Masculinization refers to the process by which individuals develop male physical characteristics, often influenced by hormones such as testosterone. This transformation can occur naturally during puberty or be induced medically in transgender men and individuals undergoing hormone therapy. Explore the rest of this article to understand the biological mechanisms and social implications of masculinization.
Table of Comparison
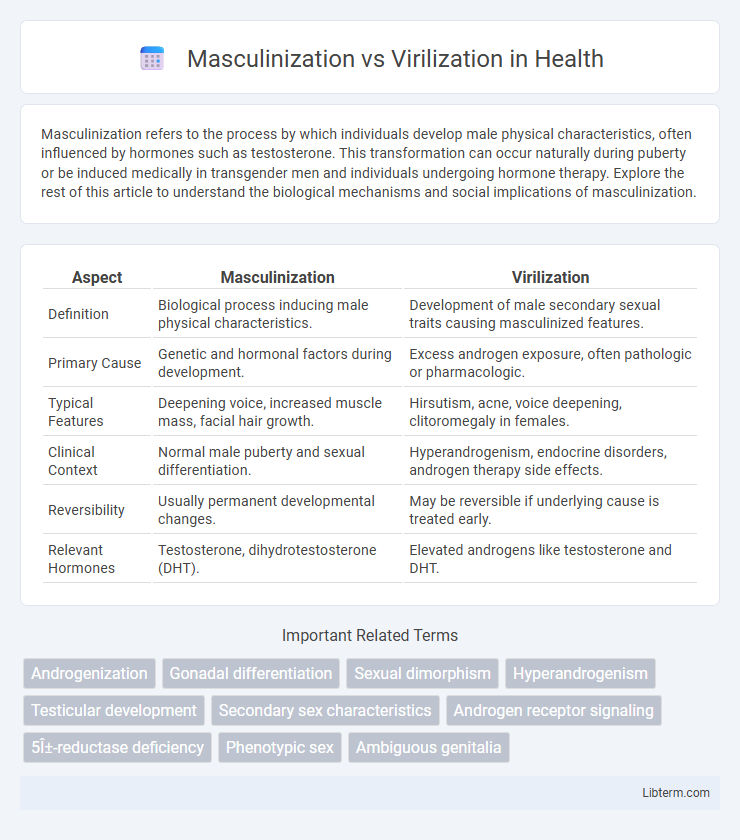
| Aspect | Masculinization | Virilization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Biological process inducing male physical characteristics. | Development of male secondary sexual traits causing masculinized features. |
| Primary Cause | Genetic and hormonal factors during development. | Excess androgen exposure, often pathologic or pharmacologic. |
| Typical Features | Deepening voice, increased muscle mass, facial hair growth. | Hirsutism, acne, voice deepening, clitoromegaly in females. |
| Clinical Context | Normal male puberty and sexual differentiation. | Hyperandrogenism, endocrine disorders, androgen therapy side effects. |
| Reversibility | Usually permanent developmental changes. | May be reversible if underlying cause is treated early. |
| Relevant Hormones | Testosterone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT). | Elevated androgens like testosterone and DHT. |
Defining Masculinization and Virilization
Masculinization refers to the biological and physiological processes that establish male characteristics, including the development of male reproductive organs, secondary sexual traits like increased muscle mass, and facial hair growth. Virilization specifically describes the emergence of male physical traits, often related to androgen hormone effects, such as deepening of the voice, increased body hair, and enhanced libido. Both terms are critical in endocrinology and developmental biology for understanding gender differentiation and hormonal impact on physical appearance.
Biological Mechanisms Behind Each Process
Masculinization involves the development of male physical characteristics driven primarily by androgen hormones such as testosterone, which influence the differentiation of male genitalia and secondary sexual traits during embryonic and pubertal stages. Virilization refers to the broader process where individuals, often females or those with hormonal imbalances, develop male secondary sexual characteristics due to excessive androgen exposure, impacting features like increased muscle mass, deepening voice, and facial hair growth. Both processes are regulated through androgen receptor activation and downstream genetic pathways affecting tissue differentiation and growth.
