Eczema and fungal infections often share similar symptoms such as redness, itching, and inflammation, making accurate diagnosis crucial for effective treatment. Understanding how these conditions differ and interact can help Your skin heal faster and prevent recurring flare-ups. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to identify symptoms and choose the right care for your skin.
Table of Comparison
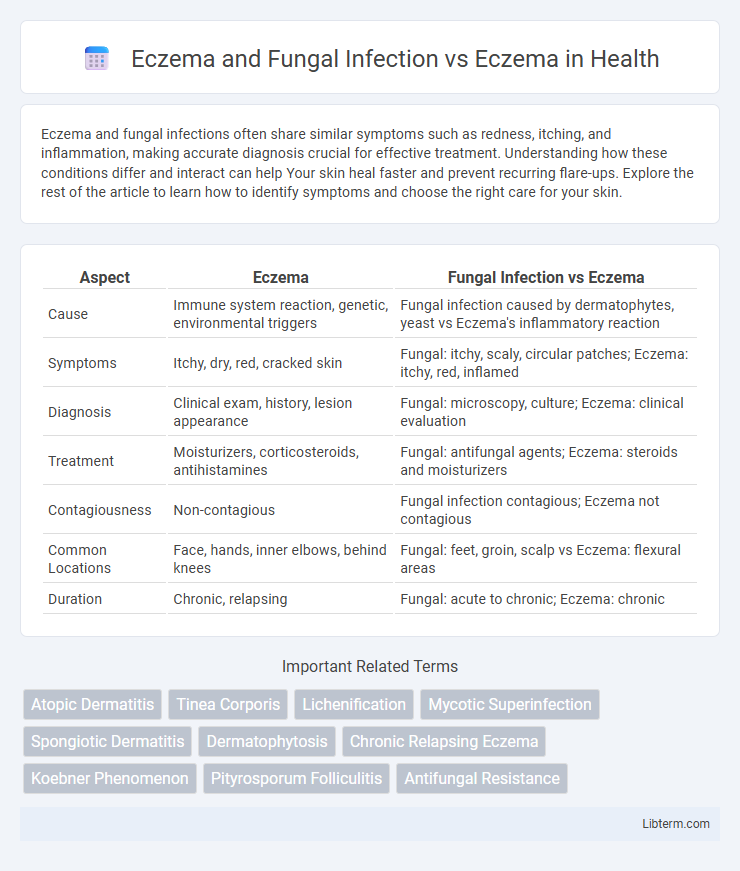
| Aspect | Eczema | Fungal Infection vs Eczema |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Immune system reaction, genetic, environmental triggers | Fungal infection caused by dermatophytes, yeast vs Eczema's inflammatory reaction |
| Symptoms | Itchy, dry, red, cracked skin | Fungal: itchy, scaly, circular patches; Eczema: itchy, red, inflamed |
| Diagnosis | Clinical exam, history, lesion appearance | Fungal: microscopy, culture; Eczema: clinical evaluation |
| Treatment | Moisturizers, corticosteroids, antihistamines | Fungal: antifungal agents; Eczema: steroids and moisturizers |
| Contagiousness | Non-contagious | Fungal infection contagious; Eczema not contagious |
| Common Locations | Face, hands, inner elbows, behind knees | Fungal: feet, groin, scalp vs Eczema: flexural areas |
| Duration | Chronic, relapsing | Fungal: acute to chronic; Eczema: chronic |
Understanding Eczema: Causes and Symptoms
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and red patches resulting from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Fungal infections can complicate eczema by causing similar symptoms such as scaling and inflammation, often leading to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment. Accurate differentiation through clinical examination and fungal cultures is essential to tailor effective management strategies and prevent exacerbation.
What Are Fungal Infections? Key Differences
Fungal infections are caused by dermatophytes, yeasts, or molds that invade the skin, leading to symptoms such as itching, redness, and scaling, often localized in moist areas. Unlike eczema, which is an inflammatory skin condition triggered by immune responses and characterized by chronic dryness and rash, fungal infections result from microbial overgrowth requiring antifungal treatment. Key differences include fungal infections having contagious potential and visible fungal elements under microscopic examination, whereas eczema involves immune dysregulation without infectious agents.
