Arrhythmia refers to an irregular heartbeat that can affect the heart's ability to pump blood efficiently, leading to symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, or fatigue. Understanding the causes, types, and treatments of arrhythmia is essential for managing your heart health effectively. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to recognize arrhythmia and when to seek medical help.
Table of Comparison
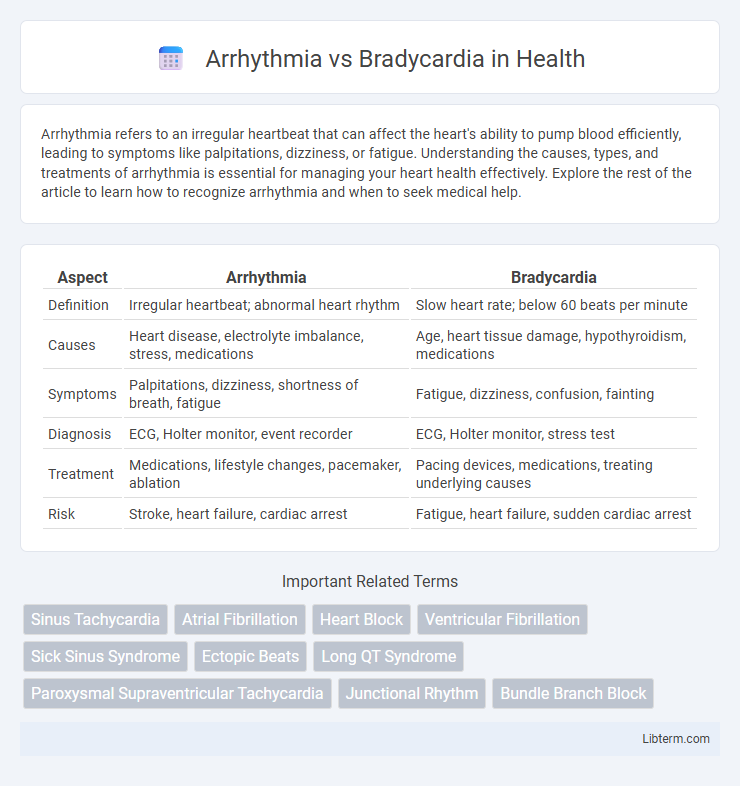
| Aspect | Arrhythmia | Bradycardia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Irregular heartbeat; abnormal heart rhythm | Slow heart rate; below 60 beats per minute |
| Causes | Heart disease, electrolyte imbalance, stress, medications | Age, heart tissue damage, hypothyroidism, medications |
| Symptoms | Palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath, fatigue | Fatigue, dizziness, confusion, fainting |
| Diagnosis | ECG, Holter monitor, event recorder | ECG, Holter monitor, stress test |
| Treatment | Medications, lifestyle changes, pacemaker, ablation | Pacing devices, medications, treating underlying causes |
| Risk | Stroke, heart failure, cardiac arrest | Fatigue, heart failure, sudden cardiac arrest |
Understanding Arrhythmia and Bradycardia
Arrhythmia refers to an abnormal heart rhythm characterized by irregular, too fast, or too slow heartbeats, whereas bradycardia specifically describes a slower-than-normal heart rate, typically below 60 beats per minute. Understanding arrhythmia involves recognizing various types such as atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, and premature contractions, each affecting the heart's electrical system differently. Bradycardia can be benign in athletes but may signal underlying issues like heart block or hypothyroidism, necessitating clinical evaluation for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Key Differences Between Arrhythmia and Bradycardia
Arrhythmia refers to any irregularity in the heart's rhythm, encompassing a range of conditions where the heartbeat can be too fast, too slow, or erratic. Bradycardia specifically denotes a slower than normal heart rate, typically below 60 beats per minute, and is a type of arrhythmia. The key difference lies in scope: arrhythmia covers all abnormal heart rhythms, while bradycardia is a distinct subset characterized solely by a decreased heart rate.
Causes of Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is caused by abnormalities in the heart's electrical signals, which can result from coronary artery disease, electrolyte imbalances, or damage from a heart attack, whereas bradycardia specifically refers to a slower than normal heart rate often linked to aging or heart tissue damage. Arrhythmias may also arise due to congenital heart defects, excessive alcohol or caffeine consumption, stress, or certain medications. Unlike bradycardia, arrhythmias encompass a broad range of irregular heart rhythms caused by disturbances in impulse generation or conduction within the sinoatrial node or atrioventricular node.
Causes of Bradycardia
Bradycardia, characterized by a slow heart rate below 60 beats per minute, commonly results from damage to the heart's electrical system due to aging, heart disease, or congenital heart defects. Other causes include hypothyroidism, electrolyte imbalances, and certain medications such as beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers. In contrast to arrhythmia, which involves irregular heartbeats, bradycardia specifically refers to an abnormally slow rhythm affecting cardiac output.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Arrhythmia, characterized by irregular heartbeats, often presents symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, and shortness of breath, while bradycardia specifically involves abnormally slow heart rates leading to fatigue, weakness, and fainting spells. Both conditions may cause chest pain and confusion, requiring prompt medical evaluation to prevent complications. Monitoring heart rhythm irregularities and associated symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment of these cardiac disorders.
Diagnostic Approaches for Heart Rhythm Disorders
Arrhythmia diagnosis often involves electrocardiograms (ECG) and Holter monitors to detect irregular heartbeats, while bradycardia specifically requires assessment of heart rate using these tools to identify abnormally slow rhythms under 60 beats per minute. Advanced methods such as event monitors and electrophysiological studies provide detailed analysis for complex arrhythmias and pinpoint the origin of abnormal rhythms. Accurate differentiation between arrhythmia subtypes and bradycardia is essential for tailored treatment, relying heavily on continuous cardiac monitoring and patient symptom correlation.
Treatment Options for Arrhythmia
Treatment options for arrhythmia include medications such as antiarrhythmics, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers to regulate heart rhythm. Invasive procedures like catheter ablation target and destroy abnormal electrical pathways causing arrhythmia, providing long-term relief. Implantable devices, including pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), help restore normal heart rhythm and prevent sudden cardiac death in severe cases.
Treatment Options for Bradycardia
Treatment options for bradycardia primarily depend on the severity and underlying cause, often including the implantation of a pacemaker to regulate heart rate effectively. Medication adjustments may be necessary if certain drugs contribute to slow heart rhythms, while addressing reversible causes like hypothyroidism or electrolyte imbalances can restore normal heart function. In severe cases, cardiologists may recommend lifestyle modifications alongside medical interventions to prevent complications associated with bradycardia.
Risk Factors and Potential Complications
Arrhythmia, characterized by irregular heartbeats, can be triggered by risk factors such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, electrolyte imbalances, and excessive alcohol consumption, while bradycardia specifically involves a slower-than-normal heart rate, often linked to aging, heart tissue damage, hypothyroidism, and certain medications. Both conditions increase the potential for severe complications including stroke, heart failure, and sudden cardiac arrest due to impaired cardiac output and inadequate blood flow to vital organs. Early diagnosis and management of underlying causes are crucial to reduce morbidity associated with these cardiac rhythm disorders.
Preventive Strategies and Lifestyle Recommendations
Preventive strategies for arrhythmia and bradycardia emphasize heart-healthy lifestyle choices such as maintaining regular physical activity, managing stress through mindfulness or meditation, and avoiding excessive alcohol or caffeine intake. Monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels, alongside a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, supports cardiac function and reduces arrhythmic risks. Regular medical check-ups and adherence to prescribed medications help detect and manage underlying conditions that contribute to abnormal heart rhythms, improving overall cardiac health.
Arrhythmia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com