Nonsurgical treatments offer effective solutions for various health and cosmetic concerns without the need for invasive procedures. These methods typically involve minimal downtime, reduced risk of complications, and faster recovery compared to surgical options. Discover how nonsurgical approaches can benefit your well-being by exploring the detailed insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
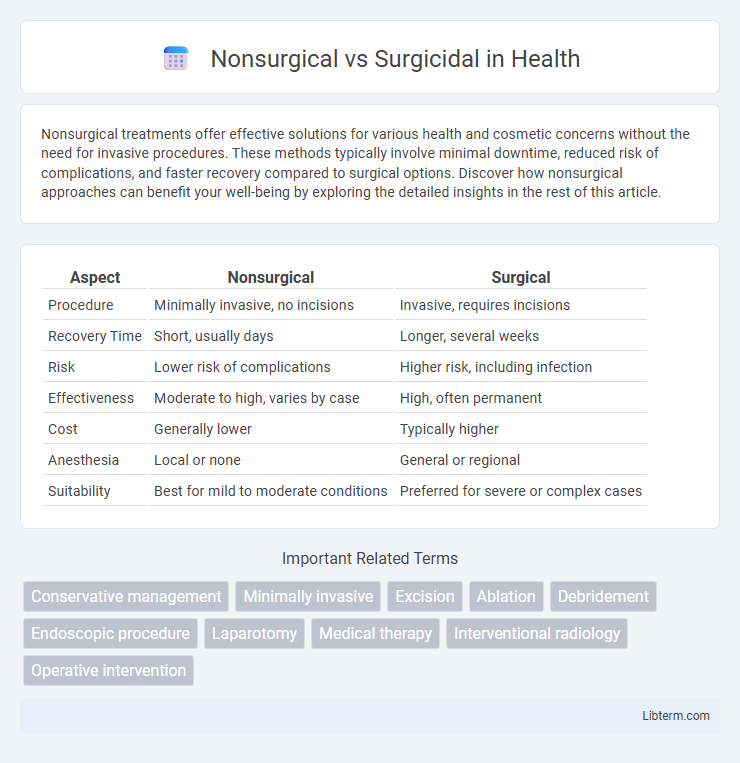
| Aspect | Nonsurgical | Surgical |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure | Minimally invasive, no incisions | Invasive, requires incisions |
| Recovery Time | Short, usually days | Longer, several weeks |
| Risk | Lower risk of complications | Higher risk, including infection |
| Effectiveness | Moderate to high, varies by case | High, often permanent |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
| Anesthesia | Local or none | General or regional |
| Suitability | Best for mild to moderate conditions | Preferred for severe or complex cases |
Understanding Nonsurgical and Surgical Treatments
Nonsurgical treatments for various medical conditions typically involve medication, physical therapy, or minimally invasive procedures that avoid incisions, aiming to reduce recovery time and minimize risks. Surgical treatments, by contrast, involve operative techniques to directly address the pathology, often providing definitive solutions but with longer recovery periods and higher risk profiles. Understanding the indications, benefits, and limitations of nonsurgical versus surgical options is crucial for personalized patient care and optimal outcome selection.
Key Differences Between Nonsurgical and Surgical Approaches
Nonsurgical approaches prioritize minimally invasive techniques, emphasizing rapid recovery, reduced risk of complications, and preservation of surrounding tissues, often relying on medications, physical therapy, or laser treatments. Surgical methods involve direct intervention through incisions or other invasive procedures, offering definitive solutions for advanced or severe conditions but accompanied by longer downtime and higher risk factors. The key differences lie in invasiveness, recovery time, risk of complications, and suitability based on condition severity and patient health status.
Benefits of Nonsurgical Treatments
Nonsurgical treatments offer significant benefits such as reduced recovery time, minimal risk of infection, and lower overall costs compared to surgicidal procedures. These methods preserve natural tissue integrity while effectively addressing conditions through techniques like laser therapy, ultrasound, or medication. Patients experience less pain and quicker return to daily activities, enhancing overall treatment satisfaction.
Advantages of Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions provide precise and permanent solutions through techniques such as excision, laparoscopy, or laser ablation, offering high success rates in treating conditions like endometriosis, fibroids, and chronic pain. These procedures enable direct visualization and removal of diseased tissue, ensuring thorough treatment and reducing recurrence risks compared to nonsurgical methods like medication or hormonal therapy. Surgical treatment also allows for immediate symptom relief and improved quality of life, particularly in cases where nonsurgical approaches have failed or are contraindicated.
Risks and Complications: Nonsurgical vs Surgical
Nonsurgical procedures generally carry fewer risks and complications compared to surgical options, as they avoid anesthesia, incisions, and prolonged recovery times. Surgical interventions, while often more effective for severe conditions, pose higher risks including infection, bleeding, scarring, and longer postoperative pain or complications. Evaluating patient health, condition severity, and potential side effects is critical to choosing between nonsurgical safety and surgical efficacy.
Recovery Time Comparison
Nonsurgical treatments typically offer significantly faster recovery times, often allowing patients to resume normal activities within a few days compared to surgical options. Surgical procedures generally require extended healing periods, ranging from several weeks to months due to tissue incision and repair. The reduced recovery duration of nonsurgical methods results in lower downtime and decreased risk of postoperative complications.
Cost Analysis: Nonsurgical Versus Surgical Options
Nonsurgical options generally incur lower upfront costs compared to surgical procedures, with expenses primarily involving consultation, imaging, and therapy sessions, while surgical interventions demand higher costs due to operating room fees, anesthesia, and postoperative care. Long-term cost-effectiveness of nonsurgical treatments can vary depending on the need for ongoing therapy or potential for recurrence, whereas surgical options may have higher initial costs but could reduce long-term expenses if successful. Detailed cost analysis should consider direct medical costs, indirect costs like recovery time, and patient-specific factors influencing treatment outcomes.
Suitability and Patient Selection Criteria
Nonsurgical treatments are best suited for patients with early-stage conditions, minimal tissue damage, and contraindications for surgery, emphasizing conservative management and quicker recovery. Surgicidal approaches target patients with advanced disease, significant anatomical abnormalities, or those unresponsive to nonsurgical methods, offering definitive resolution through invasive techniques. Patient selection criteria hinge on disease severity, overall health status, risk tolerance, and the potential for functional improvement post-treatment.
Long-Term Outcomes and Effectiveness
Nonsurgical treatments for conditions such as varicose veins or chronic sinusitis often emphasize reduced recovery time and lower immediate risks but may require ongoing management and show variable long-term effectiveness. Surgicidal approaches, including laser ablation for veins or functional endoscopic sinus surgery, tend to provide more definitive long-term outcomes with higher rates of symptom resolution and lower recurrence. Comparative studies highlight that while nonsurgical methods appeal due to minimal invasiveness, surgical interventions generally deliver superior durability and sustained effectiveness in clinical results.
Choosing the Right Treatment Path
Choosing the right treatment path between nonsurgical and surgicidal options depends on the severity of the condition, patient health, and recovery goals. Nonsurgical treatments such as medication, physical therapy, and minimally invasive procedures offer reduced risk and faster recovery but may not address severe or chronic issues effectively. Surgical solutions provide definitive treatment by directly correcting anatomical problems but involve longer healing times and potential complications.
Nonsurgical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com