A genocopy occurs when different genetic mutations produce identical or very similar clinical features, making diagnosis challenging through phenotype alone. Understanding genocopies is crucial for accurate genetic testing and personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific condition. Explore the article to learn more about identifying and managing genocopies effectively.
Table of Comparison
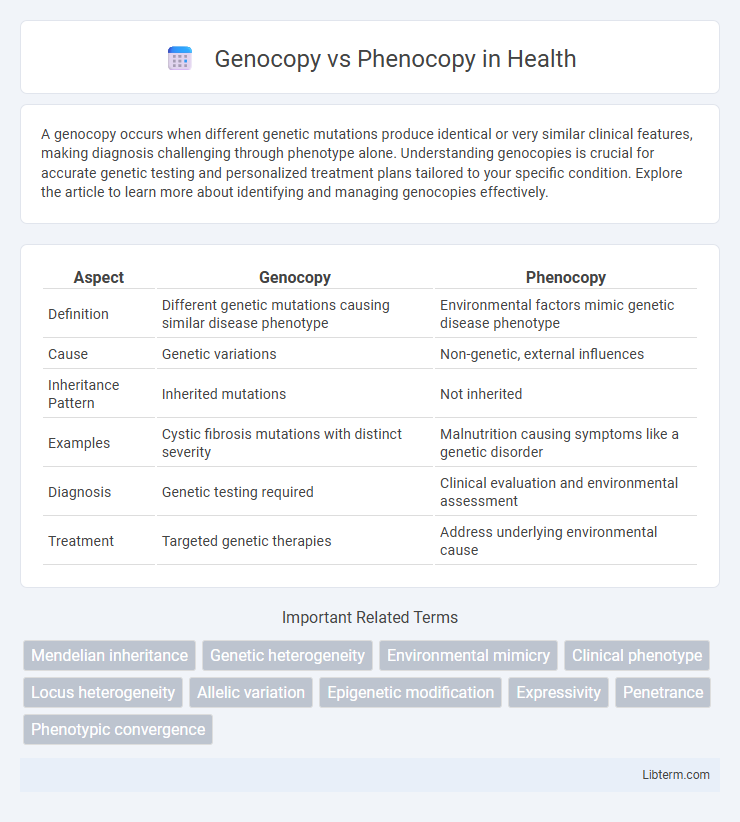
| Aspect | Genocopy | Phenocopy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Different genetic mutations causing similar disease phenotype | Environmental factors mimic genetic disease phenotype |
| Cause | Genetic variations | Non-genetic, external influences |
| Inheritance Pattern | Inherited mutations | Not inherited |
| Examples | Cystic fibrosis mutations with distinct severity | Malnutrition causing symptoms like a genetic disorder |
| Diagnosis | Genetic testing required | Clinical evaluation and environmental assessment |
| Treatment | Targeted genetic therapies | Address underlying environmental cause |
Introduction to Genocopy and Phenocopy
Genocopy refers to a genetic mutation that produces a phenotype similar to that caused by a different gene, illustrating the complexity of genotype-phenotype relationships. Phenocopy describes an environmentally induced trait that mimics a genetic condition, highlighting non-genetic influences on phenotype expression. Distinguishing between genocopy and phenocopy is essential for accurate diagnosis and understanding of hereditary versus environmental effects on traits.
Defining Genocopy: Concept and Examples
Genocopy refers to a genetic variant where different mutations in distinct genes produce a similar phenotype, illustrating genetic heterogeneity. For example, retinitis pigmentosa can result from mutations in multiple unrelated genes, each causing comparable retinal degeneration symptoms. This concept underscores the complexity of genetic disorders and emphasizes the need for precise molecular diagnosis to differentiate genocopies from phenocopies, which arise from environmental factors rather than genetic mutations.
Understanding Phenocopy: Meaning and Instances
Phenocopy refers to a phenotype that mimics the effect of a genetic mutation but arises from environmental factors rather than genetic changes. This concept is crucial in genetics and medicine, as it highlights instances where external influences like drugs, toxins, or infections induce traits resembling inherited diseases. Recognizing phenocopies aids in differentiating between hereditary conditions and environmentally caused symptoms, impacting diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Key Differences Between Genocopy and Phenocopy
Genocopy refers to a genetic mutation that produces a phenotype similar to that caused by a different gene mutation, while phenocopy occurs when environmental factors induce a phenotype resembling one caused by a genetic mutation. Key differences include the origin of the phenotype: genocopy arises strictly from genetic variation, whereas phenocopy results from non-genetic influences such as environmental conditions or exposure to chemicals. Genocopy is inheritable and transmitted through generations, unlike phenocopy, which is non-heritable and affects only the individual exposed to the environmental trigger.
Genetic Mechanisms Behind Genocopy
Genocopy involves phenotypic similarities caused by different genetic mutations at distinct loci, illustrating allelic or locus heterogeneity, whereas phenocopy results from environmental factors mimicking genetic traits. The genetic mechanisms behind genocopy include mutations in different genes within the same pathway or functional network, leading to convergent phenotypes despite distinct genotypes. This complexity underscores the importance of comprehensive genetic analysis to accurately differentiate genocopies from phenocopies in clinical genetics.
Environmental Triggers in Phenocopy Formation
Environmental triggers play a critical role in the formation of phenocopies by inducing traits that mimic genetic disorders without underlying DNA mutations. Factors such as toxins, infections, nutrition, and climate can alter gene expression or developmental pathways, resulting in phenotypic presentations similar to true genetic conditions. Unlike genocopies, which arise from specific genetic variants, phenocopies emphasize the impact of external environmental influences shaping observable traits.
Clinical Relevance: Diagnosis and Misdiagnosis
Genocopy and phenocopy pose significant challenges in clinical diagnosis due to their ability to mimic genetic disorders without corresponding genotypes, leading to potential misdiagnosis. Accurate differentiation relies on comprehensive genetic testing and detailed phenotypic analysis to avoid inappropriate management strategies. Recognizing genocopy and phenocopy patterns is crucial for precise counseling, prognosis assessment, and personalized treatment planning in genetic and acquired conditions.
Implications for Genetic Counseling
Genocopy and phenocopy present distinct challenges in genetic counseling as genocopies result from different genetic mutations causing similar phenotypes, complicating accurate genetic diagnosis and risk assessment. Phenocopies arise from environmental factors mimicking genetic disorders, requiring counselors to differentiate between inherited risks and external influences for precise patient advice. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for developing effective personalized management plans and providing accurate recurrence risk information to families.
Case Studies: Genocopy vs Phenocopy in Practice
Case studies illustrate that genocopies involve different genetic mutations producing identical phenotypes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations leading to hereditary breast cancer. Phenocopies arise from environmental factors mimicking genetic disorders, exemplified by thalidomide exposure causing limb defects resembling inherited syndromes. Analyzing patient histories and genetic testing differentiates genocopies from phenocopies, guiding accurate diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Future Research and Challenges in Distinguishing Genocopy from Phenocopy
Future research in distinguishing genocopy from phenocopy focuses on advancing genomic sequencing technologies and integrating multi-omics data to precisely identify genetic variants that mimic phenotypic traits caused by environmental factors. Challenges remain in differentiating overlapping clinical presentations, requiring development of robust bioinformatic tools and machine learning models to analyze complex genotype-phenotype correlations. Improved understanding of epigenetic modifications and gene-environment interactions will enhance diagnostic accuracy and personalized treatment strategies for conditions with genocopy and phenocopy characteristics.
Genocopy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com