Pharmacogenomics explores how your genetic makeup influences drug response, enabling personalized medicine and more effective treatments. Understanding genetic variations can help predict adverse reactions and optimize drug choices tailored to individual needs. Discover how pharmacogenomics can transform your healthcare in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
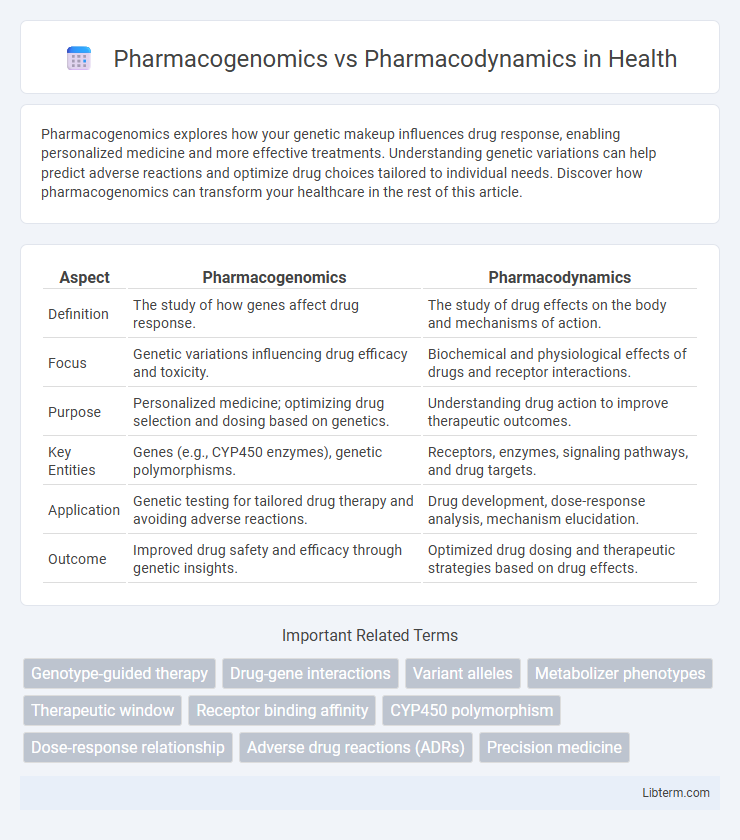
| Aspect | Pharmacogenomics | Pharmacodynamics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The study of how genes affect drug response. | The study of drug effects on the body and mechanisms of action. |
| Focus | Genetic variations influencing drug efficacy and toxicity. | Biochemical and physiological effects of drugs and receptor interactions. |
| Purpose | Personalized medicine; optimizing drug selection and dosing based on genetics. | Understanding drug action to improve therapeutic outcomes. |
| Key Entities | Genes (e.g., CYP450 enzymes), genetic polymorphisms. | Receptors, enzymes, signaling pathways, and drug targets. |
| Application | Genetic testing for tailored drug therapy and avoiding adverse reactions. | Drug development, dose-response analysis, mechanism elucidation. |
| Outcome | Improved drug safety and efficacy through genetic insights. | Optimized drug dosing and therapeutic strategies based on drug effects. |
Introduction to Pharmacogenomics and Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacogenomics studies how genetic variations influence individual responses to drugs, enabling personalized medicine by predicting drug efficacy and adverse reactions. Pharmacodynamics examines the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs and their mechanisms of action at target sites, focusing on drug-receptor interactions and dose-response relationships. Integrating pharmacogenomics with pharmacodynamics helps optimize drug therapy by tailoring treatments based on both genetic factors and drug action mechanisms.
Defining Pharmacogenomics: The Genetic Influence on Drug Response
Pharmacogenomics examines how genetic variations affect individual responses to medications, enabling personalized drug therapy based on genetic profiles. This field identifies specific gene variants that influence drug metabolism, efficacy, and risk of adverse reactions, optimizing treatment outcomes. In contrast, pharmacodynamics studies the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body, focusing on drug mechanisms rather than genetic factors.
