Oscillopsia is a visual disturbance where objects appear to oscillate or move back and forth, often caused by abnormalities in the vestibular system or eye movement control. This condition can significantly disrupt your daily activities by impairing balance and spatial orientation. Explore the rest of the article to understand its causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
Table of Comparison
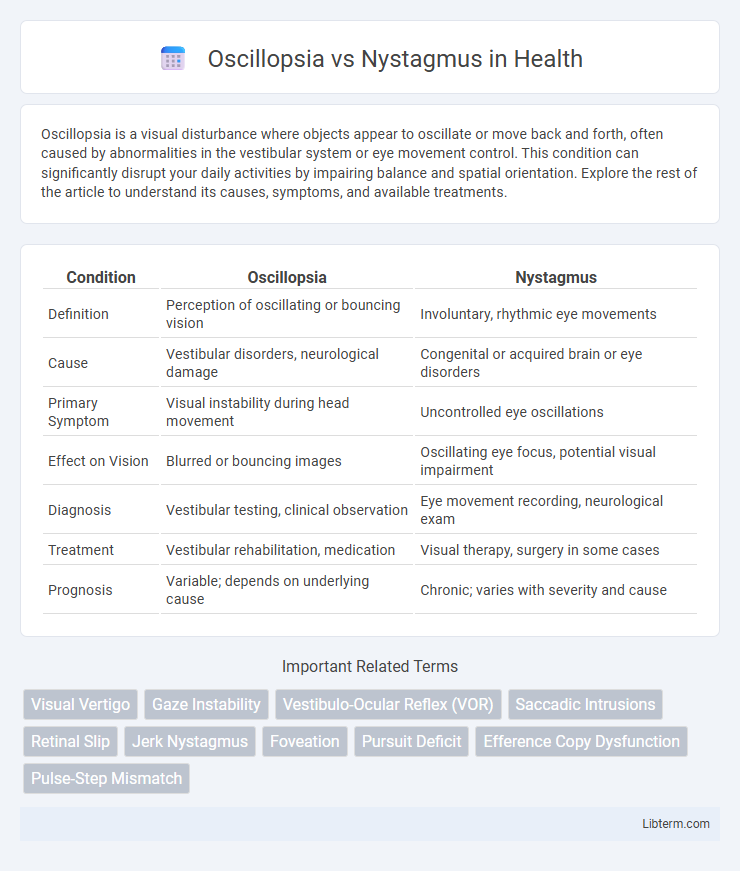
| Condition | Oscillopsia | Nystagmus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Perception of oscillating or bouncing vision | Involuntary, rhythmic eye movements |
| Cause | Vestibular disorders, neurological damage | Congenital or acquired brain or eye disorders |
| Primary Symptom | Visual instability during head movement | Uncontrolled eye oscillations |
| Effect on Vision | Blurred or bouncing images | Oscillating eye focus, potential visual impairment |
| Diagnosis | Vestibular testing, clinical observation | Eye movement recording, neurological exam |
| Treatment | Vestibular rehabilitation, medication | Visual therapy, surgery in some cases |
| Prognosis | Variable; depends on underlying cause | Chronic; varies with severity and cause |
Understanding Oscillopsia: Definition and Symptoms
Oscillopsia is a visual disturbance characterized by the sensation of objects moving or bouncing in the visual field, often caused by involuntary eye movements or vestibular dysfunction. Symptoms include blurred vision, decreased visual stability, and difficulty focusing, which significantly impact daily activities. Unlike nystagmus, which is defined by rhythmic eye oscillations, oscillopsia describes the resulting perception of motion experienced by the affected individual.
What is Nystagmus? Types and Causes
Nystagmus is a neurological condition characterized by involuntary, repetitive eye movements that can be horizontal, vertical, or rotary, significantly impacting vision stability. The main types include congenital nystagmus, which appears in infancy, and acquired nystagmus, resulting from neurological disorders, inner ear problems, or drug toxicity. Common causes encompass vestibular dysfunction, multiple sclerosis, brain injury, and certain medications, each disrupting the eye's ability to maintain steady focus.
