Astigmatism is a common vision condition caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens, leading to blurred or distorted vision. It can often be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery, improving your overall visual clarity. Explore the rest of the article to learn more about symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for astigmatism.
Table of Comparison
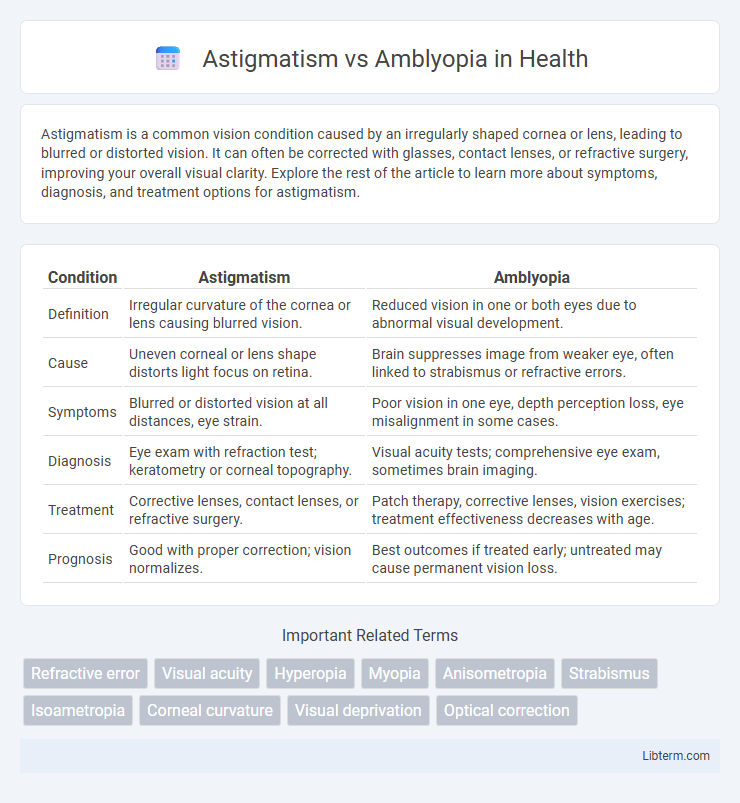
| Condition | Astigmatism | Amblyopia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Irregular curvature of the cornea or lens causing blurred vision. | Reduced vision in one or both eyes due to abnormal visual development. |
| Cause | Uneven corneal or lens shape distorts light focus on retina. | Brain suppresses image from weaker eye, often linked to strabismus or refractive errors. |
| Symptoms | Blurred or distorted vision at all distances, eye strain. | Poor vision in one eye, depth perception loss, eye misalignment in some cases. |
| Diagnosis | Eye exam with refraction test; keratometry or corneal topography. | Visual acuity tests; comprehensive eye exam, sometimes brain imaging. |
| Treatment | Corrective lenses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery. | Patch therapy, corrective lenses, vision exercises; treatment effectiveness decreases with age. |
| Prognosis | Good with proper correction; vision normalizes. | Best outcomes if treated early; untreated may cause permanent vision loss. |
Understanding Astigmatism and Amblyopia
Astigmatism is an optical imperfection causing blurred or distorted vision due to an irregularly shaped cornea or lens, leading to refractive errors. Amblyopia, commonly known as lazy eye, is a neurodevelopmental disorder where the brain favors one eye, resulting in decreased vision in the other eye despite normal ocular anatomy. Understanding these conditions involves recognizing that astigmatism affects image focusing on the retina, while amblyopia affects neural visual processing.
Key Differences Between Astigmatism and Amblyopia
Astigmatism is a refractive error caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens, leading to blurred or distorted vision, whereas amblyopia, also known as lazy eye, results from poor neural development in the brain due to unequal visual input. Astigmatism primarily affects the eye's focusing ability and can be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or surgery, while amblyopia requires early intervention such as patching or vision therapy to improve visual acuity. Unlike astigmatism, amblyopia is a developmental disorder that can cause permanent vision loss if untreated during childhood.
Causes of Astigmatism
Astigmatism is primarily caused by an irregular curvature of the cornea or lens, leading to distorted or blurred vision. This refractive error occurs when the cornea's shape deviates from a perfect sphere, resulting in uneven light refraction onto the retina. In contrast, amblyopia, often called "lazy eye," arises from neurological development issues rather than structural abnormalities in the eye.
Causes of Amblyopia
Amblyopia, commonly known as lazy eye, primarily results from conditions that disrupt normal visual development, such as strabismus, significant refractive errors like astigmatism, or deprivation caused by cataracts. When astigmatism causes blurred vision in one eye, the brain may favor the clearer image from the other eye, leading to decreased neural input and impaired vision in the affected eye. Early detection and treatment of these underlying causes are crucial to prevent permanent vision loss associated with amblyopia.
Symptoms: Astigmatism vs Amblyopia
Astigmatism causes blurred or distorted vision due to irregular curvature of the cornea, leading to symptoms like eye strain, headaches, and difficulty focusing on both near and distant objects. Amblyopia, or "lazy eye," results in reduced vision in one eye, characterized by poor depth perception and difficulty seeing fine details, often without obvious physical abnormalities. Both conditions impact visual clarity but differ in underlying causes and symptom presentation.
Diagnosis of Astigmatism and Amblyopia
Astigmatism is diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam, including a refraction test using a phoropter or automated refractor to measure the curvature of the cornea and detect irregularities. Amblyopia diagnosis involves evaluating visual acuity differences between eyes, often using a Snellen chart, alongside assessing for eye alignment and binocular function to identify suppressed or weaker vision. Early detection through these diagnostic methods is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of long-term vision impairment.
Treatment Options for Astigmatism
Astigmatism treatment options primarily include corrective lenses such as eyeglasses or toric contact lenses that compensate for irregular corneal curvature. Refractive surgeries like LASIK or PRK reshape the cornea to improve vision and reduce dependency on corrective lenses. Regular eye examinations and customized prescriptions are essential to effectively manage astigmatism symptoms and prevent associated visual discomfort.
Treatment Approaches for Amblyopia
Treatment approaches for amblyopia primarily include vision correction with eyeglasses or contact lenses to address refractive errors such as astigmatism, which often contributes to amblyopia development. Occlusion therapy, involving patching the dominant eye, forces the brain to use the weaker eye, promoting visual improvement and neural plasticity. In some cases, atropine eye drops are prescribed to blur vision in the stronger eye, encouraging the amblyopic eye to strengthen.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Astigmatism risk factors include genetic predisposition and eye injury, while amblyopia commonly arises from untreated refractive errors like astigmatism, strabismus, or cataracts during early childhood. Preventive measures involve early vision screening, corrective lenses for astigmatism, and timely treatment of amblyopia through patching or vision therapy to promote proper visual development. Addressing these risk factors promptly reduces the likelihood of permanent vision impairment associated with both conditions.
Improving Eye Health: Tips and Recommendations
Astigmatism and amblyopia impact vision differently, requiring tailored approaches for improving eye health. Regular comprehensive eye exams, using corrective lenses for astigmatism, and vision therapy for amblyopia are essential for enhancing visual acuity. Incorporating eye-friendly habits such as reducing screen time, practicing eye exercises, and ensuring adequate lighting can further support overall eye health and prevent worsening conditions.
Astigmatism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com