Understanding climatology reveals patterns in Earth's long-term weather changes and helps predict future climate trends impacting ecosystems and human activities. This scientific field studies atmospheric conditions over decades to centuries, offering insights into global warming, extreme weather events, and natural climate variability. Dive into the rest of the article to explore how climatology influences your environment and daily life.
Table of Comparison
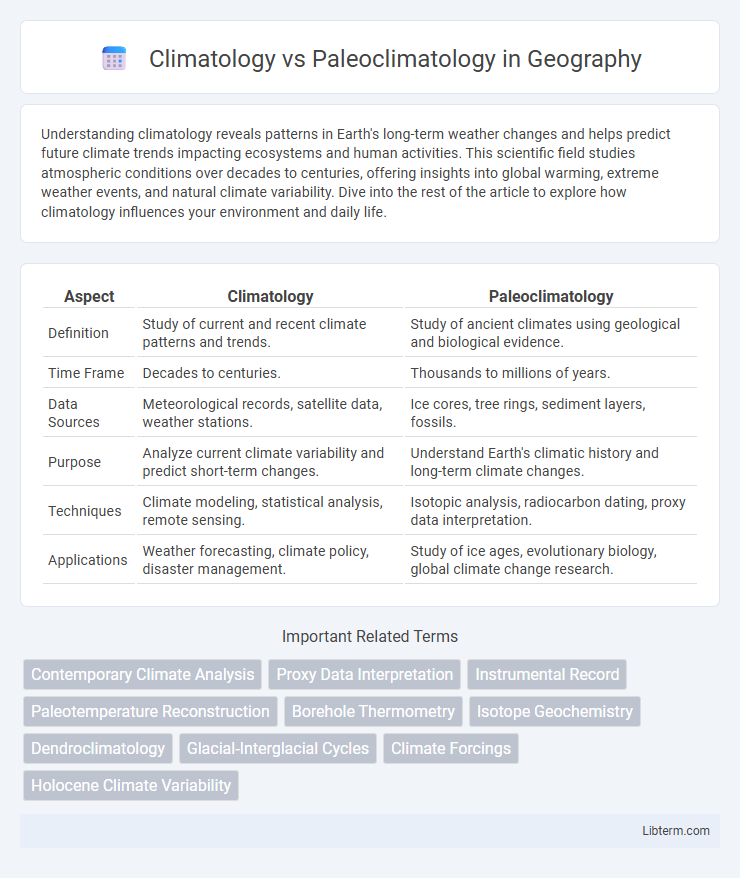
| Aspect | Climatology | Paleoclimatology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of current and recent climate patterns and trends. | Study of ancient climates using geological and biological evidence. |
| Time Frame | Decades to centuries. | Thousands to millions of years. |
| Data Sources | Meteorological records, satellite data, weather stations. | Ice cores, tree rings, sediment layers, fossils. |
| Purpose | Analyze current climate variability and predict short-term changes. | Understand Earth's climatic history and long-term climate changes. |
| Techniques | Climate modeling, statistical analysis, remote sensing. | Isotopic analysis, radiocarbon dating, proxy data interpretation. |
| Applications | Weather forecasting, climate policy, disaster management. | Study of ice ages, evolutionary biology, global climate change research. |
Introduction to Climatology and Paleoclimatology
Climatology studies current atmospheric conditions and climate patterns to understand weather variability and long-term trends on Earth. Paleoclimatology examines ancient climate data from ice cores, tree rings, and sediment layers to reconstruct past climate changes over millions of years. Together, these disciplines provide comprehensive insights into climate dynamics, both present and historical, essential for modeling future climate scenarios.
Defining Climatology: Focus and Scope
Climatology is the scientific study of climate patterns, atmospheric conditions, and their variations over time, emphasizing current and regional weather phenomena and long-term trends. It encompasses the analysis of temperature, precipitation, humidity, wind patterns, and atmospheric pressure to understand and predict climate behavior. This discipline provides critical insights into climate variability, climate change, and their impacts on ecosystems and human activities.
