Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) offers a holistic approach to health by balancing the body's energy, or Qi, through techniques like acupuncture, herbal remedies, and tai chi. This ancient practice addresses the root causes of illness rather than just symptoms, promoting overall wellness and harmony. Discover how integrating TCM into your health routine can transform your well-being by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
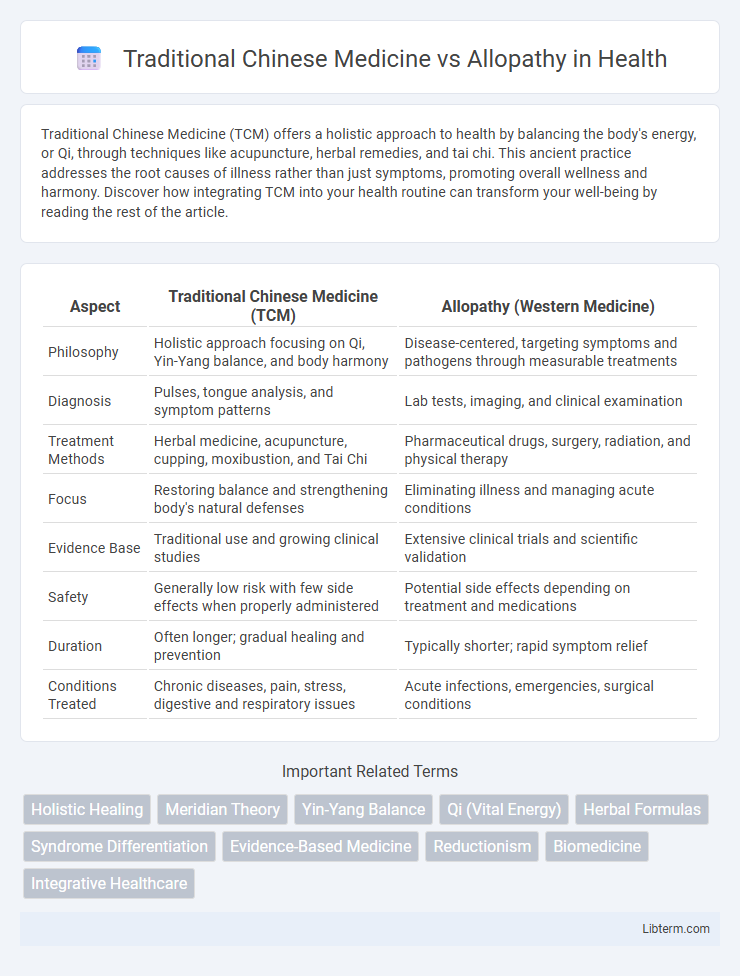
| Aspect | Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) | Allopathy (Western Medicine) |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Holistic approach focusing on Qi, Yin-Yang balance, and body harmony | Disease-centered, targeting symptoms and pathogens through measurable treatments |
| Diagnosis | Pulses, tongue analysis, and symptom patterns | Lab tests, imaging, and clinical examination |
| Treatment Methods | Herbal medicine, acupuncture, cupping, moxibustion, and Tai Chi | Pharmaceutical drugs, surgery, radiation, and physical therapy |
| Focus | Restoring balance and strengthening body's natural defenses | Eliminating illness and managing acute conditions |
| Evidence Base | Traditional use and growing clinical studies | Extensive clinical trials and scientific validation |
| Safety | Generally low risk with few side effects when properly administered | Potential side effects depending on treatment and medications |
| Duration | Often longer; gradual healing and prevention | Typically shorter; rapid symptom relief |
| Conditions Treated | Chronic diseases, pain, stress, digestive and respiratory issues | Acute infections, emergencies, surgical conditions |
Introduction to Traditional Chinese Medicine and Allopathy
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is a holistic healing system rooted in ancient Chinese philosophy, emphasizing balance between Yin and Yang and the flow of Qi through meridians to maintain health. Allopathy, or Western medicine, relies on evidence-based scientific methods, focusing on diagnosing and treating diseases primarily through pharmaceuticals, surgery, and other conventional interventions. While TCM utilizes herbal remedies, acupuncture, and lifestyle adjustments to restore harmony, allopathy prioritizes targeted biochemical mechanisms and rapid symptom alleviation.
