Eczema is a chronic skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed patches that can cause significant discomfort and affect your quality of life. Effective management involves moisturizing regularly, avoiding irritants, and using prescribed treatments to reduce flare-ups and soothe symptoms. Discover comprehensive strategies to keep your skin healthy and balanced in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
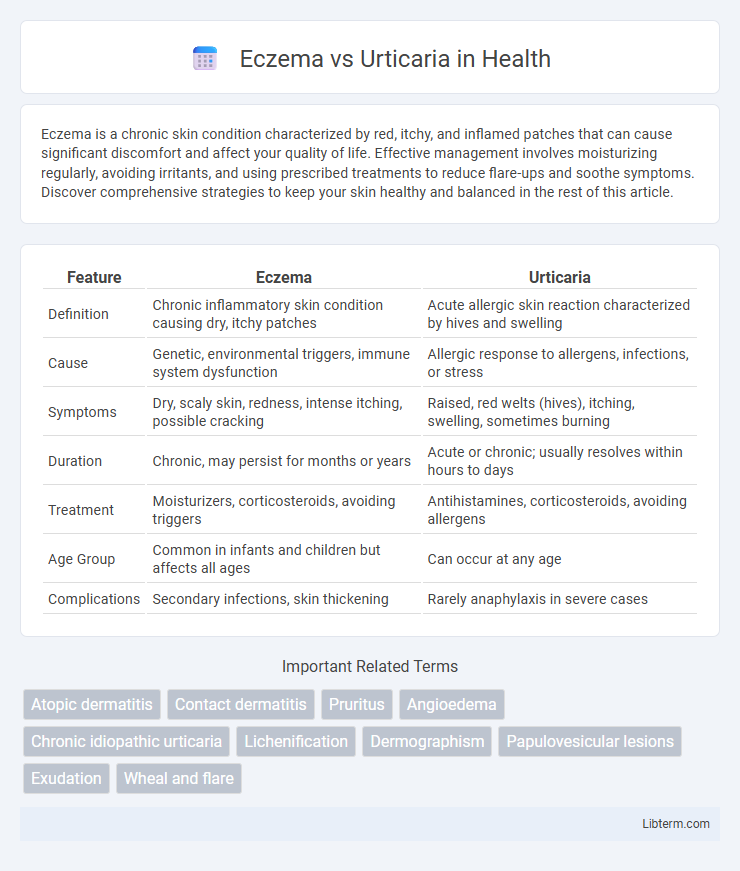
| Feature | Eczema | Urticaria |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic inflammatory skin condition causing dry, itchy patches | Acute allergic skin reaction characterized by hives and swelling |
| Cause | Genetic, environmental triggers, immune system dysfunction | Allergic response to allergens, infections, or stress |
| Symptoms | Dry, scaly skin, redness, intense itching, possible cracking | Raised, red welts (hives), itching, swelling, sometimes burning |
| Duration | Chronic, may persist for months or years | Acute or chronic; usually resolves within hours to days |
| Treatment | Moisturizers, corticosteroids, avoiding triggers | Antihistamines, corticosteroids, avoiding allergens |
| Age Group | Common in infants and children but affects all ages | Can occur at any age |
| Complications | Secondary infections, skin thickening | Rarely anaphylaxis in severe cases |
Introduction: Understanding Eczema and Urticaria
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and red patches, often triggered by allergens or irritants. Urticaria, commonly referred to as hives, presents as raised, itchy welts caused by allergic reactions, infections, or stress, typically resolving within 24 hours. Understanding the distinct pathophysiology and triggers of eczema and urticaria is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
What is Eczema? Definition and Key Features
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and dry patches. It often appears in early childhood and is linked to genetic and environmental factors causing a dysfunctional skin barrier and immune response. Key features include persistent itching, recurring flare-ups, and symptoms such as scaling, swelling, and oozing, primarily affecting areas like the face, hands, and flexural regions.
What is Urticaria? Definition and Key Features
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by raised, itchy welts that vary in size and shape, often appearing suddenly and fading within 24 hours. It results from the release of histamine and other chemicals in the skin, causing blood vessels to leak and leading to localized swelling and redness. Key features include intense itching, transient wheals, and possible angioedema, distinguishing it from eczema's chronic, inflamed, and scaly patches.
Causes of Eczema vs Urticaria
Eczema primarily results from a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers such as allergens, irritants, and dry skin, leading to inflammation and a weakened skin barrier. In contrast, urticaria, commonly known as hives, is caused by an immune system reaction that releases histamine, often triggered by allergens, infections, medications, or stress. Understanding these distinct causes aids in effective diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies for each condition.
Typical Symptoms: How Eczema and Urticaria Differ
Eczema typically presents with dry, itchy, and scaly skin patches that may become red and inflamed, often developing over days to weeks. Urticaria, or hives, is characterized by sudden, raised, red or skin-colored welts that itch intensely and usually appear within minutes or hours, often disappearing within 24 hours. Unlike eczema, urticaria lesions tend to change location rapidly and do not produce long-term skin changes.
Common Triggers for Eczema and Urticaria
Eczema is commonly triggered by allergens such as dust mites, pet dander, and certain fabrics, as well as irritants like harsh soaps and detergents. Urticaria often results from exposure to allergens including certain foods, insect stings, and medications, along with physical triggers like pressure, temperature changes, and stress. Both conditions can be exacerbated by environmental factors and immune system reactions, requiring targeted management to avoid flare-ups.
Diagnosis: How Doctors Differentiate Eczema from Urticaria
Doctors differentiate eczema from urticaria primarily through clinical examination and patient history, noting that eczema presents as chronic, itchy, dry, scaly patches often associated with a history of atopy, while urticaria manifests as transient, raised, red wheals that appear suddenly and resolve within 24 hours. Diagnostic tools include skin biopsy for persistent or unclear cases, where eczema shows spongiosis and chronic inflammation, and urticaria reveals dermal edema with sparse inflammatory infiltrate. Allergy testing and response to antihistamines further assist in distinguishing urticaria, which typically improves rapidly, unlike eczema.
Treatment Options: Comparing Eczema and Urticaria Management
Eczema treatment primarily involves moisturizing the skin, using topical corticosteroids, and avoiding triggers such as allergens and irritants to reduce inflammation and itching. Urticaria management focuses on antihistamines to control histamine release and, in chronic cases, may require immunosuppressants or biologics like omalizumab to prevent recurrent hives. Both conditions benefit from identifying and avoiding specific triggers, but eczema requires long-term skin barrier repair, while urticaria treatment targets immediate immune responses.
Prevention Tips for Eczema and Urticaria
Eczema prevention involves maintaining skin hydration with fragrance-free moisturizers and avoiding known irritants such as harsh soaps and allergens. Urticaria prevention centers on identifying and avoiding triggers like specific foods, medications, or stress, alongside using antihistamines as recommended by a healthcare provider. Both conditions benefit from wearing loose, breathable clothing and managing environmental factors like temperature and humidity to reduce flare-ups.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Persistent or worsening symptoms of eczema, such as intense itching, redness, and oozing, require medical consultation to prevent infection and manage flare-ups effectively. Urticaria with widespread hives, swelling of the face or throat, difficulty breathing, or lasting more than six weeks signals the need for urgent medical evaluation. Early diagnosis and treatment from a healthcare professional can reduce complications and improve quality of life in both conditions.
Eczema Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com