Pharmacogenomics explores how your genetic makeup influences drug efficacy and safety, enabling personalized medicine tailored to individual responses. This scientific field helps predict adverse drug reactions and optimize dosages for better treatment outcomes. Discover how pharmacogenomics can transform healthcare by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
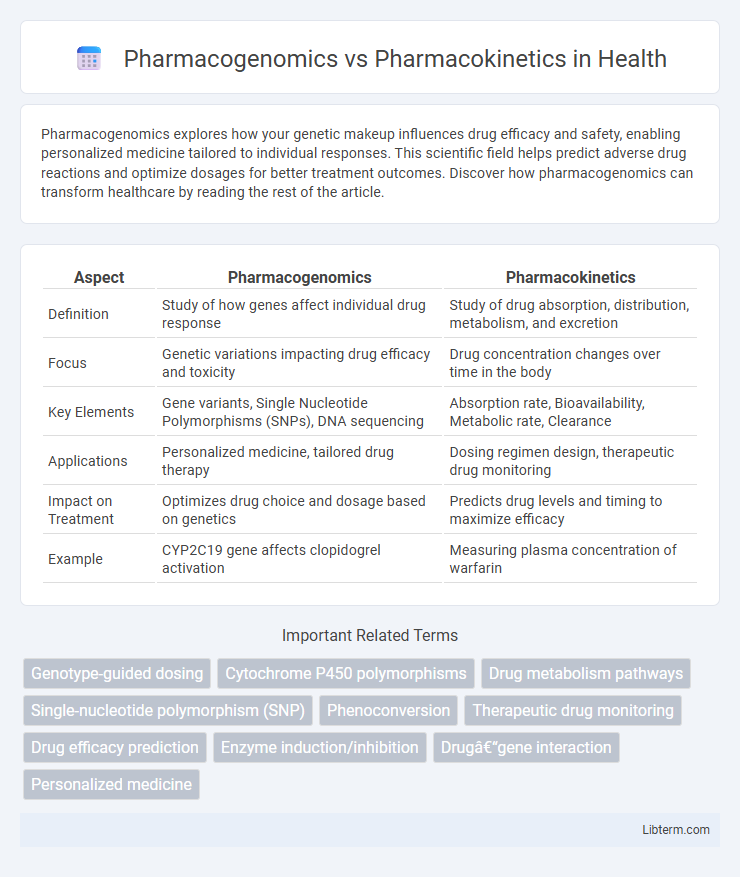
| Aspect | Pharmacogenomics | Pharmacokinetics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of how genes affect individual drug response | Study of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion |
| Focus | Genetic variations impacting drug efficacy and toxicity | Drug concentration changes over time in the body |
| Key Elements | Gene variants, Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs), DNA sequencing | Absorption rate, Bioavailability, Metabolic rate, Clearance |
| Applications | Personalized medicine, tailored drug therapy | Dosing regimen design, therapeutic drug monitoring |
| Impact on Treatment | Optimizes drug choice and dosage based on genetics | Predicts drug levels and timing to maximize efficacy |
| Example | CYP2C19 gene affects clopidogrel activation | Measuring plasma concentration of warfarin |
Introduction to Pharmacogenomics and Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacogenomics examines how genetic variations influence individual responses to drugs, enabling personalized medicine by predicting drug efficacy and adverse effects. Pharmacokinetics studies the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of drugs, determining their concentration and duration in the body. Integrating pharmacogenomics with pharmacokinetics enhances drug therapy optimization by tailoring treatments based on genetic and metabolic profiles.
Defining Pharmacogenomics
Pharmacogenomics is the study of how an individual's genetic makeup influences their response to drugs, enabling personalized medicine through tailored drug therapies. This field identifies genetic variations that affect drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity, often overlapping with pharmacokinetics, which examines the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs. Unlike pharmacokinetics, pharmacogenomics specifically focuses on genetic factors that dictate drug response, improving therapeutic outcomes and minimizing adverse effects.
Understanding Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics studies the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of drugs, impacting dosage and therapy effectiveness. Factors such as enzyme activity, organ function, and drug interactions significantly influence pharmacokinetic profiles. Understanding pharmacokinetics enables personalized medicine by optimizing drug administration based on individual metabolic and elimination rates.
Key Differences Between Pharmacogenomics and Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacogenomics studies how genetic variations influence individual drug responses, focusing on gene-drug interactions to optimize personalized therapy. Pharmacokinetics examines the body's absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of drugs, determining drug concentration over time. Key differences lie in pharmacogenomics analyzing genetic determinants of drug efficacy and toxicity, while pharmacokinetics emphasizes the drug's journey through the body and dosage optimization.
Role of Genetics in Drug Response
Pharmacogenomics studies how genetic variations influence an individual's drug response, aiming to tailor medications for optimal efficacy and minimal adverse effects. Pharmacokinetics involves the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs, where genetic polymorphisms in enzymes like CYP450 significantly affect these processes. Understanding genetic factors in pharmacokinetics enables personalized dosing and improves therapeutic outcomes by predicting drug metabolism rates and toxicity risks.
Impact of Pharmacokinetics on Drug Absorption and Distribution
Pharmacokinetics directly influences drug absorption and distribution by determining the rate and extent to which a drug enters systemic circulation and reaches target tissues. Key pharmacokinetic parameters such as bioavailability, volume of distribution, and membrane permeability critically affect therapeutic efficacy. Understanding these factors enables optimization of dosing regimens for personalized medicine and minimizes adverse effects.
Clinical Applications of Pharmacogenomics
Pharmacogenomics enables personalized medicine by tailoring drug therapies based on an individual's genetic profile, enhancing drug efficacy and minimizing adverse effects in clinical settings. It informs clinical decision-making through genetic testing, guiding dosage adjustments and drug selection to optimize therapeutic outcomes for conditions like cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and psychiatric disorders. Pharmacokinetics studies drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, providing foundational data, while pharmacogenomics applies genetic insights to predict patient-specific drug responses and improve precision medicine.
Personalized Medicine: Integrating Both Fields
Pharmacogenomics analyzes genetic variations affecting drug response, while pharmacokinetics studies drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion to determine optimal dosing. Integrating pharmacogenomics with pharmacokinetics enables personalized medicine by tailoring drug therapies based on both genetic profiles and individual metabolic rates. This combined approach enhances treatment efficacy, minimizes adverse drug reactions, and improves patient outcomes in precision healthcare.
Challenges and Limitations in Pharmacogenomics and Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacogenomics faces challenges such as genetic variability among populations, limited understanding of gene-drug interactions, and high costs associated with genetic testing, which hinder its widespread clinical implementation. Pharmacokinetics encounters limitations including individual differences in absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion influenced by non-genetic factors like age, diet, and organ function, complicating dose optimization. Both fields struggle with integrating complex data into personalized medicine, requiring advanced computational tools and robust clinical validation to improve therapeutic outcomes.
Future Perspectives in Drug Therapy Optimization
Pharmacogenomics leverages genetic profiling to tailor drug therapies, enhancing efficacy and minimizing adverse effects by predicting individual responses at the molecular level. Pharmacokinetics provides critical insights into drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, enabling precise dosing strategies based on patient-specific physiological parameters. Future drug therapy optimization integrates pharmacogenomic data with pharmacokinetic modeling, fostering personalized medicine approaches that improve therapeutic outcomes and reduce trial-and-error prescribing.
Pharmacogenomics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com