Ecchymosis is a medical condition characterized by the discoloration of the skin resulting from bleeding underneath, commonly known as bruising. It occurs when small blood vessels break and leak blood into surrounding tissues, often due to trauma or certain medical conditions. Explore the rest of the article to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for ecchymosis to better manage your health.
Table of Comparison
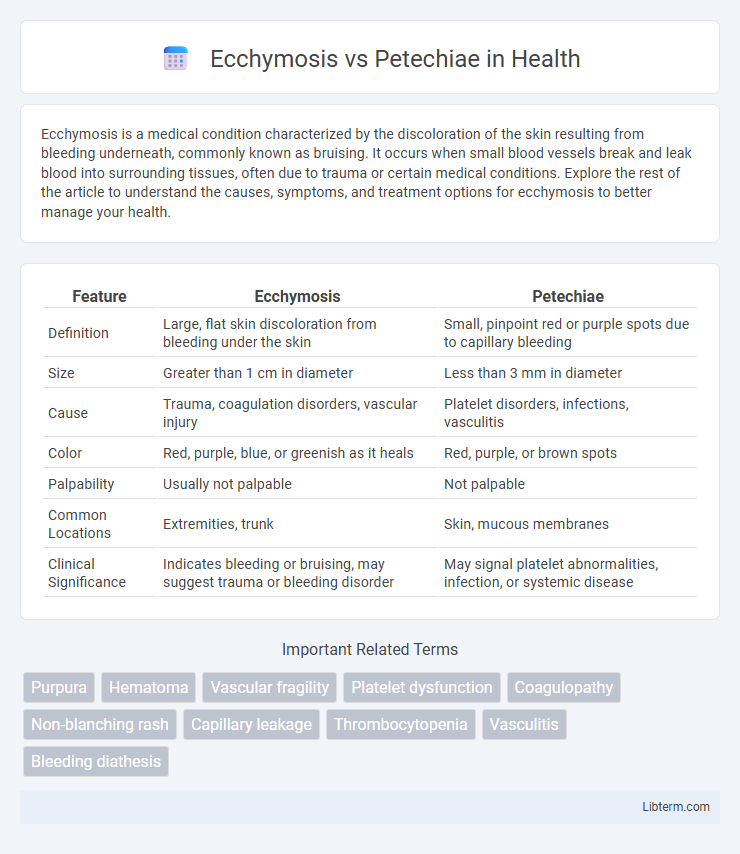
| Feature | Ecchymosis | Petechiae |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large, flat skin discoloration from bleeding under the skin | Small, pinpoint red or purple spots due to capillary bleeding |
| Size | Greater than 1 cm in diameter | Less than 3 mm in diameter |
| Cause | Trauma, coagulation disorders, vascular injury | Platelet disorders, infections, vasculitis |
| Color | Red, purple, blue, or greenish as it heals | Red, purple, or brown spots |
| Palpability | Usually not palpable | Not palpable |
| Common Locations | Extremities, trunk | Skin, mucous membranes |
| Clinical Significance | Indicates bleeding or bruising, may suggest trauma or bleeding disorder | May signal platelet abnormalities, infection, or systemic disease |
Introduction to Ecchymosis and Petechiae
Ecchymosis and petechiae are types of skin hemorrhages caused by blood leaking from damaged capillaries. Ecchymosis presents as large, flat, blue or purple bruises usually greater than 1 centimeter in diameter, often resulting from trauma or bleeding disorders. Petechiae are much smaller pinpoint spots, less than 3 millimeters, often appearing in clusters and commonly associated with conditions causing platelet dysfunction or vascular inflammation.
Definition of Ecchymosis
Ecchymosis is a medical condition characterized by the escape of blood into the tissues, resulting in a large, flat, and irregularly shaped bruise that usually measures more than 1 centimeter in diameter. It differs from petechiae, which are small, pinpoint, red or purple spots caused by minor bleeding under the skin and typically less than 3 millimeters in diameter. Ecchymosis often arises from trauma, bleeding disorders, or vascular abnormalities, serving as an indicator of underlying pathology that requires clinical evaluation.
