlement Patterns
Desert climates, characterized by extreme heat and low precipitation, force humans to adapt through building insulated, shaded structures and developing water conservation techniques such as rainwater harvesting and underground storage. Settlement patterns in deserts often concentrate around scarce water sources like oases or rivers, leading to sparse and dispersed populations. In contrast, maritime climates offer moderate temperatures and high humidity, encouraging dense coastal settlements with architecture designed for ventilation and flood resistance, supporting agriculture reliant on consistent rainfall.
Climate Change Impacts on Desert and Maritime Regions
Desert climates experience intensified heatwaves and prolonged droughts due to climate change, exacerbating water scarcity and threatening local ecosystems. Maritime climates face rising sea levels and increased storm frequency, causing coastal erosion and habitat disruption. Both regions require tailored adaptation strategies to mitigate the distinct impacts of global warming on their environments and communities.
Conclusion: Comparing and Contrasting Desert and Maritime Climates
Desert climates are characterized by extremely low precipitation and high temperature variation between day and night, while maritime climates feature moderate temperatures and consistent moisture due to proximity to large water bodies. The contrast lies primarily in humidity levels and temperature stability, with deserts being arid and maritime regions maintaining humid, mild conditions year-round. Understanding these differences is crucial for ecological management, agriculture, and urban planning in respective regions.
Desert Climate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com