Dacryocystitis is an infection of the tear sac causing pain, swelling, and redness near the inner corner of the eye, while blepharitis involves inflammation of the eyelid margins, leading to irritation, itching, and crusting. Understanding the distinct symptoms and treatment options for each condition is essential for effective relief and preventing complications. Explore the full article to learn how you can identify and manage these common eye infections.
Table of Comparison
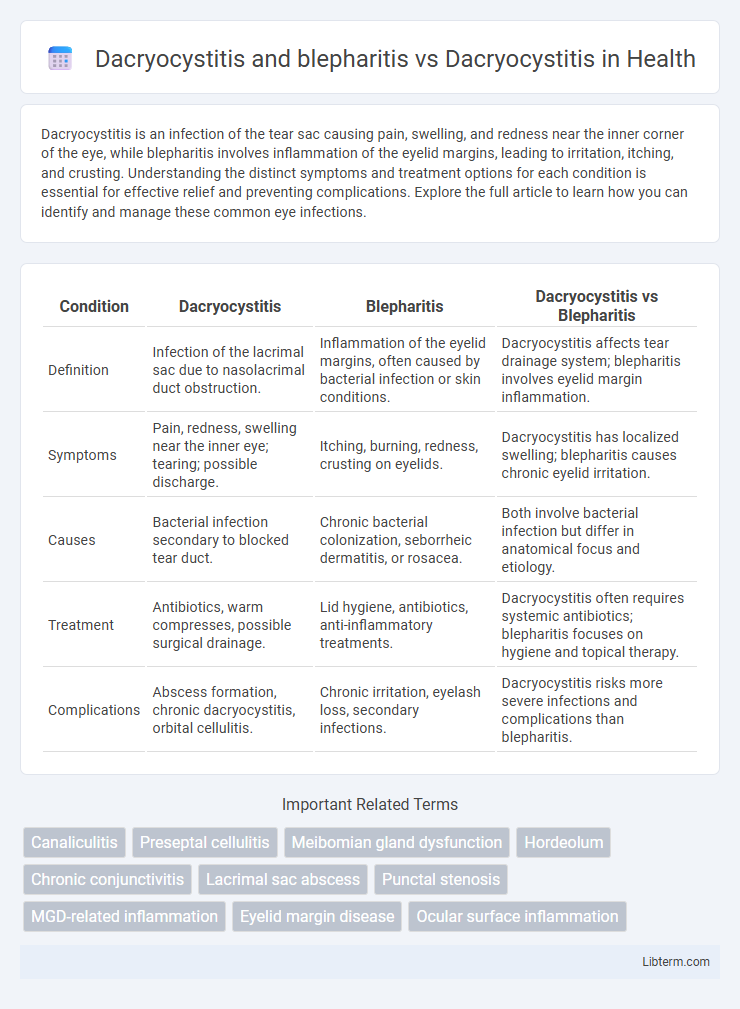
| Condition | Dacryocystitis | Blepharitis | Dacryocystitis vs Blepharitis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Infection of the lacrimal sac due to nasolacrimal duct obstruction. | Inflammation of the eyelid margins, often caused by bacterial infection or skin conditions. | Dacryocystitis affects tear drainage system; blepharitis involves eyelid margin inflammation. |
| Symptoms | Pain, redness, swelling near the inner eye; tearing; possible discharge. | Itching, burning, redness, crusting on eyelids. | Dacryocystitis has localized swelling; blepharitis causes chronic eyelid irritation. |
| Causes | Bacterial infection secondary to blocked tear duct. | Chronic bacterial colonization, seborrheic dermatitis, or rosacea. | Both involve bacterial infection but differ in anatomical focus and etiology. |
| Treatment | Antibiotics, warm compresses, possible surgical drainage. | Lid hygiene, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory treatments. | Dacryocystitis often requires systemic antibiotics; blepharitis focuses on hygiene and topical therapy. |
| Complications | Abscess formation, chronic dacryocystitis, orbital cellulitis. | Chronic irritation, eyelash loss, secondary infections. | Dacryocystitis risks more severe infections and complications than blepharitis. |
Understanding Dacryocystitis: An Overview
Dacryocystitis is an infection of the lacrimal sac caused by nasolacrimal duct obstruction, presenting with pain, swelling, and tearing near the inner eye. Blepharitis, often coexisting or confused with dacryocystitis, involves inflammation of the eyelid margins and differs by typically causing redness, crusting, and itching without lacrimal sac involvement. Effective diagnosis hinges on recognizing the distinct anatomical sites affected, enabling targeted treatment such as antibiotics for dacryocystitis and eyelid hygiene for blepharitis.
