Ayurveda is an ancient holistic healing system originating from India that emphasizes balance among mind, body, and spirit to promote overall well-being. Its natural therapies, herbal remedies, and lifestyle practices aim to prevent disease and enhance vitality. Discover how Ayurveda can transform Your health by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
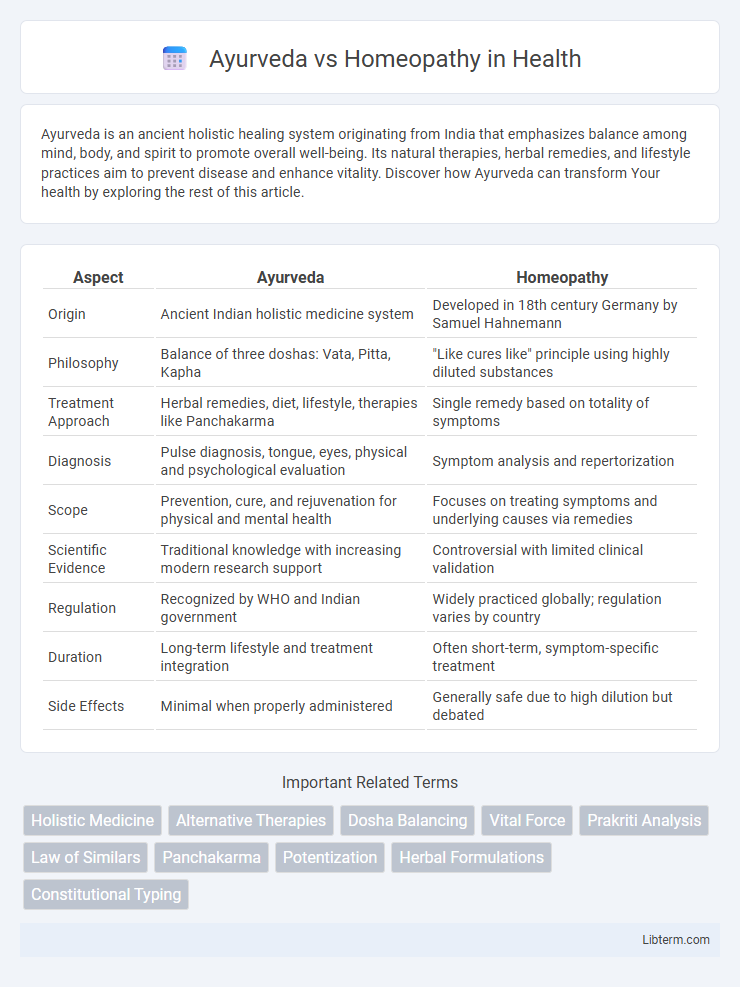
| Aspect | Ayurveda | Homeopathy |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Ancient Indian holistic medicine system | Developed in 18th century Germany by Samuel Hahnemann |
| Philosophy | Balance of three doshas: Vata, Pitta, Kapha | "Like cures like" principle using highly diluted substances |
| Treatment Approach | Herbal remedies, diet, lifestyle, therapies like Panchakarma | Single remedy based on totality of symptoms |
| Diagnosis | Pulse diagnosis, tongue, eyes, physical and psychological evaluation | Symptom analysis and repertorization |
| Scope | Prevention, cure, and rejuvenation for physical and mental health | Focuses on treating symptoms and underlying causes via remedies |
| Scientific Evidence | Traditional knowledge with increasing modern research support | Controversial with limited clinical validation |
| Regulation | Recognized by WHO and Indian government | Widely practiced globally; regulation varies by country |
| Duration | Long-term lifestyle and treatment integration | Often short-term, symptom-specific treatment |
| Side Effects | Minimal when properly administered | Generally safe due to high dilution but debated |
Introduction to Ayurveda and Homeopathy
Ayurveda, a traditional Indian system of medicine dating back over 5,000 years, emphasizes holistic healing by balancing the body's three doshas: Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. Homeopathy, developed in the late 18th century by Samuel Hahnemann, is based on the principle of "like cures like" and uses highly diluted substances to stimulate the body's self-healing mechanisms. Both systems prioritize individualized treatment and natural remedies but differ fundamentally in their philosophies and methodologies.
Historical Origins of Ayurveda and Homeopathy
Ayurveda, rooted in ancient India over 5,000 years ago, originates from the Vedic culture and ancient Sanskrit texts such as the Charaka Samhita and Sushruta Samhita, emphasizing balance among bodily doshas (Vata, Pitta, Kapha) for health. Homeopathy was developed in the late 18th century by Samuel Hahnemann in Germany, based on the principle of "like cures like" and potentization through serial dilution. While Ayurveda integrates holistic lifestyle and herbal remedies, Homeopathy relies on highly diluted substances to stimulate the body's self-healing.
