A palimpsest landscape reveals layers of history and human activity etched into the terrain, where past and present coexist in a dynamic dialogue. This concept helps you understand how natural and cultural transformations shape the environment over time, offering rich narratives embedded in soil, vegetation, and architecture. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how these intertwined layers influence our perception of place and heritage.
Table of Comparison
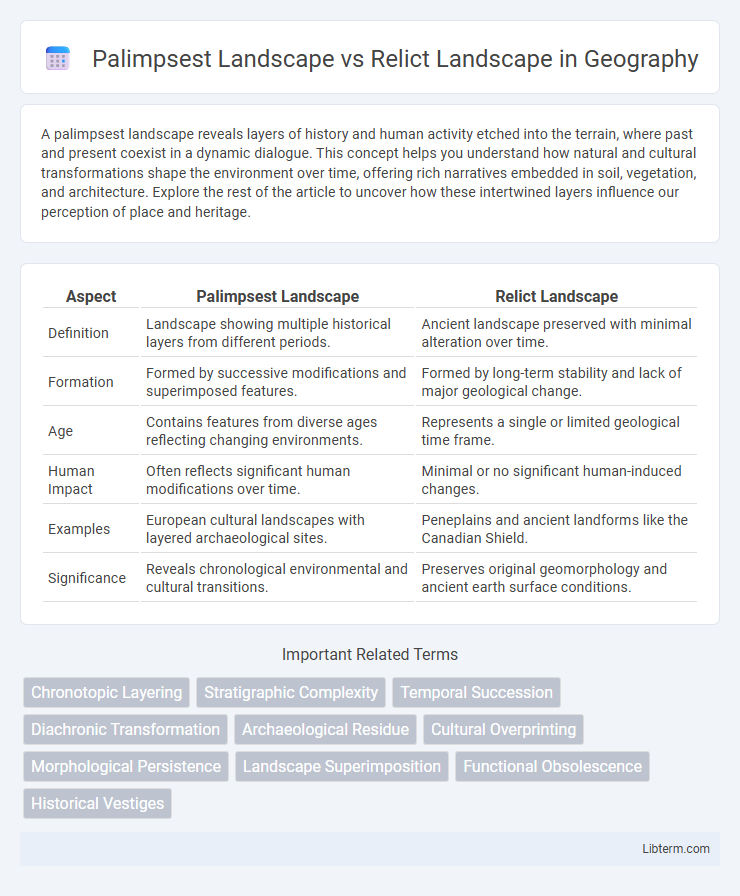
| Aspect | Palimpsest Landscape | Relict Landscape |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Landscape showing multiple historical layers from different periods. | Ancient landscape preserved with minimal alteration over time. |
| Formation | Formed by successive modifications and superimposed features. | Formed by long-term stability and lack of major geological change. |
| Age | Contains features from diverse ages reflecting changing environments. | Represents a single or limited geological time frame. |
| Human Impact | Often reflects significant human modifications over time. | Minimal or no significant human-induced changes. |
| Examples | European cultural landscapes with layered archaeological sites. | Peneplains and ancient landforms like the Canadian Shield. |
| Significance | Reveals chronological environmental and cultural transitions. | Preserves original geomorphology and ancient earth surface conditions. |
Introduction to Palimpsest and Relict Landscapes
Palimpsest landscapes are characterized by multiple layers of human and natural influences coexisting and interacting over time, creating complex, dynamic environments that reflect historical and contemporary processes. In contrast, relict landscapes represent remnants of past geographical conditions or ecosystems that have remained relatively unchanged, preserving features from previous climatic or ecological states. These landscape types provide valuable insights into environmental history, land use patterns, and the resilience of natural systems in the face of ongoing change.
Defining Palimpsest Landscape
Palimpsest Landscape refers to a terrain where multiple layers of historical land use and cultural imprints overlap, creating a complex mosaic of past and present features visible simultaneously. This contrasts with a Relict Landscape, which preserves relics of former environments or land uses that have largely ceased to influence the current landscape. Palimpsest Landscapes reveal dynamic interactions between human activity and natural processes through time, highlighting continuous transformation rather than static remnants.
