Medical advancements have revolutionized healthcare, improving diagnosis, treatment, and patient outcomes across diverse conditions. Innovations such as telemedicine and personalized medicine are transforming how care is delivered and tailored to individual needs. Explore the full article to understand how these developments impact your health and future medical options.
Table of Comparison
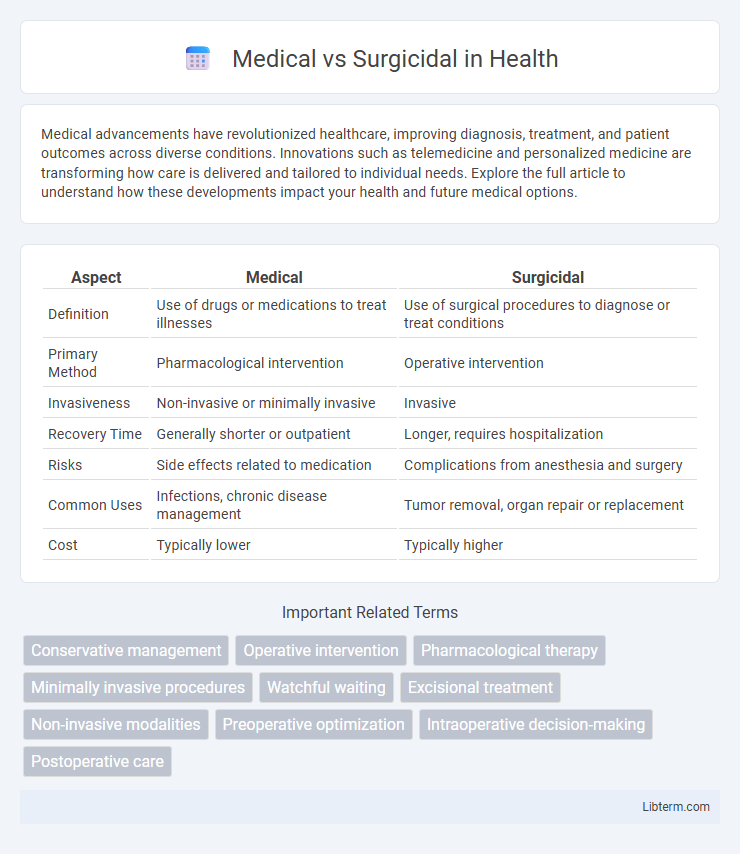
| Aspect | Medical | Surgicidal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of drugs or medications to treat illnesses | Use of surgical procedures to diagnose or treat conditions |
| Primary Method | Pharmacological intervention | Operative intervention |
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive or minimally invasive | Invasive |
| Recovery Time | Generally shorter or outpatient | Longer, requires hospitalization |
| Risks | Side effects related to medication | Complications from anesthesia and surgery |
| Common Uses | Infections, chronic disease management | Tumor removal, organ repair or replacement |
| Cost | Typically lower | Typically higher |
Introduction to Medical and Surgical Treatments
Medical treatments focus on non-invasive therapies using medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to manage diseases and improve patient outcomes. Surgical treatments involve invasive procedures to remove, repair, or alter anatomical structures, often providing definitive solutions for conditions unresponsive to medical management. Understanding the indications, risks, and benefits of both approaches is essential for optimizing patient care and treatment planning.
Defining Medical Management Approaches
Medical management approaches prioritize non-invasive treatments such as pharmacotherapy, lifestyle modifications, and physical therapy to address underlying conditions and symptoms. These methods aim to control disease progression, reduce pain, and improve patient quality of life without surgical intervention. Emphasizing diagnostic evaluation and targeted medication protocols helps tailor individualized care plans for effective disease management.
Exploring Surgical Intervention Methods
Surgical intervention methods encompass a range of procedures designed to treat medical conditions through operative techniques, contrasting with nonsurgical medical therapies that rely on pharmacological or conservative management. These methods include minimally invasive techniques such as laparoscopy, robotic surgery, and traditional open surgeries, each selected based on patient-specific factors and the pathology involved. Understanding the indications, risks, and advancements in surgical technology is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes in the decision-making process between medical and surgicidal approaches.
Key Differences Between Medical and Surgical Treatments
Medical treatments primarily involve the use of medications, therapies, and non-invasive procedures to manage or cure diseases, targeting underlying biological processes without physically altering body structures. Surgical treatments require operative intervention to remove, repair, or replace affected tissues or organs, often providing immediate physical correction but with higher associated risks and recovery times. The choice between medical and surgical approaches depends on factors like disease severity, patient health, and desired outcomes, with surgery often reserved for conditions unresponsive to medical management.
Indications for Choosing Medical Therapy
Medical therapy is typically indicated for patients with mild to moderate infections, those who are poor surgical candidates due to comorbidities, or when infections are located in areas where surgery poses a high risk. Conditions such as uncomplicated cellulitis, early-stage osteomyelitis, or superficial abscesses often respond well to antimicrobial treatment alone. Clinicians prioritize antimicrobial susceptibility, patient tolerance, and infection severity when selecting medical over surgicidal interventions.
When is Surgery the Preferred Option?
Surgery is the preferred option when medical treatments fail to control or cure a condition, particularly in cases involving structural abnormalities, severe trauma, or life-threatening diseases like certain cancers. Conditions such as appendicitis, obstructive tumors, and advanced cardiac diseases often require surgical intervention for definitive treatment and symptom relief. Surgical procedures provide targeted, immediate correction that medical therapy alone cannot achieve, improving patient outcomes in complex or acute scenarios.
Risks and Benefits: Medical vs Surgical Approaches
Medical treatments offer non-invasive risk profiles with fewer complications and faster recovery, ideal for patients seeking conservative options. Surgical approaches provide definitive results with higher efficacy but carry increased risks such as infection, anesthesia complications, and longer downtime. Evaluating patient health, condition severity, and desired outcomes is crucial to balancing benefits like precision and durability against potential surgical risks.
Patient Criteria for Medical vs Surgical Decisions
Patient criteria for medical versus surgical decisions hinge on factors such as severity of condition, comorbidities, and response to initial treatments. Medical management suits patients with mild to moderate symptoms, stable vital signs, and contraindications for anesthesia or surgery. Surgical intervention is optimal for those with refractory symptoms, anatomical abnormalities, or life-threatening complications requiring immediate correction.
Recovery and Outcomes: Medical vs Surgical Care
Medical care for conditions like infections or minor injuries often results in faster initial recovery times but may require ongoing treatment to prevent recurrence. Surgical care typically involves longer recovery periods due to tissue healing and postoperative care but can provide definitive resolution for structural or severe issues. Outcomes of surgical intervention often show higher rates of complete recovery or symptom resolution compared to medical management, especially in cases of chronic or complicated conditions.
Conclusion: Making the Optimal Treatment Choice
Medical treatments offer non-invasive options with fewer immediate risks, suitable for mild-to-moderate conditions, while surgicidal approaches provide definitive resolution for severe or refractory cases by physically removing or repairing affected tissues. Optimal treatment choice depends on patient-specific factors such as disease severity, comorbidities, and long-term prognosis, balancing efficacy, recovery time, and potential complications. Collaborative decision-making involving clinicians and patients ensures personalized care that maximizes health outcomes and quality of life.
Medical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com