Allotopic relates to the concept of occurring in different places within an organism, such as genes or proteins expressed in alternative cellular locations. This concept plays a crucial role in understanding gene therapy, cellular biology, and evolutionary adaptations. Explore the rest of the article to discover how allotopic processes influence scientific advancements and your understanding of biology.
Table of Comparison
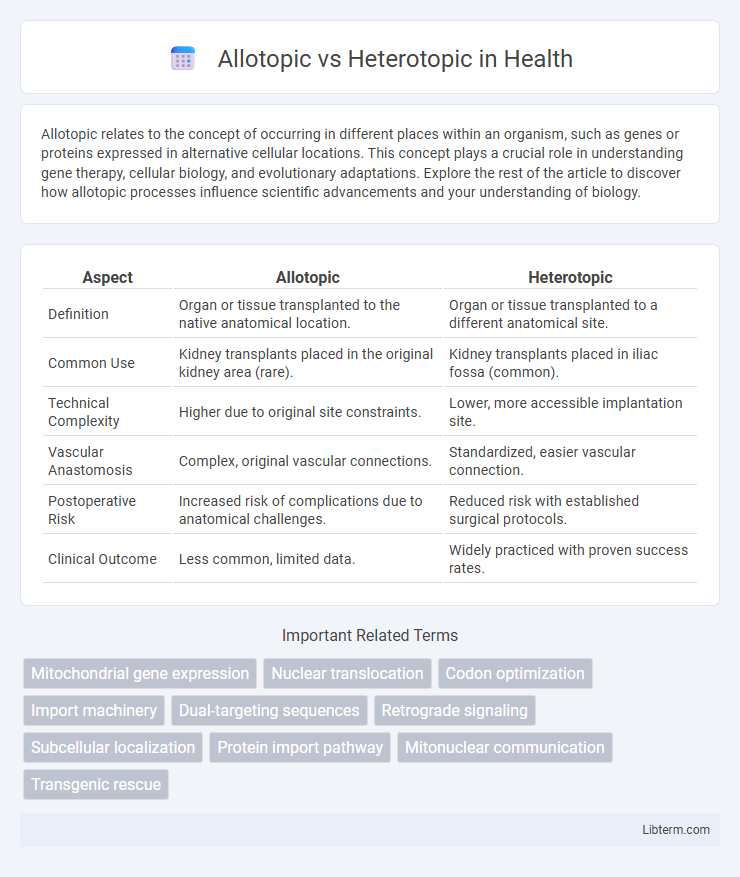
| Aspect | Allotopic | Heterotopic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organ or tissue transplanted to the native anatomical location. | Organ or tissue transplanted to a different anatomical site. |
| Common Use | Kidney transplants placed in the original kidney area (rare). | Kidney transplants placed in iliac fossa (common). |
| Technical Complexity | Higher due to original site constraints. | Lower, more accessible implantation site. |
| Vascular Anastomosis | Complex, original vascular connections. | Standardized, easier vascular connection. |
| Postoperative Risk | Increased risk of complications due to anatomical challenges. | Reduced risk with established surgical protocols. |
| Clinical Outcome | Less common, limited data. | Widely practiced with proven success rates. |
Introduction to Allotopic and Heterotopic Concepts
Allotopic refers to the placement of tissues or organs at a location different from their original, native site, while heterotopic involves transplantation or growth of tissue in an abnormal position distinct from the usual anatomical location. In medical and biological contexts, allotopic approaches often aim to restore organ function by relocating tissues within the body, whereas heterotopic scenarios may involve ectopic growths or transplantations in sites that differ from the native organ environment. Understanding these concepts is crucial for advancements in regenerative medicine, transplantation techniques, and developmental biology.
Defining Allotopic: Meaning and Applications
Allotopic refers to the expression of a gene in a different location within the genome or cellular environment than where it is naturally found, often used in genetic engineering and gene therapy. This technique allows for the correction of dysfunctional genes by relocating them to a safer, more controlled genomic site, enhancing therapeutic outcomes in diseases such as mitochondrial disorders. Applications of allotopic expression include the development of advanced treatments targeting mitochondrial DNA mutations, improving cellular function without altering the native mitochondrial genome.
