Leukopenia is a medical condition characterized by a decreased white blood cell count, which weakens the immune system and increases vulnerability to infections. Causes range from viral infections and autoimmune diseases to bone marrow disorders and certain medications. Explore the rest of the article to understand how leukopenia affects your health and discover effective management strategies.
Table of Comparison
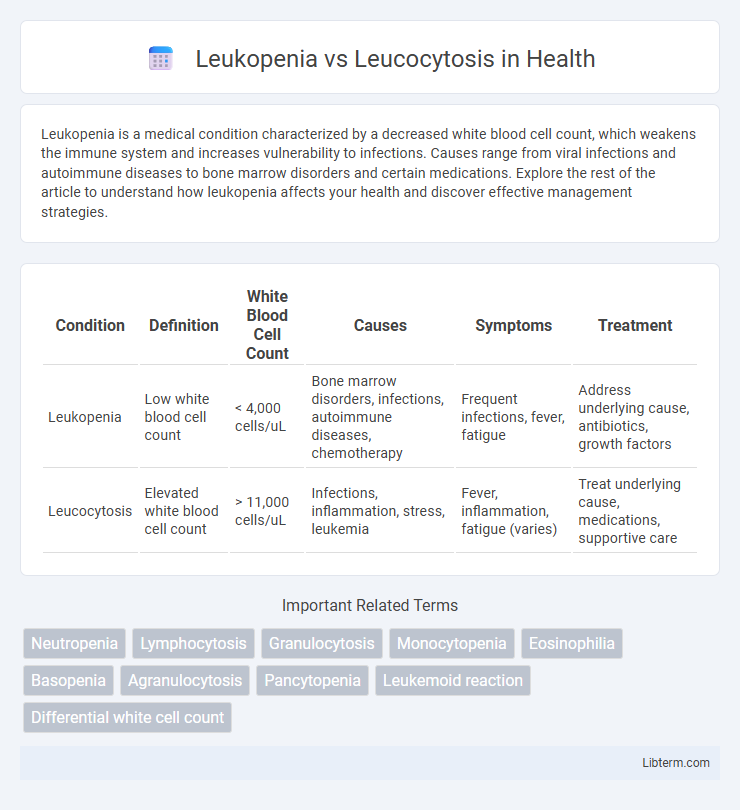
| Condition | Definition | White Blood Cell Count | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leukopenia | Low white blood cell count | < 4,000 cells/uL | Bone marrow disorders, infections, autoimmune diseases, chemotherapy | Frequent infections, fever, fatigue | Address underlying cause, antibiotics, growth factors |
| Leucocytosis | Elevated white blood cell count | > 11,000 cells/uL | Infections, inflammation, stress, leukemia | Fever, inflammation, fatigue (varies) | Treat underlying cause, medications, supportive care |
Understanding Leukopenia and Leucocytosis
Leukopenia is characterized by an abnormally low white blood cell count, increasing susceptibility to infections, while leucocytosis refers to an elevated white blood cell count, often indicating infection, inflammation, or hematologic disorders. Accurate diagnosis relies on complete blood counts (CBC) and differential analysis to determine the underlying causes such as bone marrow suppression for leukopenia or bacterial infections and stress for leucocytosis. Understanding the distinctions between leukopenia and leucocytosis is crucial for guiding appropriate clinical interventions and monitoring patient immune status.
Key Differences Between Leukopenia and Leucocytosis
Leukopenia is characterized by a decreased white blood cell (WBC) count, often below 4,000 cells per microliter, indicating a weakened immune response and increased infection risk, whereas leucocytosis involves an elevated WBC count exceeding 11,000 cells per microliter, typically signaling an active infection or inflammatory condition. Leukopenia commonly results from conditions such as bone marrow disorders, viral infections, or chemotherapy, while leucocytosis is frequently associated with bacterial infections, inflammation, stress, or malignancies like leukemia. The differential diagnosis between leukopenia and leucocytosis relies heavily on WBC count analysis, clinical context, and specific subtypes of white blood cells affected, guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
Causes of Leukopenia
Leukopenia is characterized by a decreased white blood cell (WBC) count, commonly caused by viral infections, bone marrow disorders, autoimmune diseases, and certain medications like chemotherapy or immunosuppressants. In contrast, leucocytosis involves an elevated WBC count usually triggered by infections, inflammation, stress, or hematologic malignancies. Understanding these distinct causes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies in managing abnormal white blood cell levels.
Causes of Leucocytosis
Leucocytosis is primarily caused by infections, inflammation, stress, trauma, and certain leukemias, leading to an elevated white blood cell count as the body's immune response intensifies. Other causes include corticosteroid use, smoking, and allergic reactions, which stimulate bone marrow to produce more leukocytes. Understanding these causative factors is crucial for distinguishing leucocytosis from leukopenia, where white blood cell counts are abnormally low due to conditions like bone marrow failure, autoimmune diseases, or severe infections.
Common Symptoms of Leukopenia
Leukopenia is characterized by a decreased white blood cell count, often leading to symptoms such as frequent infections, fever, chills, and fatigue due to a weakened immune system. In contrast, leucocytosis involves an elevated white blood cell count, commonly indicating infection, inflammation, or stress, with symptoms varying based on the underlying cause. Recognizing the common symptoms of leukopenia is crucial in diagnosing conditions like bone marrow disorders, autoimmune diseases, and severe infections.
Common Symptoms of Leucocytosis
Leucocytosis is characterized by an elevated white blood cell count, often reflecting an underlying infection, inflammation, or stress response, unlike leukopenia which denotes a reduced white blood cell count. Common symptoms of leucocytosis include fever, fatigue, and frequent infections due to the body's immune system reacting to various triggers. High white blood cell levels can also cause symptoms such as sweating, muscle weakness, and unintentional weight loss, indicating potential immune or hematologic disorders.
Diagnostic Approaches for White Blood Cell Disorders
Leukopenia and leucocytosis are diagnosed through complete blood count (CBC) tests measuring white blood cell (WBC) levels, where leukopenia shows reduced WBC count and leucocytosis indicates elevated WBC count. Further diagnostic approaches include bone marrow biopsy to evaluate marrow function and flow cytometry to identify abnormal cell populations. Advanced techniques such as peripheral blood smear microscopy and molecular assays help determine underlying causes, guiding targeted treatment strategies.
Treatment Options for Leukopenia
Treatment options for leukopenia focus on addressing the underlying cause, which may include infections, bone marrow disorders, or autoimmune diseases. Management strategies often involve the use of colony-stimulating factors such as filgrastim to stimulate white blood cell production, alongside antibiotics or antifungal medications to prevent or treat infections. In severe cases, bone marrow transplantation or discontinuation of causative drugs might be necessary to restore normal white blood cell counts.
Treatment Strategies for Leucocytosis
Leucocytosis treatment strategies primarily involve addressing the underlying cause, such as infections, inflammation, or stress, often through antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, or managing stressors. In cases of extreme leukocytosis caused by leukemia or other hematologic disorders, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or leukapheresis may be necessary to reduce white blood cell count. Monitoring white blood cell levels and providing supportive care are critical components in managing leucocytosis effectively.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Recommendations
Leukopenia prevention focuses on maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, regular hand hygiene to reduce infection risk, and avoiding exposure to toxins or medications that suppress bone marrow. Leucocytosis prevention involves managing underlying causes like infections or inflammation through timely medical care, stress reduction techniques, and avoiding smoking. Both conditions benefit from regular health check-ups to monitor white blood cell counts and prompt attention to symptoms signaling immunological imbalance.
Leukopenia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com