Infective diseases are caused by harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites that invade the body and multiply. Symptoms vary widely depending on the type of infection and the affected area, making accurate diagnosis crucial for effective treatment. Explore the rest of the article to learn how you can protect yourself and manage infective conditions effectively.
Table of Comparison
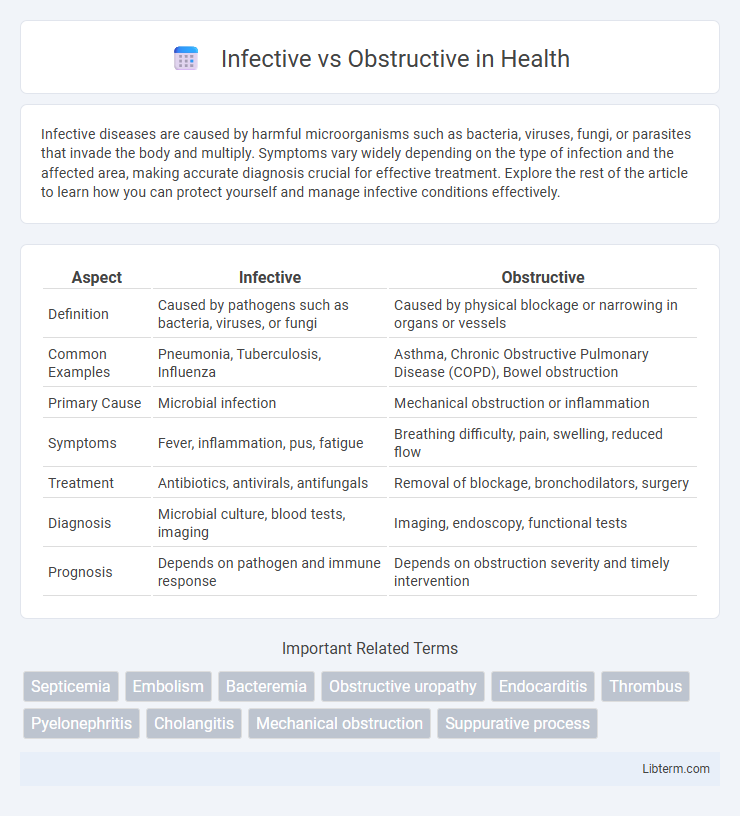
| Aspect | Infective | Obstructive |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Caused by pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi | Caused by physical blockage or narrowing in organs or vessels |
| Common Examples | Pneumonia, Tuberculosis, Influenza | Asthma, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), Bowel obstruction |
| Primary Cause | Microbial infection | Mechanical obstruction or inflammation |
| Symptoms | Fever, inflammation, pus, fatigue | Breathing difficulty, pain, swelling, reduced flow |
| Treatment | Antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals | Removal of blockage, bronchodilators, surgery |
| Diagnosis | Microbial culture, blood tests, imaging | Imaging, endoscopy, functional tests |
| Prognosis | Depends on pathogen and immune response | Depends on obstruction severity and timely intervention |
Overview of Infective and Obstructive Conditions
Infective conditions involve the invasion of pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi, leading to inflammation and tissue damage, often accompanied by symptoms like fever, pain, and swelling; examples include pneumonia and urinary tract infections. Obstructive conditions result from physical blockages within organs or vessels that impede normal flow or function, causing symptoms such as pain, swelling, and organ dysfunction; common examples are gallstones in the bile duct and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Both infective and obstructive conditions can cause significant morbidity, necessitating accurate diagnosis through clinical evaluation and imaging for appropriate management.
Key Definitions: Infective vs Obstructive
Infective conditions involve pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi causing tissue damage or systemic illness, characterized by symptoms like fever, inflammation, and pus formation. Obstructive conditions result from a physical blockage in organs or vessels, leading to impaired function or flow, exemplified by airway obstruction or urinary tract blockage. Understanding these key definitions helps differentiate between infections requiring antimicrobial treatment and obstructions needing mechanical relief or surgery.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Infective conditions often arise from bacterial, viral, or fungal pathogens, with common causes including Streptococcus pneumoniae and Escherichia coli, especially in respiratory and urinary tract infections. Obstructive disorders typically result from physical blockages such as tumors, kidney stones, or strictures that impede normal fluid or air flow. Risk factors for infective diseases include immunosuppression, poor hygiene, and close contact with infected individuals, while obstructive conditions are frequently associated with chronic inflammation, previous surgeries, or congenital abnormalities.
Pathophysiology: Mechanisms of Disease
Infective pathophysiology involves the invasion and multiplication of pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi, triggering immune responses and inflammation that damage tissues. Obstructive pathophysiology results from physical blockage in organs or vessels, leading to impaired fluid or airflow, tissue ischemia, and increased pressure proximal to the obstruction. Both mechanisms disrupt normal cellular and organ function, but infective diseases primarily cause damage through microbial toxins and immune-mediated injury, whereas obstructive diseases cause damage through mechanical stress and hypoxia.
Clinical Manifestations and Symptoms
Infective conditions often present with fever, localized pain, swelling, and purulent discharge, reflecting the presence of infection and inflammation in affected tissues. Obstructive disorders typically manifest as pain due to the blockage of normal flow channels, leading to symptoms like distension, decreased function of the involved organ, and sometimes secondary infection due to stasis. Fever and systemic signs are more common in infective cases, whereas obstructive presentations primarily involve symptoms related to impaired drainage or flow without initial systemic infection.
Diagnostic Approaches and Tools
Infective conditions typically require blood cultures, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, and imaging modalities like MRI or CT scans to detect abscesses or infections, while obstructive disorders rely heavily on ultrasound, X-rays, and endoscopic evaluations to identify blockages or structural anomalies. Laboratory tests measuring inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and white blood cell count assist in differentiating infection from obstruction. Advanced diagnostic tools like Doppler ultrasound assess blood flow changes that may distinguish vascular obstruction from infectious inflammation.
Treatment Strategies and Management
Infective conditions require targeted antimicrobial therapy based on culture sensitivity to eradicate pathogens and prevent systemic complications, with supportive care such as hydration and symptom management critical for recovery. Obstructive issues demand prompt identification and relief of the underlying cause through surgical intervention, stenting, or endoscopic procedures to restore normal flow and prevent tissue damage. Monitoring for complications and multidisciplinary management optimize patient outcomes in both infective and obstructive scenarios.
Complications and Prognosis
Infective conditions often lead to systemic complications such as sepsis, abscess formation, and chronic inflammation, significantly impacting prognosis depending on timely antibiotic treatment. Obstructive disorders primarily cause localized tissue damage, ischemia, and secondary infections, with prognosis varying based on the duration and severity of obstruction. Both conditions require prompt diagnosis and intervention to prevent irreversible organ damage and improve patient outcomes.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Infective conditions can be prevented through rigorous hygiene practices, timely vaccination, and appropriate use of antibiotics to reduce pathogen exposure and resistance. Obstructive disorders often require risk reduction strategies such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking to prevent structural blockages or tissue damage. Early detection and management of underlying health issues play a critical role in minimizing both infective and obstructive complications.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
Emerging research in infective versus obstructive pathologies highlights advances in molecular diagnostics and targeted therapies that differentiate infectious inflammation from mechanical blockage with greater precision. Novel biomarkers and imaging techniques are being developed to improve early detection and personalized treatment approaches in conditions such as infective endocarditis and obstructive pulmonary diseases. Future directions emphasize integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance diagnostic accuracy and predict therapeutic responses, potentially transforming patient outcomes in both infectious and obstructive disorders.
Infective Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com