Eczema vs Fungal Infection: Identifying the Signs
Eczema and fungal infections share symptoms such as redness and itching but differ in cause and treatment, making accurate identification crucial. Eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, often presents with dry, scaly patches and responds well to moisturizers and corticosteroids. Fungal infections, caused by dermatophytes like Candida or ringworm, typically show a distinct ring-shaped rash and require antifungal medications for effective management.
Risk Factors: Who Is More Susceptible?
Individuals with compromised immune systems, including those with eczema complicated by fungal infections, face increased susceptibility due to impaired skin barriers and altered microbiomes. Eczema alone primarily affects people with a genetic predisposition to dry, sensitive skin, while fungal infections exacerbate risks by creating moist environments conducive to fungal growth. Patients with diabetes, excessive sweating, or prolonged antibiotic use are more prone to developing eczema combined with fungal infections, increasing severity and treatment complexity.
How Eczema Can Lead to Secondary Fungal Infections
Eczema disrupts the skin's protective barrier, leading to increased vulnerability to opportunistic fungal pathogens such as Candida and dermatophytes. The inflammation and scratching associated with eczema cause microabrasions that facilitate fungal colonization and infection. Poorly managed eczema creates an environment of moisture and skin breakdown, which promotes the growth of secondary fungal infections, complicating treatment and requiring antifungal therapy alongside eczema management.
Diagnostic Strategies: Eczema Alone or Fungal Complication?
Accurate diagnosis between eczema alone and eczema complicated by fungal infection requires targeted diagnostic strategies including microscopic examination, fungal culture, and dermoscopy. Skin biopsy and fungal PCR testing enhance detection of fungal elements within eczematous lesions, ensuring appropriate antifungal treatment alongside standard eczema management. Distinguishing these conditions is crucial to prevent treatment failure and chronic skin damage due to overlooked fungal superinfection.
Treatment Options for Eczema
Treatment options for eczema primarily include topical corticosteroids, moisturizers, and antihistamines to control inflammation, reduce itching, and maintain skin hydration. In cases where eczema is complicated by fungal infection, antifungal medications such as topical azoles or oral antifungals are integrated into the treatment regimen to target the fungal component alongside standard eczema therapies. Identifying the presence of fungal infection is crucial for optimizing treatment efficacy and preventing delayed healing or exacerbation of eczema symptoms.
Managing Concomitant Eczema and Fungal Infections
Managing concomitant eczema and fungal infections requires a careful balance between treating inflammation and controlling fungal overgrowth. Topical antifungal agents like ketoconazole combined with anti-inflammatory treatments such as corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors can effectively reduce symptoms while preventing exacerbation of eczema. Regular monitoring and adherence to personalized skincare routines optimize outcomes by addressing both epidermal barrier disruption and fungal colonization simultaneously.
Prevention Tips for Eczema and Fungal Infections
Preventing eczema involves maintaining skin hydration with fragrance-free moisturizers, avoiding known irritants such as harsh soaps and detergents, and managing stress levels to reduce flare-ups. For fungal infections, keeping skin dry and clean, wearing breathable clothing, and avoiding sharing personal items are essential to minimize fungal growth and transmission. Regularly applying antifungal powders in prone areas and promptly treating athlete's foot or other fungal conditions also helps prevent complications in individuals with eczema.
When to Seek Medical Advice: Warning Signs and Red Flags
Persistent eczema accompanied by symptoms such as intense itching, unusual redness, swelling, or oozing may indicate a fungal infection requiring medical evaluation. Warning signs include rapid worsening of skin condition, presence of blisters, or spreading lesions beyond typical eczema areas. Immediate consultation with a dermatologist is essential if these red flags appear to prevent complications and ensure appropriate antifungal or eczema-specific treatment.
Eczema and Fungal Infection Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com