Arthritis causes joint pain and inflammation, significantly impacting mobility and daily activities. Understanding the different types, symptoms, and treatment options can help you manage the condition effectively. Explore the rest of this article to learn how to improve your quality of life with arthritis.
Table of Comparison
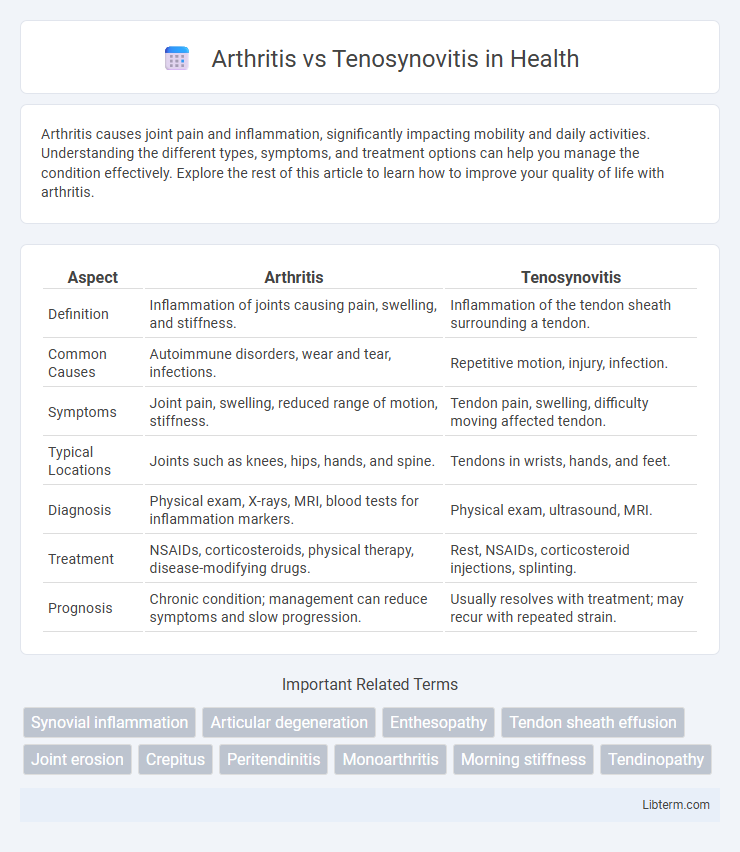
| Aspect | Arthritis | Tenosynovitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflammation of joints causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. | Inflammation of the tendon sheath surrounding a tendon. |
| Common Causes | Autoimmune disorders, wear and tear, infections. | Repetitive motion, injury, infection. |
| Symptoms | Joint pain, swelling, reduced range of motion, stiffness. | Tendon pain, swelling, difficulty moving affected tendon. |
| Typical Locations | Joints such as knees, hips, hands, and spine. | Tendons in wrists, hands, and feet. |
| Diagnosis | Physical exam, X-rays, MRI, blood tests for inflammation markers. | Physical exam, ultrasound, MRI. |
| Treatment | NSAIDs, corticosteroids, physical therapy, disease-modifying drugs. | Rest, NSAIDs, corticosteroid injections, splinting. |
| Prognosis | Chronic condition; management can reduce symptoms and slow progression. | Usually resolves with treatment; may recur with repeated strain. |
Introduction: Understanding Arthritis and Tenosynovitis
Arthritis and tenosynovitis are inflammatory conditions affecting joints and tendons, respectively, often causing pain and stiffness. Arthritis encompasses various types such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, characterized by joint inflammation, cartilage degradation, and swelling. Tenosynovitis involves inflammation of the tendon sheath, leading to restricted movement and tenderness around affected tendons, commonly in the hands and wrists.
What Is Arthritis?
Arthritis is a chronic condition characterized by inflammation of the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling. It encompasses more than 100 different types, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, which primarily affect joint cartilage and synovial membranes. In contrast to tenosynovitis, which targets the tendon sheaths, arthritis primarily impacts the joint structures themselves.
What Is Tenosynovitis?
Tenosynovitis is the inflammation of the fluid-filled sheath (synovium) that surrounds a tendon, typically causing pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected joint. Unlike arthritis, which primarily involves inflammation of the joint itself, tenosynovitis affects the tendon's protective covering, often resulting from repetitive motion or injury. Common sites include the wrists, hands, and feet, with conditions like De Quervain's tenosynovitis frequently diagnosed in affected patients.
Key Differences Between Arthritis and Tenosynovitis
Arthritis primarily involves inflammation of the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling within the joint capsule, whereas tenosynovitis affects the synovial sheath surrounding tendons, leading to localized tendon pain and restricted movement. Arthritis includes various types such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis, each with distinct pathological mechanisms involving cartilage and bone degradation. Tenosynovitis often results from repetitive strain or infection and is characterized by tendon sheath inflammation without direct joint involvement.
Common Causes of Arthritis vs Tenosynovitis
Arthritis commonly results from autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, wear and tear in osteoarthritis, or infections leading to joint inflammation. Tenosynovitis is typically caused by repetitive motions, strain, or infections affecting the tendon sheath, leading to inflammation and pain. Both conditions share inflammation as a key feature but differ fundamentally in their primary sites and underlying causes.
Symptoms Comparison: Arthritis and Tenosynovitis
Arthritis commonly presents with joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion, often affecting multiple joints symmetrically. Tenosynovitis primarily causes localized tendon sheath pain, swelling, and tenderness, especially during movement or repetitive activity in a single joint area. Unlike arthritis, tenosynovitis symptoms are more focused on inflammation along the tendon, without the widespread joint damage or chronic stiffness typical of arthritis.
Diagnostic Methods for Arthritis and Tenosynovitis
Arthritis diagnosis primarily relies on clinical examination, blood tests such as rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibodies, and imaging techniques including X-rays, MRI, and ultrasound to detect joint inflammation and damage. Tenosynovitis diagnosis involves physical assessment of tendon pain and swelling, along with ultrasound or MRI to visualize inflammation of the tendon sheath. Both conditions benefit from advanced imaging for accurate differentiation and targeted treatment planning.
Treatment Options for Arthritis and Tenosynovitis
Treatment options for arthritis primarily include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to control inflammation and prevent joint damage. Tenosynovitis treatment focuses on rest, splinting, NSAIDs, and sometimes corticosteroid injections to reduce tendon sheath inflammation and promote healing. Physical therapy and, in severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary for both conditions to restore function and alleviate symptoms.
Prevention Tips for Joint and Tendon Health
Maintaining joint and tendon health requires consistent measures such as regular low-impact exercise, which enhances flexibility and reduces stiffness commonly associated with arthritis and tenosynovitis. Adequate hydration and a nutrient-rich diet high in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamin D support tissue repair and reduce inflammation in affected areas. Ergonomic adjustments during repetitive tasks and proper warm-up routines before physical activity can prevent tendon strain and joint stress, minimizing the risk of developing these musculoskeletal conditions.
When to See a Doctor: Arthritis vs Tenosynovitis
Seek medical attention for arthritis if you experience persistent joint pain, swelling, stiffness, or reduced range of motion lasting more than a few weeks, as early diagnosis can prevent joint damage. For tenosynovitis, consult a doctor if you notice localized tendon pain, tenderness, or swelling near a joint, especially if accompanied by difficulty moving the affected finger, wrist, or thumb. Prompt evaluation is crucial to distinguish between these conditions and initiate appropriate treatment to avoid chronic complications.
Arthritis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com