Defining Blepharitis: Basics and Causes
Blepharitis is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the eyelid margins, often caused by bacterial infections, seborrheic dermatitis, or meibomian gland dysfunction. Unlike dacryocystitis, which involves infection and inflammation of the lacrimal sac, blepharitis primarily impacts the eyelash follicles and surrounding skin. Key symptoms include eyelid redness, itching, and crusting, distinguishing it from the tear duct-related swelling and pain seen in dacryocystitis.
Pathophysiology of Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac typically caused by obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct, leading to bacterial infection and accumulation of tears and debris, primarily involving Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species. Blepharitis, unlike dacryocystitis, affects the eyelid margins and is characterized by chronic inflammation often linked to seborrheic dermatitis or bacterial colonization such as Staphylococcus epidermidis. The pathophysiology of dacryocystitis centers on impaired tear drainage causing stasis and subsequent infection, whereas blepharitis involves localized eyelid inflammation without lacrimal sac involvement.
Pathophysiology of Blepharitis
Blepharitis involves chronic inflammation of the eyelid margins caused by bacterial colonization and dysfunction of the meibomian glands, leading to disrupted tear film and ocular surface irritation. This contrasts with dacryocystitis, which is an infection and inflammation of the lacrimal sac often due to nasolacrimal duct obstruction causing tear stasis. The pathophysiology of blepharitis centers on bacterial biofilm formation and lipid layer abnormalities, whereas dacryocystitis results primarily from mechanical blockage and secondary microbial proliferation.
Clinical Features of Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis presents with acute pain, swelling, and redness over the lacrimal sac, often accompanied by tearing and mucopurulent discharge due to nasolacrimal duct obstruction. In contrast, blepharitis primarily affects the eyelid margins, causing irritation, itching, and flaking without significant lacrimal sac involvement. Clinical features of dacryocystitis include tenderness to palpation, fever in acute cases, and possible abscess formation requiring prompt medical intervention.
Clinical Features of Blepharitis
Blepharitis is characterized by chronic inflammation of the eyelid margins, presenting with symptoms such as redness, irritation, itching, and crusting around the eyelashes. Patients with blepharitis often experience eyelid swelling, flaky skin, and a burning sensation, which differ from the localized pain, swelling, and redness over the medial canthus seen in dacryocystitis. Unlike dacryocystitis, which involves infection of the lacrimal sac causing lacrimal system obstruction, blepharitis primarily affects the eyelid margin and Meibomian glands without lacrimal sac involvement.
Key Differences: Dacryocystitis vs. Dacryocystitis with Blepharitis
Dacryocystitis is an infection of the lacrimal sac typically caused by obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct, leading to pain, swelling, and discharge near the inner corner of the eye. When combined with blepharitis, inflammation extends to the eyelid margins, resulting in additional symptoms such as redness, crusting, and irritation along the eyelid edges. Key differences include the involvement of eyelid pathology in dacryocystitis with blepharitis, necessitating combined treatments targeting both lacrimal sac infection and eyelid inflammation for effective management.
Diagnostic Approaches: Differentiating Conditions
Dacryocystitis diagnosis relies on clinical examination revealing swelling and tenderness over the lacrimal sac, often supported by dacryocystography or lacrimal drainage system probing to confirm obstruction. Blepharitis, in contrast, is identified through slit-lamp examination showing eyelid margin inflammation, scaling, and crusting without lacrimal sac involvement. Differentiating these conditions hinges on imaging and physical findings: lacrimal sac distention indicates dacryocystitis, while eyelid margin erythema suggests blepharitis.
Treatment Strategies: Solo Dacryocystitis vs. Combined Presentation
Treatment strategies for solo dacryocystitis primarily involve systemic antibiotics targeting common pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species, alongside warm compresses to reduce inflammation. In cases of combined dacryocystitis and blepharitis, therapy must address both conditions simultaneously using topical antibiotics like erythromycin or bacitracin for blepharitis, combined with systemic agents for dacryocystitis, while emphasizing eyelid hygiene to control blepharitis-related eyelid margin inflammation. Early intervention with both antibiotic regimens and eyelid care in combined presentations reduces complications and promotes faster resolution compared to treatment of isolated dacryocystitis alone.
Prognosis and Complications in Isolated vs. Overlapping Cases
Dacryocystitis prognosis improves with timely antibiotic therapy, but untreated cases risk chronic infection, lacrimal sac abscess, and fistula formation, especially in isolated presentations. Blepharitis overlapping with dacryocystitis complicates management, increasing risks of eyelid margin scarring, chronic inflammation, and potential spread to adjacent ocular tissues, prolonging recovery. Overlapping cases show higher rates of recurrent inflammation and require integrated treatment targeting both lacrimal sac and eyelid margins for optimal outcomes.
Dacryocystitis and blepharitis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com