Spot height refers to the precise elevation of a specific point on a map, typically marked with a dot and its exact height above sea level. It helps in understanding terrain features, planning construction projects, and navigating landscapes. Discover how spot height measurements can enhance your geographic and engineering knowledge in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
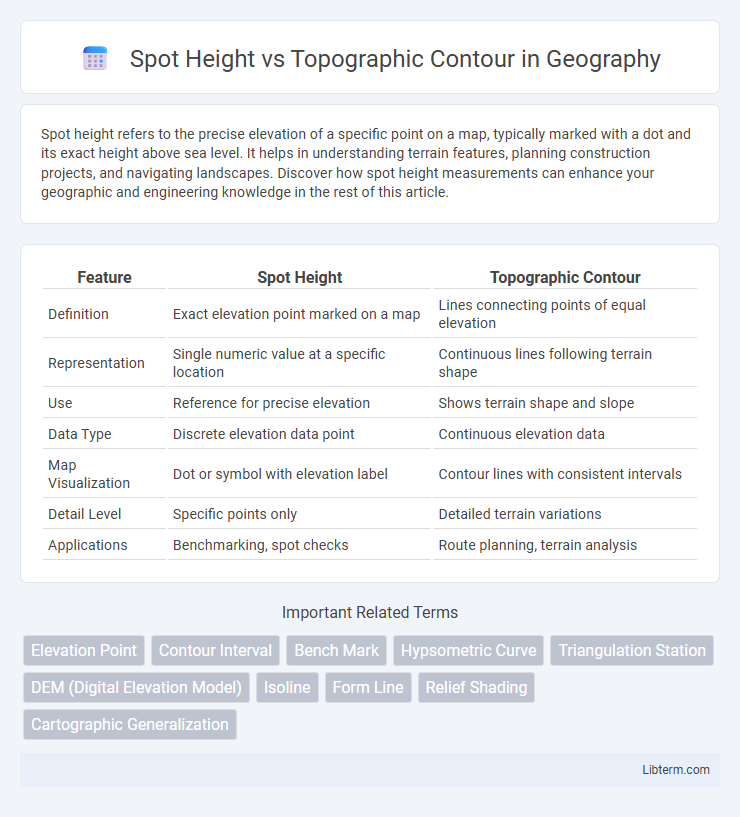
| Feature | Spot Height | Topographic Contour |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exact elevation point marked on a map | Lines connecting points of equal elevation |
| Representation | Single numeric value at a specific location | Continuous lines following terrain shape |
| Use | Reference for precise elevation | Shows terrain shape and slope |
| Data Type | Discrete elevation data point | Continuous elevation data |
| Map Visualization | Dot or symbol with elevation label | Contour lines with consistent intervals |
| Detail Level | Specific points only | Detailed terrain variations |
| Applications | Benchmarking, spot checks | Route planning, terrain analysis |
Introduction to Spot Heights and Topographic Contours
Spot heights represent specific points on a map with exact elevation values indicated by a dot and a number, providing precise altitude information at that location. Topographic contours are continuous lines connecting points of equal elevation, illustrating the shape and slope of the terrain across an area. Together, spot heights and contour lines enable accurate interpretation of landforms and elevation changes in geographical mapping.
Defining Spot Height: Concept and Applications
Spot height represents a specific point on a map where the exact elevation above sea level is measured and recorded, providing precise altitude data critical for surveying and navigation. Unlike topographic contours, which illustrate continuous elevation changes through lines connecting points of equal altitude, spot heights pinpoint exact locations for high accuracy in construction planning and geographic information systems (GIS). These precise elevation markers enhance the detail and reliability of topographic maps, supporting infrastructure development, flood risk assessment, and land use planning.
Understanding Topographic Contours: Meaning and Usage
Topographic contours represent continuous lines on a map that connect points of equal elevation, illustrating the shape and elevation changes of the terrain. Spot heights are specific points marked with exact elevation values, providing precise data for key locations such as peaks or landmarks. Understanding these contours enables accurate interpretation of landscape features, slope steepness, and elevation variations essential for navigation and planning.
Methods of Representing Elevation on Maps
Spot heights represent specific points of exact elevation using symbols or numbers on maps, providing precise altitude information at a single location. Topographic contours display continuous lines connecting points of equal elevation, illustrating the shape and slope of terrain across a broader area. Both methods are essential for accurate terrain visualization, with spot heights offering exact measurements and contours depicting elevation patterns.
Key Differences Between Spot Height and Topographic Contour
Spot height represents a precise elevation point marked on a map, providing exact vertical measurement at a specific location, while topographic contours illustrate continuous lines connecting points of equal elevation, depicting the terrain's shape and slope. Spot heights offer discrete data points useful for pinpointing exact elevations, whereas contours enable visualization of landform gradients and elevation changes over an area. The key difference lies in spot heights giving individual elevation values, contrasted with topographic contours representing elevation patterns across larger regions.
Advantages of Using Spot Heights
Spot heights provide precise elevation points that allow for accurate measurement of specific locations, surpassing the general elevation representation of topographic contours. This precision enhances detailed mapping, engineering projects, and navigation by offering exact altitude data. Spot heights also enable better assessment of terrain features that might be overlooked or generalized in contour lines, improving terrain analysis and planning accuracy.
Benefits of Topographic Contours in Mapping
Topographic contours provide a continuous and detailed representation of terrain elevation, enabling accurate visualization of landforms and slope gradients essential for planning and navigation. Unlike spot heights, which offer isolated elevation points, contour lines allow for the interpretation of landscape features such as ridges, valleys, and plateaus with greater precision. This comprehensive elevation data improves decision-making in engineering, environmental management, and outdoor activities by facilitating a clearer understanding of topography.
Common Applications in Surveying and Cartography
Spot heights provide precise elevation points essential for detailed land surveying and construction planning, allowing accurate measurement of specific locations. Topographic contours depict continuous elevation changes, facilitating terrain visualization and route planning in mapping and environmental studies. Both methods complement each other by offering point-specific data and comprehensive terrain analysis for accurate cartographic representation.
Interpreting Elevation Data: Best Practices
Spot height provides precise elevation at a specific point, offering exact altitude data crucial for detailed topographic analysis. Topographic contours illustrate continuous elevation changes along a line, enabling visualization of terrain shape and slope gradients. Combining spot heights with contour lines ensures accurate terrain interpretation and supports effective decision-making in mapping and land planning.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Spot Height and Topographic Contour
Spot height provides precise elevation data at a specific point, making it ideal for detailed surveying and engineering projects requiring exact altitude measurements. Topographic contours offer continuous elevation information across an area, facilitating terrain visualization and spatial analysis for activities like hiking, urban planning, and geological studies. Selecting between spot height and topographic contours depends on the need for pinpoint accuracy versus broader terrain representation, with many applications benefiting from combining both for comprehensive elevation understanding.
Spot Height Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com