A furuncle, commonly known as a boil, is a painful, pus-filled infection of a hair follicle caused by bacteria, often Staphylococcus aureus. Proper hygiene and timely treatment can prevent the spread and complications of this skin infection. Discover effective ways to manage and treat furuncles by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
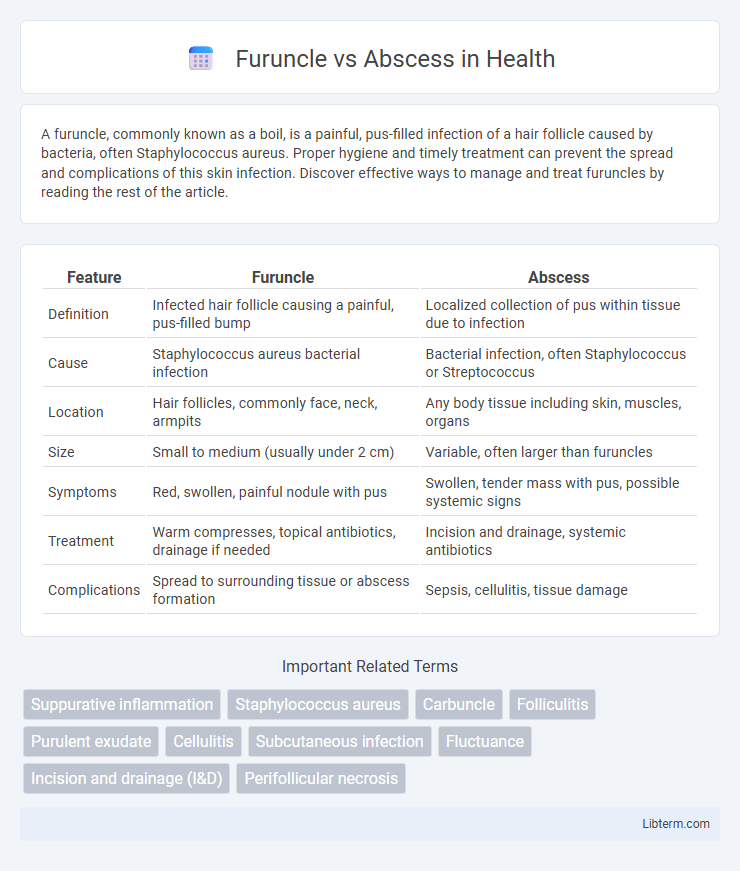
| Feature | Furuncle | Abscess |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Infected hair follicle causing a painful, pus-filled bump | Localized collection of pus within tissue due to infection |
| Cause | Staphylococcus aureus bacterial infection | Bacterial infection, often Staphylococcus or Streptococcus |
| Location | Hair follicles, commonly face, neck, armpits | Any body tissue including skin, muscles, organs |
| Size | Small to medium (usually under 2 cm) | Variable, often larger than furuncles |
| Symptoms | Red, swollen, painful nodule with pus | Swollen, tender mass with pus, possible systemic signs |
| Treatment | Warm compresses, topical antibiotics, drainage if needed | Incision and drainage, systemic antibiotics |
| Complications | Spread to surrounding tissue or abscess formation | Sepsis, cellulitis, tissue damage |
Understanding Furuncle and Abscess
A furuncle, commonly known as a boil, is a painful, pus-filled infection of a hair follicle typically caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. An abscess is a larger, localized collection of pus that can develop in various tissues, often resulting from the body's immune response to infection. Both conditions require proper drainage and antibiotic treatment to prevent further complications and promote healing.
Key Differences Between Furuncle and Abscess
A furuncle, commonly known as a boil, is a localized infection of a hair follicle characterized by a small, tender, pus-filled nodule, whereas an abscess is a broader collection of pus that forms in deeper tissues and can occur anywhere in the body. Furuncles typically arise from Staphylococcus aureus infection and present as single, painful lumps, while abscesses may result from various bacterial infections and often require more extensive drainage due to their larger size and depth. The key differences between furuncle and abscess include the infection site--hair follicle involvement versus deeper tissue involvement--the extent of pus accumulation, and the severity of symptoms necessitating different medical treatment approaches.
Causes of Furuncle and Abscess
Furuncles and abscesses both result from bacterial infections, primarily caused by Staphylococcus aureus infiltrating hair follicles or deeper skin layers. Furuncles develop when the bacteria invade and inflame a hair follicle, leading to localized pus formation and swelling. Abscesses form from a deeper accumulation of pus due to the body's immune response to bacterial invasion, often in soft tissues beyond the hair follicle.
Symptoms: Furuncle vs Abscess
Furuncles typically present as painful, red, swollen nodules with a central pus-filled core, often accompanied by localized warmth and tenderness. Abscesses manifest as larger, deeper collections of pus causing significant swelling, severe pain, and sometimes systemic symptoms like fever and malaise. Differentiating symptoms include furuncles being smaller and superficial, while abscesses are more extensive and may require drainage due to their size and depth.
Risk Factors and Predisposing Conditions
Furuncles and abscesses commonly develop in individuals with compromised skin integrity, such as those with diabetes mellitus, obesity, or immunosuppressive conditions. Chronic skin conditions like eczema or acne increase susceptibility by disrupting the skin barrier, while poor hygiene and repeated friction further elevate risk. Staphylococcus aureus infection, especially methicillin-resistant strains (MRSA), acts as a key microbial factor promoting abscess and furuncle formation.
Diagnosis: Clinical Evaluation and Testing
Furuncles and abscesses are diagnosed primarily through clinical evaluation involving physical examination of localized, painful, erythematous nodules, with furuncles typically presenting as single inflamed hair follicle infections while abscesses are larger, fluctuant collections of pus. Diagnostic testing may include ultrasound imaging to differentiate deep abscesses from superficial furuncles and culture of purulent material to identify causative pathogens, commonly Staphylococcus aureus. Laboratory tests such as complete blood count and inflammatory markers aid in assessing systemic involvement and guiding appropriate antibiotic therapy.
Treatment Options for Furuncle
Treatment options for a furuncle primarily include warm compresses to promote drainage and reduce pain, while in some cases, incision and drainage by a healthcare professional may be necessary to remove pus and accelerate healing. Antibiotics are prescribed if there is extensive surrounding cellulitis, systemic symptoms, or immunocompromised conditions. Proper wound care and hygiene are essential to prevent recurrence and secondary infections.
Treatment Approaches for Abscess
Treatment approaches for abscesses typically involve incision and drainage (I&D) to remove pus and reduce infection. Antibiotic therapy may be prescribed based on the abscess size, location, and patient immune status, often including agents targeting Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species. In more complex or deep abscess cases, imaging-guided drainage or surgical intervention might be necessary to ensure complete resolution.
Prevention Strategies for Skin Infections
Effective prevention strategies for furuncles and abscesses emphasize maintaining proper skin hygiene and promptly treating minor cuts or abrasions to reduce bacterial invasion. Using antiseptic cleansers and avoiding sharing personal items like towels can significantly lower the risk of Staphylococcus aureus infections. Regular moisturizing and wearing breathable clothing help preserve skin integrity, creating a natural barrier against skin infections.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention for a furuncle if it is unusually large, painful, or persists beyond two weeks without improvement, as these signs may indicate deeper infection. An abscess requires prompt medical evaluation when accompanied by fever, spreading redness, or if it impairs normal function, signaling potential systemic infection. Early intervention with a healthcare provider reduces complications and ensures appropriate treatment such as drainage or antibiotics.
Furuncle Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com