What is Paleoclimatology?
Paleoclimatology is the scientific study of Earth's past climates, using data derived from natural recorders such as ice cores, tree rings, sediment layers, and coral reefs. It aims to reconstruct climate conditions over millions of years to understand long-term environmental changes and natural climate variability. This field provides crucial insights into how Earth's climate system has responded to factors like volcanic activity, solar radiation, and greenhouse gas concentrations throughout geological history.
Key Differences Between Climatology and Paleoclimatology
Climatology examines current and recent atmospheric conditions to understand weather patterns and climate trends, emphasizing data recorded from the modern era such as temperature, precipitation, and wind measurements. Paleoclimatology investigates Earth's ancient climates by analyzing proxy data sources like ice cores, tree rings, and sediment layers to reconstruct climate changes over millions of years. The key difference lies in climatology's focus on present and near-present climate dynamics, whereas paleoclimatology explores long-term climate variability and evolutionary climate shifts in the geological past.
Research Methods in Climatology
Research methods in climatology primarily involve the analysis of contemporary atmospheric data collected through weather stations, satellite observations, and climate models to study current climate patterns and predict future trends. Techniques such as remote sensing, climate simulation models, and statistical analysis enable climatologists to understand temperature fluctuations, precipitation rates, and atmospheric circulation. These methods differ from paleoclimatology, which relies on proxy data like ice cores, tree rings, and sediment records to reconstruct past climate conditions.
Techniques Used in Paleoclimatology
Paleoclimatology employs techniques such as ice core analysis, dendrochronology, and sediment layer examination to reconstruct past climate conditions, providing insights beyond the temporal scope of climatology. These methods analyze proxies like trapped gas bubbles, tree ring patterns, and mineral deposits, enabling scientists to infer temperature, atmospheric composition, and precipitation changes over millennia. By contrast, climatology primarily uses modern observational data and climate models to study current and future climate dynamics.
Sources of Data: Modern vs Ancient Climate Records
Climatology relies on modern climate records collected through instruments like weather stations, satellites, and ocean buoys, which provide real-time data on temperature, precipitation, and atmospheric composition. Paleoclimatology derives ancient climate information from proxy data sources such as ice cores, tree rings, sediment layers, and fossil records, allowing reconstruction of climate patterns over thousands to millions of years. The integration of these data sources enhances understanding of climate variability and long-term trends across different temporal scales.
Applications in Understanding Climate Change
Climatology provides real-time data analysis for predicting and modeling current climate trends through satellite observations and atmospheric monitoring networks. Paleoclimatology reconstructs past climate conditions using proxy data such as ice cores, tree rings, and sediment records, offering critical context for understanding natural climate variability over millennia. Combining both disciplines enhances the accuracy of climate change projections by integrating historical baselines with contemporary atmospheric dynamics.
Challenges and Limitations in Both Fields
Climatology faces challenges such as the complexity of modern climate systems and the accuracy of predictive models affected by anthropogenic factors. Paleoclimatology is limited by the availability and resolution of proxy data like ice cores, tree rings, and sediment records, which can introduce uncertainties in reconstructing past climates. Both fields struggle with integrating diverse datasets across temporal and spatial scales to improve the understanding of climate variability and change.
Future Trends in Climatology and Paleoclimatology
Future trends in climatology emphasize the integration of advanced climate models with real-time data from satellite technology to improve the accuracy of weather predictions and climate change projections. Paleoclimatology is increasingly leveraging high-resolution proxy data, such as ice cores and sediment records, combined with sophisticated computational techniques to reconstruct past climate variations with greater precision. Both fields are converging towards a multidisciplinary approach, utilizing machine learning and big data analytics to better understand climate dynamics and inform adaptive strategies for mitigating climate change impacts.
Climatology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com