Hormonal Influences: Testosterone and Androgens
Testosterone and other androgens play crucial roles in masculinization by promoting the development of male secondary sexual characteristics such as increased muscle mass, facial hair, and deepening of the voice. Virilization refers specifically to the manifestation of these male physical traits in females or prepubertal individuals due to excessive androgen exposure or hormonal imbalances. The hormonal influence of testosterone and androgens is central to both natural male differentiation and pathological conditions involving abnormal androgen levels.
Key Physical Changes: Masculinization vs Virilization
Masculinization involves the development of male secondary sexual characteristics such as increased muscle mass, deepening of the voice, facial and body hair growth, and enlargement of the larynx. Virilization, often used interchangeably but with subtle differences, specifically refers to the appearance of male traits in females due to higher androgen levels, leading to symptoms like clitoral enlargement, male-pattern baldness, and hirsutism. Key physical changes in masculinization center on overall male phenotype development, whereas virilization highlights atypical male characteristic manifestation in females or prepubertal individuals.
Clinical Perspectives on Sexual Differentiation
Masculinization and virilization refer to processes influencing male sexual differentiation, where masculinization involves the development of male physical characteristics during fetal growth, primarily driven by androgens like testosterone. Virilization describes the appearance of male secondary sexual features in females or prepubertal males, often linked to excess androgen exposure or disorders such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Clinical evaluation includes hormonal assays, genetic testing, and imaging to distinguish conditions affecting sexual differentiation, guiding appropriate medical or surgical interventions.
Disorders and Syndromes Associated with Each Process
Masculinization involves the development of male physical characteristics primarily influenced by androgens, with disorders such as androgen insensitivity syndrome and 5-alpha-reductase deficiency disrupting typical male differentiation. Virilization refers to the acquisition of male secondary sexual characteristics in females or prepubertal individuals, often linked to conditions like congenital adrenal hyperplasia and polycystic ovary syndrome. Both processes are associated with distinct syndromes that result from hormonal imbalances affecting sexual development and differentiation.
Masculinization and Virilization in Puberty
Masculinization during puberty refers to the development of male secondary sexual characteristics driven primarily by testosterone, including increased muscle mass, deepening of the voice, and growth of facial and body hair. Virilization, a more intense form of masculinization, involves exaggerated male features such as pronounced hirsutism, clitoromegaly, or male-pattern baldness, often due to abnormal androgen exposure or endocrine disorders. Both processes are crucial for the physical transformation in adolescent males, but virilization may indicate pathological hormone imbalances requiring medical evaluation.
Medical Treatments and Their Effects
Masculinization involves medical treatments such as testosterone therapy that promote the development of male secondary sexual characteristics, including increased muscle mass, facial and body hair growth, and voice deepening. Virilization refers to the appearance of male physical traits in females or individuals assigned female at birth, often resulting from excess androgen exposure due to hormone therapy or medical conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or adrenal hyperplasia. Both processes require careful monitoring to manage side effects such as skin changes, mood fluctuations, and metabolic alterations, with endocrinologists tailoring treatments to individual patient goals and health profiles.
Psychosocial and Gender Identity Implications
Masculinization refers to the development of male physical characteristics typically influenced by androgens, while virilization describes the process in which females develop male secondary sexual traits, often due to hormonal imbalances or medical conditions. Psychosocial implications include challenges in gender identity formation, social acceptance, and psychological well-being, with affected individuals experiencing varying degrees of gender dysphoria or identity confusion. Understanding the distinction between masculinization and virilization is crucial for healthcare providers to support mental health outcomes and develop gender-affirming interventions.
Future Research and Ethical Considerations
Future research on masculinization and virilization aims to clarify distinct molecular pathways and long-term health impacts, emphasizing personalized medical approaches. Ethical considerations focus on informed consent, especially in gender-affirming treatments, and preventing misuse in non-therapeutic contexts like performance enhancement. Advancing guidelines to balance innovation with patient autonomy and safety remains a critical priority.
Masculinization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com