Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and improved patient outcomes. Utilizing advanced imaging techniques and laboratory tests can enhance the precision of identifying conditions early. Explore the rest of the article to learn about the latest diagnostic methods and how they can benefit your healthcare journey.
Table of Comparison
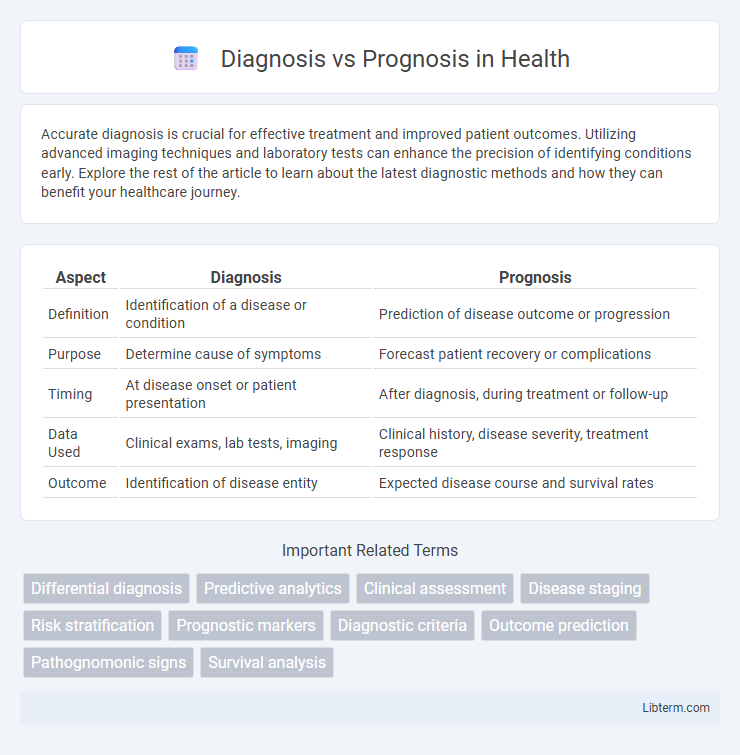
| Aspect | Diagnosis | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identification of a disease or condition | Prediction of disease outcome or progression |
| Purpose | Determine cause of symptoms | Forecast patient recovery or complications |
| Timing | At disease onset or patient presentation | After diagnosis, during treatment or follow-up |
| Data Used | Clinical exams, lab tests, imaging | Clinical history, disease severity, treatment response |
| Outcome | Identification of disease entity | Expected disease course and survival rates |
Understanding Diagnosis: Definition and Importance
Diagnosis involves identifying a disease or condition from its signs, symptoms, and medical tests, serving as the foundation for effective treatment planning. Accurate diagnosis enables targeted therapies, improves patient outcomes, and reduces unnecessary interventions. Understanding diagnosis is crucial for healthcare providers to deliver timely and precise care, minimizing complications and healthcare costs.
What is Prognosis? Key Concepts Explained
Prognosis refers to the predicted outcome or course of a disease based on clinical data, patient history, and diagnostic findings. It helps estimate the chances of recovery, potential complications, and survival rates, providing valuable insights for treatment planning. Key concepts in prognosis include disease progression, response to therapy, and risk stratification, which guide healthcare providers in making informed decisions.
Diagnosis vs Prognosis: Core Differences
Diagnosis identifies the specific disease or condition causing a patient's symptoms through medical tests, imaging, and clinical evaluation, confirming what is currently affecting the patient. Prognosis predicts the likely course, outcome, and chance of recovery or complications based on the diagnosis, patient history, and clinical factors. Diagnostic accuracy directly impacts the reliability of prognosis, as understanding the disease allows clinicians to estimate its progression and potential treatment outcomes.
The Role of Diagnosis in Patient Care
Accurate diagnosis is essential in patient care as it identifies the underlying cause of symptoms, enabling targeted treatment plans that improve outcomes. Diagnostic procedures such as imaging, laboratory tests, and clinical evaluations provide critical data for determining disease presence, severity, and progression. Early and precise diagnosis facilitates timely intervention, reduces complications, and guides prognosis assessment, optimizing patient management strategies.
Prognosis: Predicting Health Outcomes
Prognosis involves predicting the likely course and outcome of a disease based on clinical data, patient history, and diagnostic results. Accurate prognosis enables healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans, anticipate complications, and improve patient management strategies. Advanced predictive models, including machine learning algorithms, enhance prognostic accuracy by analyzing large datasets and identifying risk factors for health outcomes.
Methods and Tools Used in Diagnosis
Diagnosis relies heavily on clinical evaluations, medical imaging technologies such as MRI, CT scans, and X-rays, as well as laboratory tests like blood panels and biopsies to identify the nature and cause of a disease. Advanced diagnostic tools include molecular assays, genetic testing, and point-of-care devices that provide rapid and precise results. These methods enable healthcare professionals to confirm diseases accurately, guiding effective treatment strategies and patient management.
Factors Influencing Prognostic Assessment
Prognostic assessment is influenced by various factors including patient age, comorbidities, and disease severity, which collectively impact outcome predictions. Biomarkers and genetic profiles provide critical data that refine prognosis accuracy beyond initial diagnostic findings. Treatment response variability and patient adherence further modify long-term prognosis, making continuous evaluation essential for optimal care planning.
Clinical Examples: Applying Diagnosis and Prognosis
Diagnosis identifies the presence and nature of diseases such as diabetes by analyzing symptoms and test results, enabling targeted treatment plans. Prognosis estimates the likely course and outcome of these conditions, for example predicting 5-year survival rates in cancer patients based on tumor stage and response to therapy. Clinical application integrates diagnosis for immediate intervention and prognosis for long-term management, improving patient care strategies in chronic illnesses like heart failure.
Improving Accuracy in Diagnosis and Prognosis
Improving accuracy in diagnosis involves integrating advanced imaging technologies, molecular biomarkers, and machine learning algorithms to enhance the identification and classification of diseases at early stages. Prognosis accuracy is boosted by using longitudinal patient data combined with genetic profiles and environmental factors to model disease progression more precisely. Incorporating real-time monitoring tools and artificial intelligence-driven predictive analytics enables personalized treatment plans and better outcome predictions.
Diagnosis and Prognosis: Impact on Treatment Decisions
Diagnosis identifies the specific disease or condition affecting a patient, enabling clinicians to select targeted treatments based on established clinical guidelines and diagnostic criteria. Prognosis predicts the likely course and outcome of the disease, influencing treatment intensity, duration, and follow-up strategies to optimize patient care. Accurate diagnosis and prognosis together inform personalized treatment decisions that maximize efficacy and improve patient outcomes.
Diagnosis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com