Cataracts cause clouding of the eye's lens, leading to blurred vision and difficulty seeing clearly. This common condition often develops slowly and can affect one or both eyes, impacting daily activities like reading or driving. Discover effective treatment options and how you can protect your sight by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
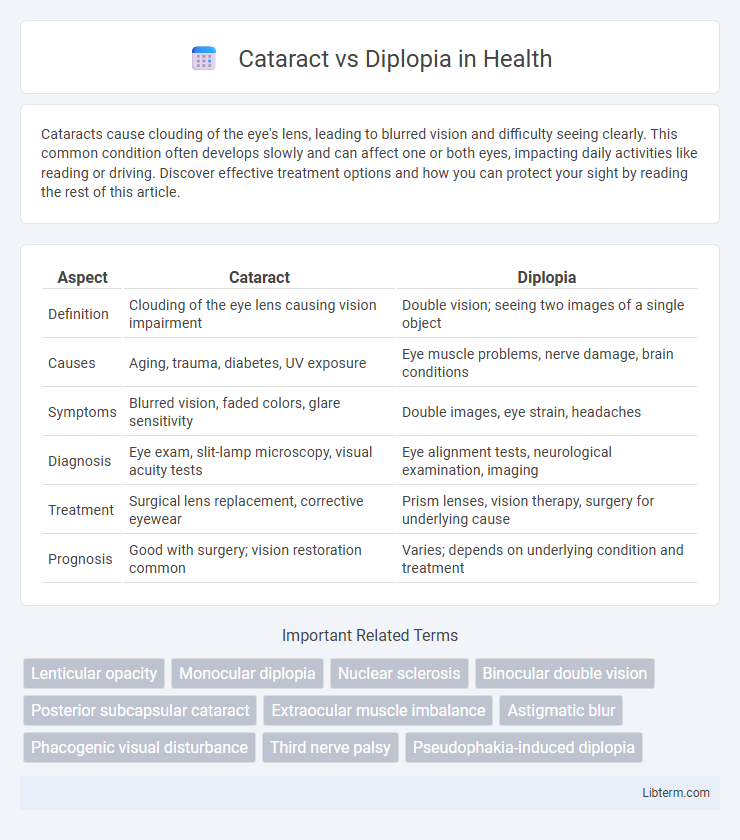
| Aspect | Cataract | Diplopia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clouding of the eye lens causing vision impairment | Double vision; seeing two images of a single object |
| Causes | Aging, trauma, diabetes, UV exposure | Eye muscle problems, nerve damage, brain conditions |
| Symptoms | Blurred vision, faded colors, glare sensitivity | Double images, eye strain, headaches |
| Diagnosis | Eye exam, slit-lamp microscopy, visual acuity tests | Eye alignment tests, neurological examination, imaging |
| Treatment | Surgical lens replacement, corrective eyewear | Prism lenses, vision therapy, surgery for underlying cause |
| Prognosis | Good with surgery; vision restoration common | Varies; depends on underlying condition and treatment |
Understanding Cataract and Diplopia
Cataract is a clouding of the eye's natural lens, leading to blurred vision and decreased visual clarity, primarily caused by aging, trauma, or certain medical conditions. Diplopia, or double vision, results from misalignment of the eyes or dysfunction in the eye muscles or nerves, causing the perception of two images instead of one. Distinguishing cataract's lens opacity from diplopia's binocular or monocular image duplication is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Key Differences Between Cataract and Diplopia
Cataract primarily involves the clouding of the eye's natural lens, leading to blurred or dim vision, while diplopia refers to double vision caused by misalignment or malfunction of the eyes or brain processing. Cataracts usually develop gradually with aging or due to trauma, impacting clarity and light perception, whereas diplopia often occurs suddenly due to neurological issues, muscle weakness, or eye injury. Treatment for cataract typically involves surgical lens replacement, whereas diplopia treatment depends on correcting the underlying cause, such as eye muscle therapy, prisms, or neurological interventions.
Causes of Cataract
Cataracts primarily develop due to protein clumping in the eye's lens, often triggered by aging, ultraviolet light exposure, diabetes, smoking, or prolonged corticosteroid use. In contrast, diplopia, or double vision, arises from misalignment of the eyes, neurological disorders, or muscle abnormalities rather than lens opacity. Understanding cataract causes helps differentiate it from diplopia, highlighting the lens clouding versus neuromuscular origins of visual impairment.
Causes of Diplopia
Diplopia, or double vision, often results from neurological disorders, cranial nerve palsies, or muscle imbalances affecting ocular alignment, contrasting with cataracts which are caused by lens opacity. Common causes include conditions like multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, thyroid eye disease, or trauma impacting eye muscles and nerves. Unlike cataracts, which mainly impair clarity of vision, diplopia arises from miscommunication between the brain and eyes, leading to the perception of two images.
Symptoms: Cataract vs Diplopia
Cataract symptoms primarily include blurry vision, faded colors, glare sensitivity, and difficulty seeing at night, resulting from clouding of the eye's lens. Diplopia, or double vision, manifests as seeing two images of a single object, either horizontally, vertically, or diagonally, caused by misalignment of the eyes or neurological issues. Unlike cataracts, diplopia does not affect color perception but leads to distortion and spatial confusion.
Diagnosis Procedures for Each Condition
Cataract diagnosis involves a comprehensive eye examination, including visual acuity tests, slit-lamp examination to assess lens opacity, and dilated eye exams to evaluate the extent of clouding in the lens. Diplopia diagnosis requires a detailed patient history, eye movement tests, and neurological evaluations such as MRI or CT scans to identify the underlying cause of double vision. Both conditions necessitate specialized diagnostic tools to confirm the presence and severity, with cataract relying on ophthalmic imaging and diplopia involving neuro-ophthalmologic assessment.
Treatment Options for Cataract
Cataract treatment primarily involves surgical removal of the clouded lens, typically replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) to restore clear vision. Non-surgical options like eyeglasses or magnifying lenses can temporarily improve symptoms but do not cure cataracts. Cataract surgery remains the most effective and widely used method to permanently resolve vision impairment caused by cataracts.
Treatment Approaches for Diplopia
Treatment approaches for diplopia primarily involve addressing the underlying cause, which may include prism glasses to realign images or occlusion therapy to block one eye's vision. In cases related to nerve or muscle dysfunction, strabismus surgery or botulinum toxin injections can help restore proper eye alignment. Neurological or systemic conditions causing diplopia may require tailored medical management, such as corticosteroids for inflammation or surgery for tumors.
Preventive Measures and Risk Factors
Cataract prevention centers on controlling risk factors such as prolonged UV exposure, smoking, diabetes, and aging by wearing protective eyewear and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Diplopia risk factors include neurological conditions, eye muscle disorders, and head injuries, with prevention focusing on managing underlying health issues and avoiding trauma. Early eye examinations and timely medical intervention are critical for reducing complications related to both cataract and diplopia.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Seek medical advice immediately if experiencing sudden onset of cataracts symptoms such as blurred vision, difficulty with glare, or cloudy vision, as these indicate lens opacity requiring evaluation. Diplopia, characterized by double vision, demands prompt consultation when associated with neurological symptoms, eye muscle weakness, or sudden vision changes to rule out serious conditions like stroke or cranial nerve palsy. Early diagnosis and treatment of cataract or underlying causes of diplopia are crucial to prevent vision loss and complications.
Cataract Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com