Understanding Heterotopic: Overview and Significance
Heterotopic transplantation involves relocating tissue or organs to a different anatomical site within the same organism, preserving the original organ while adding new function or support elsewhere. This technique is significant in clinical settings such as heart or liver transplants, where the native organ remains intact, reducing the risk associated with complete organ removal. Understanding heterotopic transplantation advances regenerative medicine and organ replacement strategies by offering alternative solutions for organ failure and improving patient outcomes.
Key Differences Between Allotopic and Heterotopic
Allotopic refers to substances or processes occurring at different locations within an organism or system, while heterotopic denotes entities existing in distinct or abnormal anatomical sites. Allotopic involves spatial separation but maintains functional similarity, whereas heterotopic often implies atypical positioning leading to functional or structural variation. Understanding these key differences aids in fields like genetics, transplantation, and developmental biology where location-specific interactions are crucial.
Allotopic Expression in Genetics and Cellular Biology
Allotopic expression in genetics involves the artificial expression of a gene, typically mitochondrial DNA, within the nuclear genome to overcome mitochondrial dysfunctions. This technique enables the cellular machinery to produce mitochondrial proteins in the cytoplasm, which are then targeted back to mitochondria, offering potential therapeutic strategies for mitochondrial diseases. Research in allotopic expression focuses on optimizing gene transfer methods, protein targeting sequences, and expression efficiency to improve mitochondrial bioenergetics and cell viability.
Heterotopic Transplantation in Medical Science
Heterotopic transplantation involves implanting an organ or tissue at a site different from its original anatomical location, commonly used in kidney transplantation where the donor kidney is placed in the iliac fossa. This approach allows the native organ to remain in place, reducing surgical complexity and providing an alternative blood supply while maintaining the original organ's function. It offers advantages in cases where the diseased organ cannot be removed safely or when retransplantation is needed without disturbing the primary site.
Clinical Implications: Allotopic vs Heterotopic Approaches
Allotopic and heterotopic approaches differ significantly in clinical applications, with allotopic strategies involving gene expression within the native organ site, enhancing targeted therapeutic outcomes, while heterotopic methods transplant tissue or organs to alternative anatomical locations, often used in organ transplantation to bypass damaged native sites. Allotopic techniques can reduce immune rejection risks and improve functional integration, whereas heterotopic procedures provide critical options when orthotopic transplantation is contraindicated or unfeasible. Understanding these distinctions aids clinicians in selecting appropriate interventions that optimize patient prognosis and minimize complications.
Research Advances and Emerging Trends
Research advances in allotopic and heterotopic transplantation have significantly improved graft survival and functional integration through novel gene editing and immunomodulation techniques. Emerging trends emphasize the use of stem cell technologies and 3D bioprinting to enhance tissue compatibility and reduce rejection rates. Machine learning algorithms are increasingly applied to optimize donor-recipient matching and predict post-transplant outcomes, driving personalized medicine approaches in transplantation science.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Method
Allotopic expression enables gene therapy by introducing modified genes into a different cellular location than their native one, improving delivery efficiency and reducing immune responses but facing challenges in accurate protein targeting and functional integration. Heterotopic transplantation places tissue or organs in an alternative anatomical site, offering flexibility in graft placement and potential for enhanced vascularization while risking suboptimal functional outcomes due to non-native environmental conditions. Both methods present innovative therapeutic strategies with trade-offs between targeting accuracy, functional effectiveness, and procedural complexity.
Future Perspectives in Allotopic and Heterotopic Studies
Emerging research in allotopic and heterotopic transplantation emphasizes advancements in gene editing and immunomodulation to improve graft survival and integration. Future perspectives include leveraging CRISPR-Cas9 technology for precise genetic modifications in allotopic sites and developing biomaterials that enhance vascularization in heterotopic environments. These innovations aim to overcome current limitations by optimizing cellular compatibility and minimizing immune rejection in both transplantation modalities.
Allotopic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com