Dry Eye Syndrome occurs when your eyes do not produce enough tears or the tears evaporate too quickly, leading to irritation and discomfort. Common symptoms include redness, burning, and a gritty feeling that can affect daily activities and overall eye health. Learn more about effective treatments and prevention strategies in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
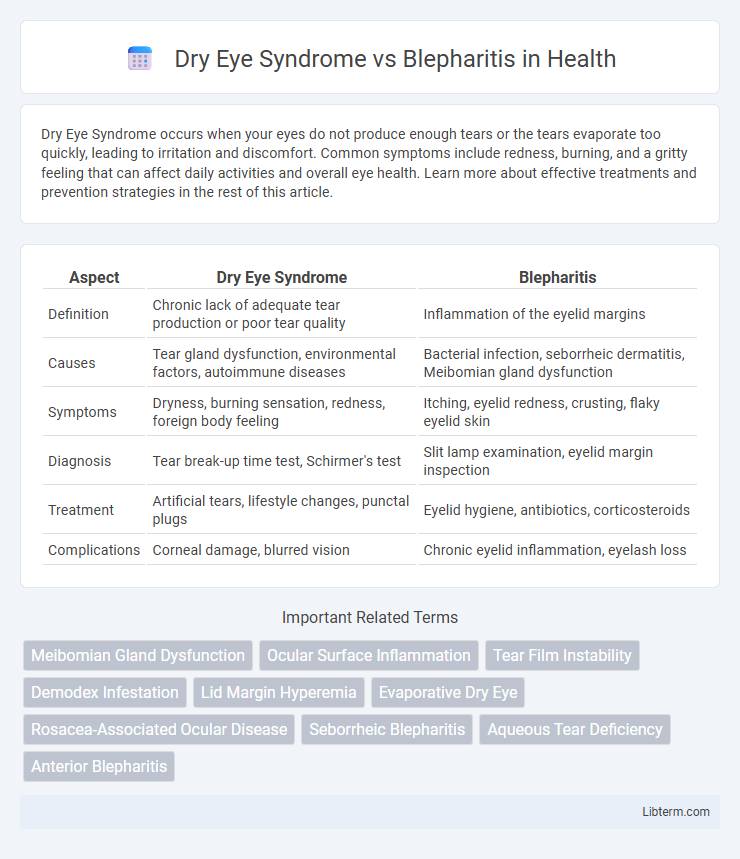
| Aspect | Dry Eye Syndrome | Blepharitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic lack of adequate tear production or poor tear quality | Inflammation of the eyelid margins |
| Causes | Tear gland dysfunction, environmental factors, autoimmune diseases | Bacterial infection, seborrheic dermatitis, Meibomian gland dysfunction |
| Symptoms | Dryness, burning sensation, redness, foreign body feeling | Itching, eyelid redness, crusting, flaky eyelid skin |
| Diagnosis | Tear break-up time test, Schirmer's test | Slit lamp examination, eyelid margin inspection |
| Treatment | Artificial tears, lifestyle changes, punctal plugs | Eyelid hygiene, antibiotics, corticosteroids |
| Complications | Corneal damage, blurred vision | Chronic eyelid inflammation, eyelash loss |
Introduction to Dry Eye Syndrome and Blepharitis
Dry Eye Syndrome is a chronic condition characterized by insufficient tear production or poor tear quality, leading to eye irritation, redness, and a gritty sensation. Blepharitis involves inflammation of the eyelid margins, often caused by bacterial infection or dysfunction of the Meibomian glands, resulting in redness, swelling, and flaky skin around the eyelashes. Both conditions significantly impact ocular surface health but differ in their underlying causes and treatment approaches.
Understanding Dry Eye Syndrome: Causes and Symptoms
Dry Eye Syndrome occurs when tear production is insufficient or tears evaporate too quickly, leading to eye dryness and irritation. Key symptoms include burning sensation, redness, blurred vision, and a gritty feeling in the eyes. Common causes involve aging, environmental factors, prolonged screen use, and certain medications, distinguishing it from Blepharitis, which primarily affects the eyelid margins.