Understanding Relict Landscape
Relict landscapes are ancient landforms preserved in their original state despite significant environmental and geological changes over time, offering valuable insights into past climatic and tectonic conditions. Unlike palimpsest landscapes, which display multiple overprinted features reflecting successive geological processes, relict landscapes retain primary characteristics from their formation period with minimal alteration. Understanding relict landscapes involves analyzing stable geomorphic surfaces, such as peneplains or fossil river terraces, that reveal the Earth's historical surface evolution and long-term landscape stability.
Key Differences Between Palimpsest and Relict Landscapes
Palimpsest landscapes exhibit multiple layers of human or natural modifications accumulated over time, creating a complex, overlapping spatial pattern, whereas relict landscapes represent ancient, largely unchanged landforms that preserve evidence of past environmental conditions. Palimpsest landscapes often show dynamic interactions between old and new features, while relict landscapes maintain a stable morphology with minimal recent alteration. The key difference lies in the degree of temporal alteration and layering: palimpsest landscapes are characterized by continuous transformation, whereas relict landscapes retain their original form as historical ecological or geological records.
Historical Development of Palimpsest Landscapes
Palimpsest landscapes exhibit complex historical development characterized by successive layers of human activity and natural processes, where earlier features are partially erased yet still detectable beneath newer modifications. These landscapes reflect a dynamic temporal palimpsest, integrating past land uses, cultural imprints, and environmental changes, unlike relict landscapes that remain largely untouched and preserve a single period's characteristics. The historical development of palimpsest landscapes involves continuous adaptation and transformation, offering rich archaeological and geomorphological insights into evolving human-environment interactions over centuries or millennia.
Evolution and Significance of Relict Landscapes
Relict landscapes represent ancient landforms that have remained largely unchanged despite environmental or climatic shifts, providing crucial insights into Earth's geological history and past surface processes. These landscapes evolve through the preservation of older geomorphic features that resist transformation, contrasting with palimpsest landscapes where newer processes overwrite previous landforms. The significance of relict landscapes lies in their role as natural archives, helping scientists reconstruct paleoenvironments and understand long-term geological evolution.
Methods for Identifying Landscape Types
Palimpsest landscapes are identified through multi-temporal remote sensing techniques and stratigraphic analysis that reveal overlapping landforms from different periods, while relict landscapes are recognized by geomorphological mapping and sediment analysis indicating preserved ancient features unaffected by recent processes. Geochronological methods such as radiocarbon dating and optically stimulated luminescence help differentiate palimpsest sites with sequential modifications from stable relict landscapes. Integrating GIS-based spatial analysis with field surveys enhances the accuracy of distinguishing between dynamic palimpsests and static relict landforms.
Case Studies: Examples of Palimpsest Landscapes
Palimpsest landscapes exhibit layers of historical and cultural modifications superimposed over natural landforms, illustrated by examples like the city of Rome, where ancient ruins coexist with modern urban development. Another case study is the English Lake District, where agricultural terraces, prehistoric monuments, and contemporary settlements overlap, reflecting continuous human interaction with the environment. These examples highlight how palimpsest landscapes reveal complex narratives through stratified spatial and temporal imprints, contrasting with relict landscapes that preserve predominantly untouched natural or historical features.
Case Studies: Examples of Relict Landscapes
Relict landscapes, preserved through minimal human alteration, showcase ancient geomorphological features such as the Scottish Highlands, where glacial landforms remain prominent. The Australian Outback presents another example, retaining prehistoric desert pavements and erosion surfaces that reflect climatic stability over millennia. These case studies highlight the significance of relict landscapes in understanding long-term environmental processes and natural heritage conservation.
Implications for Conservation and Landscape Management
Palimpsest landscapes, characterized by multiple layers of human and natural modifications over time, present complex conservation challenges requiring integrated management approaches that respect historical and ecological contexts. Relict landscapes, meanwhile, retain more pristine or minimally altered features, offering clearer baselines for biodiversity preservation and ecosystem restoration. Effective conservation strategies must differentiate these landscape types to tailor habitat protection, cultural heritage preservation, and sustainable land-use planning.
Palimpsest Landscape Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com