Historical Origins and Philosophical Foundations
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) originates from ancient Chinese philosophy, emphasizing the balance of Yin and Yang and the flow of Qi through meridians to maintain health. Allopathy, or modern Western medicine, is based on scientific methods and the germ theory of disease, focusing on diagnosis and treatment through pharmacology and surgery. The contrasting historical origins reflect TCM's holistic approach rooted in Taoism and Confucianism, while allopathy derives from Enlightenment-era empiricism and biological sciences.
Core Principles and Treatment Modalities
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) emphasizes balance and harmony within the body through concepts like Qi, Yin-Yang, and the Five Elements, using treatments such as acupuncture, herbal medicine, and tui na massage. Allopathy, or modern Western medicine, relies on evidence-based diagnosis and treatment, primarily utilizing pharmaceuticals, surgery, and advanced technology to target specific diseases and symptoms. While TCM focuses on holistic approaches and prevention, allopathy prioritizes immediate symptom relief and disease eradication through scientifically validated methods.
Diagnostic Methods: East vs West
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) employs diagnostic methods such as pulse diagnosis, tongue inspection, and holistic assessment of physical and emotional symptoms to determine imbalances in Qi, Yin, and Yang. In contrast, Allopathy relies on laboratory tests, imaging technologies like MRI and CT scans, and evidence-based criteria to identify specific pathogens or physiological abnormalities. The Eastern approach emphasizes pattern recognition and energy flow, while the Western approach prioritizes precise, measurable biomarkers and anatomical diagnosis.
Herbal Remedies vs Pharmaceutical Drugs
Herbal remedies in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) utilize natural plant extracts like ginseng, licorice root, and astragalus to promote balance and holistic healing, emphasizing individualized treatment based on syndrome differentiation. Pharmaceutical drugs in allopathy rely on synthetic compounds or isolated active ingredients, targeting specific biological pathways to treat symptoms or diseases with rigorous clinical trials supporting efficacy and safety. The integration of TCM herbal formulas and pharmaceutical drugs necessitates careful consideration of herb-drug interactions, metabolism, and evidence-based approaches to optimize patient outcomes.
Approaches to Chronic Disease Management
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) approaches chronic disease management through holistic methods, emphasizing balance in the body's energy flow (Qi) using acupuncture, herbal remedies, and lifestyle adjustments to restore health. Allopathy relies on evidence-based pharmaceuticals and surgical interventions targeting specific symptoms or pathogens to control chronic conditions. Combining TCM's personalized, preventive strategies with Allopathy's targeted treatments can enhance overall patient outcomes in chronic disease management.
Role of Prevention and Holistic Care
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) emphasizes prevention through balancing the body's energy (Qi) and holistic care involving physical, emotional, and environmental factors. Allopathy focuses on diagnosing and treating specific diseases primarily through pharmaceuticals and surgical interventions. TCM's preventive approach aims to maintain health and avoid illness onset, while allopathy targets symptom relief and acute care management.
Safety, Side Effects, and Regulation
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) utilizes natural herbs and holistic therapies with generally lower risk of severe side effects compared to allopathy, which often involves synthetic drugs that may cause adverse reactions and toxicity. Regulatory frameworks for TCM vary widely, with some countries enforcing strict quality control and certification, while allopathic medicines typically undergo rigorous clinical trials and standardized approval processes by agencies like the FDA or EMA. Patients seeking safer options may consider TCM's individualized treatments, but should remain informed about potential interactions and consult healthcare professionals to ensure regulated, safe use alongside allopathic care.
Integration and Collaboration in Modern Healthcare
Integration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and allopathy in modern healthcare enhances patient outcomes by combining holistic approaches with evidence-based treatments. Collaborative efforts between TCM practitioners and allopathic physicians facilitate personalized care plans, leveraging the strengths of acupuncture, herbal medicine, and pharmaceuticals. Research on integrative therapies demonstrates improved management of chronic diseases, pain relief, and reduced medication side effects.
Choosing the Right Path: Patient Experiences and Outcomes
Patient experiences with Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) emphasize personalized treatments based on balancing Qi and holistic health, often reporting improved chronic pain and stress management. Allopathy, or modern Western medicine, prioritizes evidence-based protocols and rapid symptom relief through pharmaceuticals and surgery, yielding measurable outcomes in acute conditions and emergencies. Outcome comparisons reveal TCM excels in long-term wellness and prevention, while allopathy offers superior efficacy in life-threatening situations and infection control.
Traditional Chinese Medicine Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com