Constipation occurs when bowel movements become infrequent or difficult, often causing discomfort and bloating. Causes can include low fiber intake, dehydration, lack of physical activity, or certain medications. Discover effective strategies and remedies to relieve your constipation and improve digestive health by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
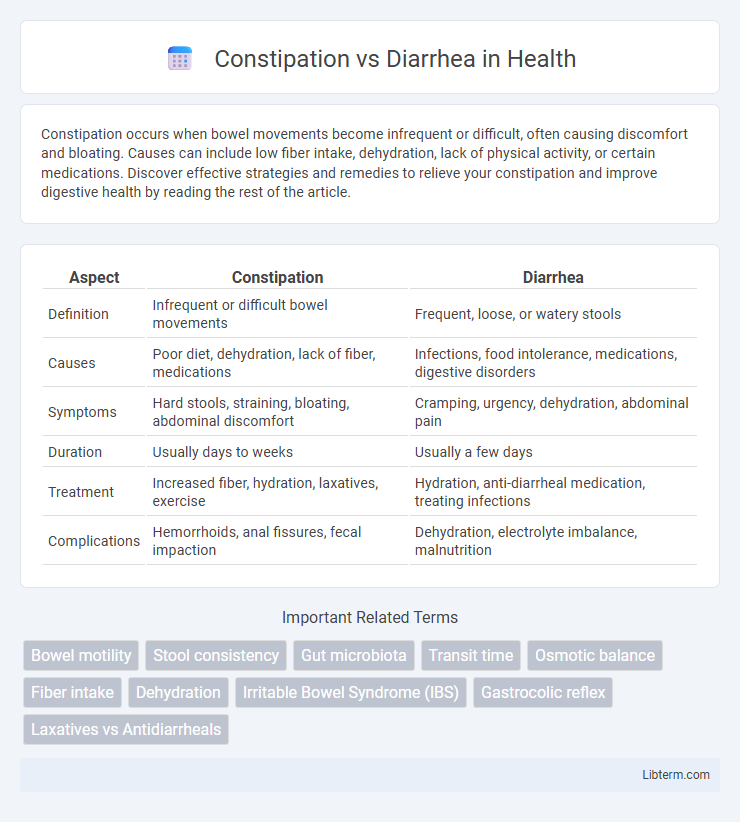
| Aspect | Constipation | Diarrhea |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Infrequent or difficult bowel movements | Frequent, loose, or watery stools |
| Causes | Poor diet, dehydration, lack of fiber, medications | Infections, food intolerance, medications, digestive disorders |
| Symptoms | Hard stools, straining, bloating, abdominal discomfort | Cramping, urgency, dehydration, abdominal pain |
| Duration | Usually days to weeks | Usually a few days |
| Treatment | Increased fiber, hydration, laxatives, exercise | Hydration, anti-diarrheal medication, treating infections |
| Complications | Hemorrhoids, anal fissures, fecal impaction | Dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, malnutrition |
Understanding Constipation and Diarrhea
Constipation is characterized by infrequent bowel movements or difficulty passing stools, often caused by low fiber intake, dehydration, or certain medications. Diarrhea involves frequent, loose, or watery stools and can result from infections, food intolerances, or digestive disorders. Understanding the underlying causes and symptoms of both conditions is essential for effective treatment and maintaining digestive health.
Key Differences Between Constipation and Diarrhea
Constipation is characterized by infrequent, hard, and difficult-to-pass stools, while diarrhea involves frequent, loose, or watery bowel movements. The underlying causes of constipation often include slow colonic transit or dehydration, whereas diarrhea is commonly caused by infections, inflammation, or malabsorption. Treatment for constipation typically focuses on increasing dietary fiber and hydration, whereas diarrhea management targets the underlying infection or inflammation and maintaining electrolyte balance.
Common Causes of Constipation
Constipation commonly results from insufficient fiber intake, dehydration, and lack of physical activity, leading to hardened stools and infrequent bowel movements. Other factors include certain medications such as opioids, antacids with aluminum, and iron supplements that slow gastrointestinal motility. Medical conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), hypothyroidism, and neurological disorders also contribute to chronic constipation.
Common Causes of Diarrhea
Diarrhea commonly results from infections caused by bacteria such as Escherichia coli, viruses like norovirus, and parasites including Giardia lamblia. Food intolerances, such as lactose intolerance, and the use of certain medications, especially antibiotics, disrupt normal gut flora leading to diarrhea. Digestive disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), also contribute significantly to recurrent diarrhea episodes.
Signs and Symptoms: Constipation vs Diarrhea
Constipation is characterized by infrequent bowel movements, hard or lumpy stools, and difficulty or pain during defecation, often accompanied by bloating and abdominal discomfort. Diarrhea presents as frequent, loose or watery stools, urgency to defecate, and cramping abdominal pain, sometimes leading to dehydration. Both conditions affect normal bowel function but differ significantly in stool consistency, frequency, and associated gastrointestinal symptoms.
Risk Factors Associated With Each Condition
Constipation risk factors include low dietary fiber intake, inadequate hydration, sedentary lifestyle, use of certain medications such as opioids or antacids, and underlying medical conditions like hypothyroidism or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Diarrhea risk factors primarily involve infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites, use of antibiotics that disrupt gut microbiota, food intolerances, and chronic diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and celiac disease. Both conditions can be influenced by psychological stress and dietary habits, but their distinct pathophysiological mechanisms necessitate targeted approaches for prevention and management.
Diagnostic Approaches: Identifying the Issue
Accurate diagnosis of constipation versus diarrhea involves detailed patient history and stool analysis to evaluate bowel movement frequency, consistency, and accompanying symptoms. Diagnostic approaches include physical examination, abdominal imaging, and laboratory tests such as complete blood count, electrolytes, and inflammatory markers to identify underlying causes. Advanced techniques like colonoscopy or stool culture may be employed to detect infections, inflammation, or structural abnormalities contributing to dysfunction.
Treatment Options for Constipation
Treatment options for constipation primarily include dietary changes such as increasing fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to improve stool consistency and bowel movements. Over-the-counter laxatives, including bulk-forming agents, stool softeners, osmotic laxatives, and stimulant laxatives, are commonly used to alleviate symptoms. Regular physical activity and adequate hydration also play crucial roles in managing chronic constipation effectively.
Treatment Options for Diarrhea
Treatment options for diarrhea primarily include oral rehydration therapy (ORT) to prevent dehydration by replenishing fluids and electrolytes. Over-the-counter medications like loperamide may help reduce bowel movements, while probiotics can restore normal gut flora. In cases of bacterial or parasitic infections, targeted antibiotics or antiparasitic medications are necessary for effective management.
Preventive Tips for Healthy Digestion
Maintaining adequate hydration and consuming a diet rich in fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are essential to prevent constipation and diarrhea. Regular physical activity supports healthy bowel movements by stimulating intestinal function and reducing digestive transit time. Probiotics found in yogurt and fermented foods help balance gut microbiota, promoting overall digestive health and reducing the risk of gastrointestinal disturbances.
Constipation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com