Estuaries are dynamic coastal areas where freshwater from rivers meets and mixes with saltwater from the ocean, creating unique and highly productive ecosystems. These environments serve as vital habitats for diverse wildlife, support commercial fisheries, and act as natural buffers against storms and flooding. Explore the rest of this article to understand how estuaries impact your environment and contribute to ecological balance.
Table of Comparison
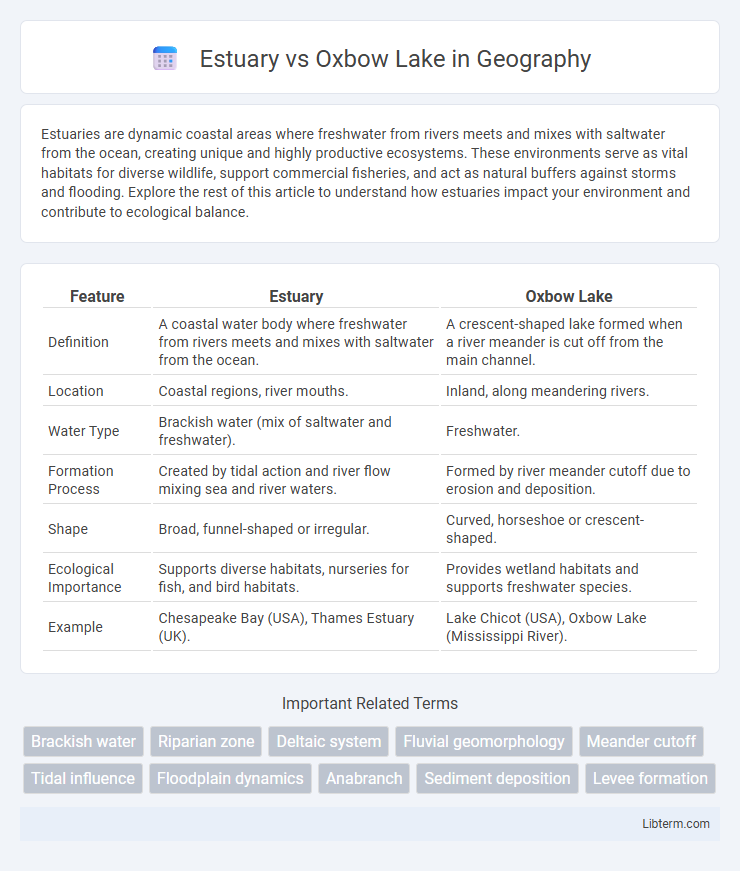
| Feature | Estuary | Oxbow Lake |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A coastal water body where freshwater from rivers meets and mixes with saltwater from the ocean. | A crescent-shaped lake formed when a river meander is cut off from the main channel. |
| Location | Coastal regions, river mouths. | Inland, along meandering rivers. |
| Water Type | Brackish water (mix of saltwater and freshwater). | Freshwater. |
| Formation Process | Created by tidal action and river flow mixing sea and river waters. | Formed by river meander cutoff due to erosion and deposition. |
| Shape | Broad, funnel-shaped or irregular. | Curved, horseshoe or crescent-shaped. |
| Ecological Importance | Supports diverse habitats, nurseries for fish, and bird habitats. | Provides wetland habitats and supports freshwater species. |
| Example | Chesapeake Bay (USA), Thames Estuary (UK). | Lake Chicot (USA), Oxbow Lake (Mississippi River). |
Introduction to Estuaries and Oxbow Lakes
Estuaries are dynamic coastal water bodies where freshwater from rivers meets and mixes with saltwater from the ocean, creating nutrient-rich environments that support diverse ecosystems. Oxbow lakes form from abandoned river meanders, creating isolated freshwater bodies that serve as important habitats for various plant and animal species. Both estuaries and oxbow lakes play crucial roles in maintaining ecological balance and supporting biodiversity in their respective regions.
