Antibody levels indicate the concentration of antibodies in your blood, reflecting your immune system's response to infections or vaccinations. Monitoring these levels helps assess your immunity status and guide medical decisions. Discover more about how antibody levels impact your health and what you need to know by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
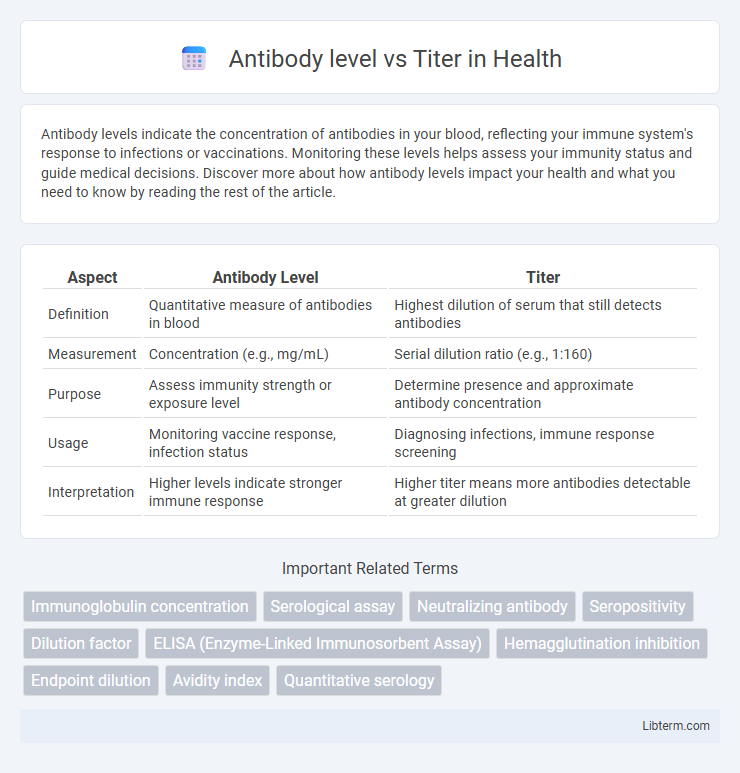
| Aspect | Antibody Level | Titer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Quantitative measure of antibodies in blood | Highest dilution of serum that still detects antibodies |
| Measurement | Concentration (e.g., mg/mL) | Serial dilution ratio (e.g., 1:160) |
| Purpose | Assess immunity strength or exposure level | Determine presence and approximate antibody concentration |
| Usage | Monitoring vaccine response, infection status | Diagnosing infections, immune response screening |
| Interpretation | Higher levels indicate stronger immune response | Higher titer means more antibodies detectable at greater dilution |
Understanding Antibody Levels and Titers
Antibody levels measure the concentration of specific antibodies in the blood, reflecting the immune system's response intensity to an infection or vaccine. Titers quantify antibody presence by determining the highest serum dilution that still produces a detectable reaction, providing a standardized method to assess immunity strength. Understanding the relationship between antibody levels and titers is essential for interpreting vaccine effectiveness, infection status, and immune protection.
Key Differences Between Antibody Levels and Titers
Antibody levels quantify the concentration of antibodies present in a specific volume of blood, typically expressed in units such as micrograms per milliliter (ug/mL). In contrast, antibody titers measure the highest dilution of a serum sample that still produces a detectable immune response, reflecting the strength or potency of antibodies rather than their absolute amount. The key difference lies in antibody levels providing a direct quantitative measurement, whereas titers indicate functional antibody activity through serial dilution assays.
How Are Antibody Levels Measured?
Antibody levels are measured through quantitative assays like ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay), which determines the concentration of antibodies in a blood sample by detecting antigen-antibody binding. Titer refers to the highest dilution of serum that still produces a detectable reaction in tests such as agglutination or neutralization assays, indicating the strength of the antibody response. Both measurements provide critical insights into immune status, with antibody levels offering precise amounts and titers reflecting functional activity.
What Does Titer Mean in Immunology?
In immunology, a titer refers to the concentration of specific antibodies present in a blood sample, indicating the strength of the immune response against a particular antigen. Antibody level measures the amount of antibodies, while the titer quantifies this concentration through serial dilution, revealing the highest dilution at which antibodies remain detectable. This titer value helps assess immunity status, vaccine efficacy, or infection severity by providing a precise, semi-quantitative estimate of antibody presence.
Methods for Testing Antibody Titers
Testing antibody titers primarily involves quantitative assays such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and chemiluminescent immunoassays (CLIA), which measure the concentration of specific antibodies in the blood. Neutralization assays assess the functional ability of antibodies to inhibit pathogen infectivity, offering insight into protective immunity. These methods provide precise antibody level quantification, essential for evaluating immune response strength or vaccine efficacy.
Clinical Significance of Antibody Levels
Antibody levels, often quantified as titers, reflect the concentration of specific antibodies in the blood, providing crucial clinical information on immune status and infection history. Measuring antibody titers aids in diagnosing infections, monitoring vaccine efficacy, and assessing immunity duration or the need for booster doses. Clinically, precise antibody quantification guides personalized treatment plans and public health decisions related to infectious disease control.
Interpreting Titer Results in Medical Practice
Titer measures the concentration of specific antibodies in the blood, indicating the immune response strength to infections or vaccinations. Interpreting titer results involves comparing antibody levels against established protective thresholds to determine immunity status or need for revaccination. Accurate titer interpretation guides clinical decisions in diagnosing infections, assessing vaccine efficacy, and managing immunodeficiency conditions.
Factors Affecting Antibody Levels and Titers
Antibody levels and titers are influenced by factors such as the timing of sample collection post-infection or vaccination, the individual's immune status, and the type of antigen exposure. Host factors like age, genetics, and immunosuppressive conditions significantly modulate antibody production and persistence. Variations in assay sensitivity and specificity also affect the measured titers, impacting clinical interpretation.
Applications in Vaccine Efficacy and Immunity Assessment
Antibody levels, measured as concentration in blood, provide quantitative data critical for assessing immunity strength, while titers indicate the highest dilution still yielding detectable antibody response, reflecting antibody potency. In vaccine efficacy studies, precise antibody level measurement helps determine protective thresholds, whereas titers guide clinical decisions on booster dose timing. Combining both metrics enables robust evaluation of immune response durability and population-level immunity monitoring post-vaccination.
Antibody Levels vs Titers: Frequently Asked Questions
Antibody levels measure the concentration of antibodies in the blood, expressed in units such as micrograms per milliliter, while antibody titers represent the highest dilution of serum that still produces a detectable immune response. Titers provide a relative measure of antibody presence, often used in diagnostic tests to assess immunity or infection status. Understanding the difference between absolute antibody levels and titers is crucial for accurate interpretation of serological assays in clinical and research settings.
Antibody level Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com