Normal sinus rhythm represents the heart's natural electrical activity originating from the sinoatrial node, ensuring a consistent and healthy heartbeat between 60 and 100 beats per minute. This rhythm reflects proper cardiovascular function and plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal blood circulation throughout the body. Discover more about what normal sinus rhythm means for your heart health and how to identify it in the following article.
Table of Comparison
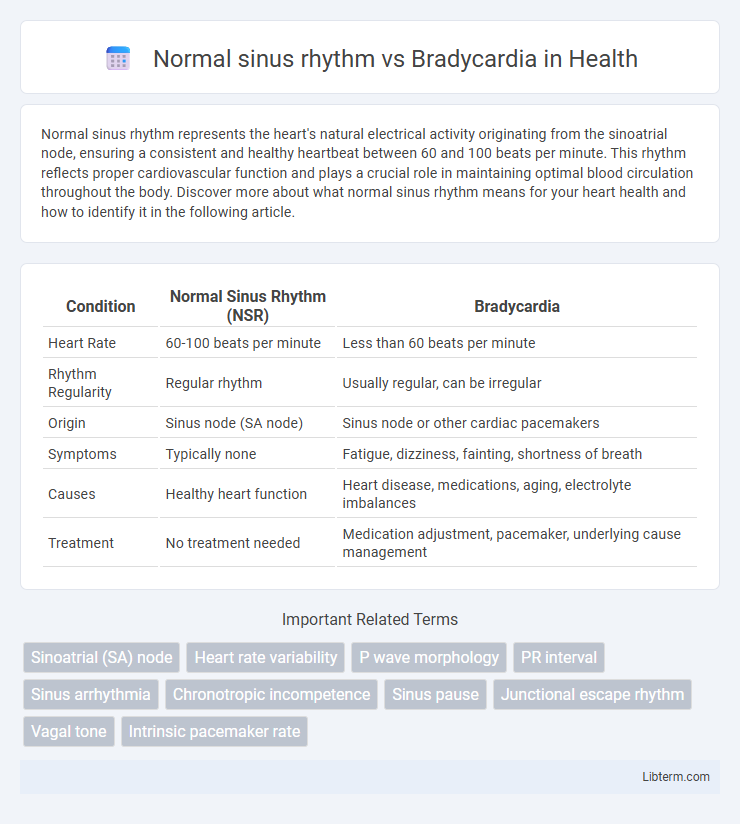
| Condition | Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) | Bradycardia |
|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate | 60-100 beats per minute | Less than 60 beats per minute |
| Rhythm Regularity | Regular rhythm | Usually regular, can be irregular |
| Origin | Sinus node (SA node) | Sinus node or other cardiac pacemakers |
| Symptoms | Typically none | Fatigue, dizziness, fainting, shortness of breath |
| Causes | Healthy heart function | Heart disease, medications, aging, electrolyte imbalances |
| Treatment | No treatment needed | Medication adjustment, pacemaker, underlying cause management |
Understanding Normal Sinus Rhythm
Normal sinus rhythm is characterized by a heart rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute, originating from the sinoatrial node, which ensures regular and coordinated electrical impulses for effective cardiac function. This rhythm maintains optimal blood flow and oxygen delivery throughout the body, supporting overall cardiovascular health. Deviations from this pattern, such as bradycardia with heart rates below 60 beats per minute, may indicate underlying cardiac issues requiring clinical evaluation.
Key Features of Bradycardia
Bradycardia is characterized by a heart rate of fewer than 60 beats per minute, often causing fatigue, dizziness, or fainting due to reduced cardiac output. Unlike normal sinus rhythm, which maintains a regular heart rate between 60 and 100 beats per minute, bradycardia may result from sinoatrial node dysfunction or enhanced parasympathetic tone. Electrocardiogram findings in bradycardia show prolonged R-R intervals with preserved P wave morphology, distinguishing it from arrhythmias affecting rhythm regularity.
Causes of Normal Sinus Rhythm
Normal sinus rhythm originates from the sinoatrial node, maintaining a heart rate between 60-100 beats per minute, representing a healthy cardiac cycle. It results from balanced autonomic nervous system input, where parasympathetic and sympathetic influences regulate pacing. Adequate oxygenation, electrolyte homeostasis, and absence of pathological conditions support the generation of normal sinus rhythm.
Common Causes of Bradycardia
Normal sinus rhythm maintains a heart rate between 60-100 beats per minute, ensuring efficient cardiac output and oxygen delivery. Bradycardia, defined as a heart rate below 60 beats per minute, often results from intrinsic sinoatrial node dysfunction, increased vagal tone, or pathologies such as hypothyroidism and electrolyte imbalances. Common causes also include medications like beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers, as well as conditions like sleep apnea or ischemic heart disease.
ECG Differences: Normal Sinus Rhythm vs Bradycardia
Normal sinus rhythm (NSR) on an ECG displays a regular heart rate between 60-100 beats per minute with consistent P waves preceding each QRS complex, indicating normal atrial depolarization and effective electrical conduction. In contrast, bradycardia is characterized by a heart rate below 60 beats per minute with similar P wave morphology but an extended R-R interval, reflecting slower ventricular response. The prolonged R-R intervals and unchanged P wave patterns help differentiate bradycardia from normal sinus rhythm on electrocardiographic analysis.
Symptoms Associated With Bradycardia
Bradycardia, characterized by a heart rate below 60 beats per minute, often presents symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, and fainting episodes due to inadequate cardiac output. In contrast, normal sinus rhythm maintains a rate between 60 and 100 beats per minute, supporting efficient blood circulation and stable oxygen delivery to tissues. Identifying bradycardia-related symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications like syncope or heart failure.
Clinical Significance of Sinus Rhythm
Normal sinus rhythm represents a heart rate between 60 and 100 beats per minute, originating from the sinoatrial node, indicating efficient electrical conduction and optimal cardiac function. Bradycardia, defined as a heart rate below 60 beats per minute, may signal underlying conditions such as hypothyroidism, electrolyte imbalances, or sinoatrial node dysfunction, requiring clinical evaluation. Maintaining normal sinus rhythm is critical for ensuring adequate cardiac output and tissue perfusion, preventing symptoms like dizziness, fatigue, or syncope associated with aberrant rhythms.
Risk Factors for Bradycardia
Normal sinus rhythm maintains an average heart rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute, ensuring efficient blood circulation throughout the body. Bradycardia, defined as a heart rate below 60 beats per minute, can result from aging, hypothyroidism, electrolyte imbalances, or the use of beta-blockers and other medications affecting cardiac conduction. Risk factors for bradycardia also include underlying heart diseases such as sick sinus syndrome, myocardial infarction, and excessive vagal tone from conditions like sleep apnea or athletic training.
Treatment Approaches for Bradycardia
Treatment approaches for bradycardia primarily involve addressing the underlying cause, which may include medication adjustments if drugs like beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers are involved. In symptomatic cases or when bradycardia leads to hemodynamic instability, implantation of a permanent pacemaker is often necessary to maintain adequate heart rate and cardiac output. Monitoring and managing electrolyte imbalances or ischemic heart disease are also critical components of effective bradycardia treatment strategies.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Normal sinus rhythm typically ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute and is considered healthy for adults, while bradycardia is defined as a heart rate below 60 beats per minute. Seek medical advice if bradycardia is accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, shortness of breath, or fainting, as these could indicate underlying heart conditions or electrical conduction issues. Immediate emergency care is necessary if severe symptoms occur, including chest pain, confusion, or loss of consciousness.
Normal sinus rhythm Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com