Defining Estuaries
Estuaries are dynamic coastal water bodies where freshwater from rivers meets and mixes with saltwater from the ocean, creating a unique brackish environment rich in biodiversity. These transitional zones act as nurseries for marine life, support diverse ecosystems, and serve essential roles in nutrient cycling and water filtration. Unlike oxbow lakes, which are isolated, crescent-shaped water bodies formed from abandoned river meanders, estuaries maintain continuous tidal flow and ecological connectivity to both river and ocean systems.
Understanding Oxbow Lakes
Oxbow lakes form when a meandering river creates a cutoff, isolating a curved section of the river and transforming it into a crescent-shaped water body. These lakes are characterized by their distinct shape and are typically found in floodplains where sediment deposition seals off the former river channel. Understanding oxbow lakes involves recognizing their role in river dynamics, supporting diverse ecosystems, and serving as indicators of past fluvial processes.
Formation Processes: Estuary vs Oxbow Lake
Estuaries form where freshwater rivers meet and mix with ocean saltwater, creating a dynamic environment shaped by tidal forces and sediment accumulation. Oxbow lakes develop from meandering river bends that become cut off due to sediment deposition, isolating a water body from the main river channel. Estuary formation involves tidal interaction and sediment exchange, whereas oxbow lakes result primarily from fluvial erosion and depositional processes.
Key Physical Characteristics
Estuaries are coastal water bodies where freshwater from rivers meets and mixes with saltwater from the ocean, characterized by brackish water, tidal flows, and high nutrient levels supporting diverse ecosystems. Oxbow lakes form as crescent-shaped bodies of water created when a meander of a river is cut off from the main channel, featuring freshwater, stagnant water, and often surrounded by floodplain vegetation. Estuaries typically have dynamic salinity gradients and tidal influences, whereas oxbow lakes have stable freshwater conditions with limited water exchange.
Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Estuaries support diverse ecosystems due to the mixing of freshwater and saltwater, creating habitats for numerous species such as fish, birds, and invertebrates. Oxbow lakes, formed from cut-off river meanders, provide freshwater habitats that support amphibians, aquatic plants, and specific fish adapted to calmer waters. The high nutrient levels in estuaries enhance productivity, while oxbow lakes often serve as important breeding grounds and refuge for freshwater biodiversity.
Hydrological Differences
Estuaries are dynamic coastal bodies of water where freshwater from rivers mixes with saltwater from the ocean, creating brackish water and tidal influences that drive complex hydrological processes. Oxbow lakes form inland as isolated, crescent-shaped freshwater bodies created when a meander from a river is cut off, resulting in stagnant or slow-moving water without tidal effects or salinity gradients. The primary hydrological difference lies in estuaries exhibiting continuous water exchange and salinity variation, whereas oxbow lakes experience limited water flow and stable freshwater conditions.
Human Impact and Significance
Estuaries serve as crucial habitats for diverse aquatic species and act as natural filters that improve water quality, but urban development and industrial pollution threaten their ecological balance. Oxbow lakes, formed from abandoned river channels, provide important wetlands that support biodiversity and help regulate flooding; however, they are vulnerable to drainage and land reclamation driven by agricultural expansion. Both ecosystems hold significant cultural and economic value through fishing, recreation, and tourism, yet human activities increasingly challenge their preservation and sustainability.
Conservation Challenges
Estuaries face conservation challenges such as pollution from agricultural runoff, habitat destruction due to urban development, and vulnerability to climate change-induced sea level rise. Oxbow lakes encounter threats like sedimentation, invasive species colonization, and water quality deterioration from nearby land use activities. Both ecosystems require targeted management strategies to preserve their biodiversity and ecological functions amid increasing anthropogenic pressures.
Summary: Comparing Estuaries and Oxbow Lakes
Estuaries are dynamic coastal water bodies where freshwater from rivers mixes with saltwater from the ocean, creating nutrient-rich habitats that support diverse ecosystems and commercial fisheries. Oxbow lakes form inland as curved lakes created by the meandering and cutoff of river bends, characterized by freshwater with limited tidal influence and lower biodiversity compared to estuaries. Both feature water-based habitats but differ significantly in salinity, formation processes, and ecological roles within their respective environments.
Estuary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com