Understanding Pharmacodynamics: Mechanisms of Drug Action
Pharmacodynamics explores the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body, focusing on receptor interactions, signal transduction pathways, and dose-response relationships. Understanding these mechanisms provides insight into how drugs activate or inhibit specific targets, influencing therapeutic outcomes and adverse effects. This knowledge is essential for optimizing drug efficacy and minimizing toxicity in personalized medicine.
Key Differences Between Pharmacogenomics and Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacogenomics studies how genetic variations influence an individual's response to drugs, aiming to tailor medication based on genetic profiles. Pharmacodynamics examines the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body, focusing on drug mechanisms and receptor interactions. The key difference lies in pharmacogenomics addressing genetic factors affecting drug response, while pharmacodynamics centers on the drug's effects regardless of genetic variation.
How Genetics Shape Drug Efficacy: The Role of Pharmacogenomics
Pharmacogenomics examines how individual genetic variations influence drug metabolism, response, and toxicity, enabling personalized medication strategies that improve efficacy and reduce adverse effects. Unlike pharmacodynamics, which studies how drugs affect the body at molecular and cellular levels, pharmacogenomics focuses on the genetic factors that modulate these drug responses. Understanding gene variants in enzymes such as CYP450 plays a critical role in predicting patient-specific drug efficacy and safety profiles.
Clinical Implications of Pharmacodynamics in Drug Therapy
Pharmacodynamics examines the effects of drugs on the body, including receptor interactions, dose-response relationships, and therapeutic outcomes, which directly influence drug efficacy and safety in clinical practice. Understanding pharmacodynamic variability helps tailor drug dosages, minimize adverse effects, and optimize therapeutic regimens based on individual patient responses. Clinical implications emphasize monitoring biomarkers, drug-receptor binding affinities, and physiological effects to improve personalized medicine and enhance patient care outcomes.
Real-World Applications: Pharmacogenomics vs Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacogenomics applies genetic data to tailor drug therapies, improving efficacy and minimizing adverse effects based on individual genetic variants, which is critical in oncology and psychiatry. Pharmacodynamics focuses on the drug's biological effects and mechanisms of action at target sites, guiding dose adjustments and predicting therapeutic outcomes in cardiovascular and pain management treatments. Real-world applications integrate pharmacogenomics and pharmacodynamics to optimize personalized medicine, enhance drug safety, and refine clinical decision-making in complex diseases.
Challenges in Integrating Pharmacogenomics and Pharmacodynamics
Integrating pharmacogenomics and pharmacodynamics faces challenges such as variability in gene expression affecting drug target interactions and difficulties in translating genetic data into precise dosing guidelines. Complex interplay between genetic polymorphisms and dynamic biochemical pathways complicates predictive modeling for drug efficacy and toxicity. Limited clinical validation and heterogeneous patient responses hinder the development of standardized protocols for personalized medicine implementation.
Future Trends in Personalized Medicine
Pharmacogenomics leverages genetic information to predict individual drug responses, enabling tailored therapies that maximize efficacy and minimize adverse effects, while pharmacodynamics studies the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body to optimize dosage and treatment protocols. Emerging trends in personalized medicine emphasize integrating pharmacogenomic data with pharmacodynamic profiles through advanced AI algorithms and machine learning models to enhance precision dosing and therapeutic outcomes. Innovations such as CRISPR gene editing and multi-omics approaches are expected to refine drug targeting and resistance prediction, shaping the future of individualized treatment strategies.
Conclusion: Optimizing Drug Therapy Through Combined Approaches
Pharmacogenomics and pharmacodynamics together enhance drug therapy by integrating genetic variations with drug response mechanisms, enabling more precise dosage and improved efficacy. Understanding how genetic factors influence pharmacodynamic pathways allows personalization of treatment to minimize adverse effects and maximize therapeutic outcomes. Combining these approaches supports the development of individualized medicine, optimizing drug therapy through tailored interventions based on a patient's unique genetic and biochemical profile.
Pharmacogenomics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com