Key Differences Between Oscillopsia and Nystagmus
Oscillopsia is the subjective sensation of the visual environment oscillating or moving, often caused by unstable eye movements or vestibular dysfunction, while nystagmus refers to involuntary, rhythmic eye movements that can be horizontal, vertical, or rotary. Oscillopsia results from impaired gaze stabilization mechanisms leading to blurred or bouncing vision, whereas nystagmus is a clinical sign indicating abnormal eye motor control and can cause oscillopsia as a symptom. Diagnostically, oscillopsia is reported by patients describing visual disturbance, whereas nystagmus is observed objectively during an eye examination.
How Oscillopsia Relates to Nystagmus
Oscillopsia is a visual disturbance characterized by the perception of oscillating or bouncing images, often resulting from involuntary eye movements associated with nystagmus. Nystagmus involves rapid, repetitive eye movements that disrupt stable gaze, directly causing oscillopsia by preventing the eyes from maintaining steady fixation. Understanding the connection between nystagmus-induced eye movements and oscillopsia is crucial for diagnosing and managing visual instability in affected patients.
Common Causes of Oscillopsia and Nystagmus
Oscillopsia commonly results from vestibular disorders such as bilateral vestibular hypofunction, vestibular neuritis, or inner ear infections, causing a false perception of motion during head movement. Nystagmus is often caused by neurological conditions including multiple sclerosis, brainstem or cerebellar lesions, and congenital abnormalities affecting eye movement control. Both conditions may also arise from drug toxicity, head trauma, or optic nerve damage, yet oscillopsia primarily involves impaired vestibular input, while nystagmus is characterized by involuntary rhythmic eye oscillations.
Diagnostic Approaches for Oscillopsia vs Nystagmus
The informal sector often lacks legal protections, social security, and minimum wage guarantees, exposing workers to exploitation and poor working conditions. In contrast, the formal sector provides regulated employment with enforced labor laws, social benefits, and access to healthcare and pensions, promoting worker stability and well-being. The disparity significantly impacts social equity, as informal workers face higher vulnerability without formal rights or institutional support.
Impact on Vision and Quality of Life
Oscillopsia causes a sensation of visual instability or bouncing, severely impairing the ability to focus on objects, leading to difficulties with reading, driving, and balance, which significantly reduces quality of life. Nystagmus involves involuntary eye movements that result in blurred or shaky vision, affecting depth perception and visual clarity, often causing challenges in social interactions and daily activities. Both conditions disrupt stable vision but differ in mechanisms and symptom presentation, with oscillopsia primarily affecting visual stability and nystagmus impacting eye movement control and visual processing.
Treatment Options for Oscillopsia
Oscillopsia treatment primarily focuses on managing the underlying vestibular or neurological disorders causing the symptom, such as vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT) which aims to improve gaze stability and balance through customized exercises. Pharmacological options may include medications like benzodiazepines or anticholinergics to reduce vestibular hyperactivity, though their use is typically limited due to side effects. In cases related to nystagmus, interventions such as botulinum toxin injections or surgical procedures to correct abnormal eye movements can indirectly alleviate oscillopsia by stabilizing vision.
Managing Nystagmus: Therapies and Interventions
Managing nystagmus involves tailored therapies such as vision therapy, which aims to improve eye movement control and reduce symptoms, and pharmacological treatments that target underlying neurological causes. Interventions like prism glasses and specialized contact lenses can help stabilize images and improve visual clarity. Surgical options may be considered in severe cases to reposition eye muscles and minimize involuntary oscillations, enhancing overall quality of life for patients.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Eye Movement Disorders
Persistent oscillopsia and nystagmus, especially when accompanied by dizziness, blurred vision, or balance issues, warrant prompt medical evaluation to prevent worsening symptoms or underlying neurological disorders. Immediate medical advice is crucial if these eye movement abnormalities suddenly worsen, occur after head trauma, or are associated with headaches and weakness, indicating potential serious conditions like vestibular dysfunction or brainstem pathology. Early diagnosis through comprehensive neuro-ophthalmic and vestibular testing ensures timely treatment to improve quality of life and reduce the risk of permanent vision disturbances.
Oscillopsia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com