Philosophical Foundations: Ayurveda vs Homeopathy
Ayurveda is rooted in ancient Indian philosophy emphasizing the balance of the three doshas--Vata, Pitta, and Kapha--to maintain health, whereas Homeopathy is based on the principle of "like cures like," using highly diluted substances to stimulate the body's self-healing. Both systems prioritize individualized treatment but differ in conceptual frameworks: Ayurveda integrates mind, body, and spirit through holistic lifestyle approaches, while Homeopathy focuses on symptom similarity and energetic imprints of remedies. The distinct metaphysical perspectives influence diagnostic methods, therapeutic interventions, and overall health paradigms within each tradition.
Key Principles and Practices Compared
Ayurveda centers on balancing the three doshas--Vata, Pitta, and Kapha--through personalized treatments involving herbal medicines, dietary regulations, and lifestyle modifications to restore harmony in the body and mind. Homeopathy operates on the principle of "like cures like," using highly diluted substances to stimulate the body's self-healing response, with remedies tailored to individual symptoms and overall constitution. While Ayurveda emphasizes preventive care and holistic wellness integrating mind, body, and spirit, Homeopathy primarily targets symptom relief through individualized remedies designed to trigger natural healing mechanisms.
Diagnosis and Assessment Methods
Ayurveda employs a comprehensive diagnostic approach called Panchakarma, emphasizing pulse diagnosis (Nadi Pariksha), tongue examination, and analysis of bodily doshas (Vata, Pitta, Kapha) to assess health imbalances. Homeopathy relies on detailed patient interviews and symptom analysis, focusing on mental, emotional, and physical characteristics to individualize remedy selection based on the principle of "like cures like." While Ayurveda integrates physical, mental, and environmental factors through holistic evaluation, Homeopathy prioritizes personalized symptomatology for remedy matching.
Treatment Approaches and Modalities
Ayurveda emphasizes a holistic treatment approach focusing on balance among the three doshas--Vata, Pitta, and Kapha--using herbal medicines, diet, detoxification therapies (Panchakarma), and lifestyle modifications to restore health. Homeopathy relies on the principle of "like cures like," administering highly diluted substances tailored to individual symptoms, aiming to stimulate the body's self-healing mechanisms through remedies such as tinctures and pellets. Both systems prioritize individualized care but differ fundamentally in their diagnostic methods and therapeutic modalities, with Ayurveda integrating physical, mental, and spiritual health, and Homeopathy concentrating on symptom matching and energetic effects.
Safety, Efficacy, and Scientific Evidence
Ayurveda employs natural herbs and holistic approaches with a strong emphasis on individualized treatments, supported by centuries of traditional use but limited rigorous scientific validation. Homeopathy uses highly diluted substances aimed at triggering the body's self-healing, though extensive clinical studies have shown mixed efficacy and ongoing debates about its scientific plausibility. Safety profiles for both systems are generally favorable when practiced under qualified supervision, but risks arise from improper use or contamination, highlighting the need for standardized regulation and further clinical research.
Common Ailments Treated by Each System
Ayurveda primarily treats common ailments such as digestive disorders, arthritis, skin conditions, and respiratory issues by balancing the body's doshas using herbal remedies, diet, and lifestyle changes. Homeopathy addresses conditions like allergies, chronic infections, migraines, and stress-related disorders through highly diluted substances aimed at stimulating the body's natural healing processes. Both systems offer holistic approaches but differ in methodology and treatment principles for managing health problems.
Global Acceptance and Regulatory Status
Ayurveda, rooted in ancient Indian traditions, is recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a traditional medicine system and is officially regulated in countries like India, Sri Lanka, and Nepal, with growing acceptance in Western nations through integrative health frameworks. Homeopathy, developed in the late 18th century in Germany, enjoys widespread use in Europe, India, and Latin America, with regulatory bodies such as the European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines (EDQM) overseeing its medicines, while some countries like the United States provide limited regulatory oversight through the FDA under the category of complementary and alternative medicine. The global market for both Ayurveda and Homeopathy continues to expand, driven by increasing consumer demand for natural and holistic healthcare solutions despite varying degrees of regulatory recognition and scientific scrutiny.
Choosing Between Ayurveda and Homeopathy
Choosing between Ayurveda and Homeopathy depends on individual health needs, with Ayurveda emphasizing holistic balance through herbal treatments, diet, and lifestyle changes, while Homeopathy relies on highly diluted substances targeting symptoms at the energetic level. Both systems are personalized but differ fundamentally in approach--Ayurveda is rooted in ancient Indian principles addressing body, mind, and spirit equilibrium, whereas Homeopathy operates on the "like cures like" principle using minimal doses. Evaluating factors like chronic versus acute conditions, practitioner expertise, and personal health philosophy helps in making an informed decision between these traditional healing modalities.
Ayurveda Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com