Definition of Petechiae
Petechiae are small, flat, pinpoint red or purple spots on the skin caused by minor bleeding from broken capillaries. They differ from ecchymosis, which are larger areas of bruising due to blood leakage under the skin. Petechiae typically measure less than 3 millimeters, indicating localized capillary hemorrhage often linked to conditions like thrombocytopenia or infections.
Key Differences Between Ecchymosis and Petechiae
Ecchymosis and petechiae both refer to types of bleeding under the skin but differ significantly in size and appearance. Ecchymosis presents as a larger, bruise-like discoloration over 1 centimeter in diameter, often caused by trauma or vascular injury, while petechiae are small, pinpoint, non-blanching red or purple spots less than 3 millimeters, typically resulting from platelet abnormalities or capillary fragility. Recognizing these distinctions is crucial for accurate diagnosis, guiding investigations into bleeding disorders, vascular integrity, or systemic diseases.
Causes of Ecchymosis
Ecchymosis occurs due to blunt trauma or injury causing blood vessels to rupture beneath the skin, leading to larger, bruise-like discolorations often over 1 centimeter in diameter. Other causes include clotting disorders such as hemophilia, platelet abnormalities, anticoagulant medication use, and vascular diseases that impair blood vessel integrity. Unlike petechiae, which are pinpoint-sized pinpoint hemorrhages caused by capillary bleeding, ecchymosis reflects more extensive bleeding from larger blood vessels.
Causes of Petechiae
Petechiae are small, pinpoint red or purple spots caused by bleeding under the skin due to capillary hemorrhage or platelet abnormalities. Common causes include low platelet count (thrombocytopenia), infections such as meningococcemia, vasculitis, certain medications, and physical trauma. Unlike ecchymosis, which results from larger blood vessel rupture leading to bruising, petechiae primarily indicate microvascular bleeding and require evaluation for underlying systemic conditions.
Clinical Presentation and Appearance
Ecchymosis presents as larger, irregularly shaped bruises typically exceeding 1 centimeter in diameter, often resulting from trauma or underlying bleeding disorders. Petechiae are pinpoint, round spots less than 3 millimeters in size, caused by capillary hemorrhages and commonly associated with platelet abnormalities or infections. Both manifest as skin discolorations but differ in size, shape, and underlying pathology, aiding clinical differentiation during physical examination.
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnostic approaches for ecchymosis and petechiae primarily involve clinical evaluation and laboratory tests to determine underlying causes. Ecchymosis, characterized by larger, bruise-like discolorations, often prompts coagulation studies and imaging to assess for trauma or bleeding disorders, while petechiae, presenting as pinpoint red or purple spots, require platelet counts and vascular integrity assessments. Skin biopsy and blood smear analysis help differentiate between vascular damage and platelet abnormalities, guiding targeted treatment strategies.
Treatment and Management Options
Ecchymosis treatment typically involves addressing underlying causes such as trauma or clotting disorders, with options including rest, ice application, compression, and elevation to reduce bleeding and swelling. Petechiae management focuses on identifying and treating the root cause, which might involve controlling infections, adjusting medications, or managing systemic diseases like thrombocytopenia. Both conditions may require medical evaluation for disorders affecting platelet function or coagulation pathways to guide appropriate therapy.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Ecchymosis presents as larger, bruise-like patches caused by blood leakage under the skin, whereas petechiae are tiny red or purple spots resulting from pinpoint hemorrhages. Seek medical attention if ecchymosis appears without injury, is unusually large or painful, or if petechiae occur suddenly, spread rapidly, or accompany symptoms like fever, unexplained bleeding, or fatigue. These signs may indicate underlying conditions such as blood clotting disorders, infections, or platelet abnormalities requiring prompt evaluation.
Ecchymosis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com