What is Blepharitis? Key Factors and Indicators
Blepharitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the eyelid margins, characterized by redness, swelling, itching, and crusting of the eyelashes. Key factors include bacterial infection, seborrheic dermatitis, and malfunctioning Meibomian glands, leading to oily debris buildup and chronic eyelid irritation. Indicators of blepharitis often involve flaky skin around the eyelids, frequent eye redness, and a gritty or burning sensation, which distinguishes it from dry eye syndrome symptoms.
Comparing Risk Factors: Dry Eye Syndrome vs Blepharitis
Dry Eye Syndrome primarily arises from insufficient tear production and environmental factors such as prolonged screen use, low humidity, and aging, while Blepharitis is mainly linked to bacterial infection, seborrheic dermatitis, and meibomian gland dysfunction. Risk factors for Dry Eye Syndrome include autoimmune diseases like Sjogren's syndrome, contact lens wear, and hormonal changes, whereas Blepharitis is often associated with chronic skin conditions like rosacea and scalp dandruff. Both conditions share risks like poor eyelid hygiene and inflammatory responses but differ significantly in their underlying causes and triggering factors.
Diagnostic Differences: How Are They Identified?
Dry Eye Syndrome is primarily diagnosed through tear film tests such as the Schirmer test and tear breakup time, highlighting insufficient or unstable tear production, while Blepharitis is identified by clinical examination showing inflammation, redness, and crusting along the eyelid margins. Specialized tools like slit-lamp biomicroscopy help differentiate blepharitis by revealing clogged meibomian glands and eyelid margin abnormalities. Both conditions may require ocular surface staining with dyes like fluorescein or lissamine green to assess damage, but the distinct presence of eyelid margin inflammation is key in diagnosing blepharitis compared to the tear deficiency seen in dry eye syndrome.
Overlapping Symptoms: How to Tell Them Apart
Dry Eye Syndrome and Blepharitis share overlapping symptoms such as redness, irritation, and a gritty sensation in the eyes, making accurate diagnosis challenging. Differentiation lies in symptom specifics: Dry Eye Syndrome typically presents with persistent dryness and a burning feeling, while Blepharitis often involves eyelid inflammation, crusting, and flaking around the eyelashes. Comprehensive eye examination, including eyelid margin evaluation and tear film assessment, is essential to distinguish between these conditions and guide effective treatment.
Treatment Approaches for Dry Eye Syndrome
Dry Eye Syndrome treatment primarily involves the use of artificial tears, lubricating eye drops, and lifestyle modifications such as reducing screen time and increasing humidity. In more severe cases, prescription medications like cyclosporine or lifitegrast and procedures such as punctal plugs help retain moisture on the ocular surface. Managing underlying factors like inflammation and meibomian gland dysfunction through warm compresses and eyelid hygiene enhances overall treatment effectiveness.
Effective Management Strategies for Blepharitis
Blepharitis management requires consistent eyelid hygiene, including warm compresses and gentle lid scrubs to reduce bacterial load and inflammation. Topical antibiotics or corticosteroids may be prescribed for bacterial or seborrheic blepharitis to control symptoms and prevent complications. Regular follow-up with an ophthalmologist ensures tailored treatment adjustments and effective symptom control, distinguishing it from dry eye syndrome, which often focuses more on tear supplementation and alleviating ocular surface dryness.
Prevention Tips: Protecting Your Eyes from Both Conditions
Maintaining proper eyelid hygiene is essential for preventing Dry Eye Syndrome and Blepharitis, as regular cleansing helps reduce oil buildup and bacterial growth. Using warm compresses daily can unclog meibomian glands, improving tear film stability and reducing inflammation. Limiting screen time and wearing UV-protective sunglasses minimize eye strain and environmental irritants, further protecting eye health.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Eye Discomfort
Persistent eye redness, pain, or vision changes with Dry Eye Syndrome or Blepharitis warrant prompt medical evaluation to prevent complications such as corneal ulcers or infections. Seek immediate care if symptoms worsen despite over-the-counter treatments, or if you experience intense discomfort, swelling, or discharge from the eyes. Early diagnosis and targeted therapy by an ophthalmologist ensure effective management and reduce the risk of chronic damage.
Dry Eye Syndrome Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com