Gout is a form of arthritis characterized by intense joint pain, swelling, and redness, often affecting the big toe. Caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, it leads to the formation of sharp crystals in the joints. Discover effective treatments and lifestyle changes to manage your gout symptoms in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
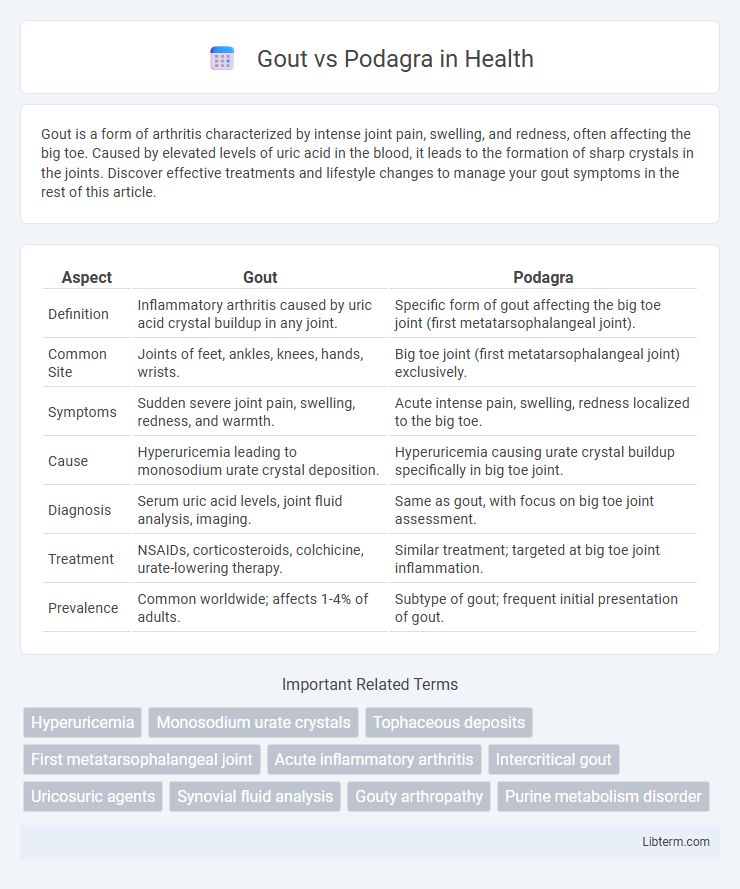
| Aspect | Gout | Podagra |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflammatory arthritis caused by uric acid crystal buildup in any joint. | Specific form of gout affecting the big toe joint (first metatarsophalangeal joint). |
| Common Site | Joints of feet, ankles, knees, hands, wrists. | Big toe joint (first metatarsophalangeal joint) exclusively. |
| Symptoms | Sudden severe joint pain, swelling, redness, and warmth. | Acute intense pain, swelling, redness localized to the big toe. |
| Cause | Hyperuricemia leading to monosodium urate crystal deposition. | Hyperuricemia causing urate crystal buildup specifically in big toe joint. |
| Diagnosis | Serum uric acid levels, joint fluid analysis, imaging. | Same as gout, with focus on big toe joint assessment. |
| Treatment | NSAIDs, corticosteroids, colchicine, urate-lowering therapy. | Similar treatment; targeted at big toe joint inflammation. |
| Prevalence | Common worldwide; affects 1-4% of adults. | Subtype of gout; frequent initial presentation of gout. |
Understanding Gout and Podagra: Key Differences
Gout is a chronic inflammatory arthritis caused by elevated uric acid levels leading to joint inflammation, while podagra specifically refers to gout affecting the big toe's metatarsophalangeal joint. Gout manifests with symptoms such as intense joint pain, swelling, and redness, whereas podagra presents these symptoms localized mainly in the first toe. Understanding these distinctions aids in accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies for effective management of urate crystal deposition in joints.
What Is Gout? Causes and Risk Factors
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and swelling in joints, caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals. Podagra specifically refers to gout affecting the big toe joint, a common initial site of gout flare-ups. Risk factors for gout include high purine diets, obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, certain medications, and genetic predisposition leading to hyperuricemia.
Defining Podagra: The Classic Gout Presentation
Podagra is the classic presentation of gout characterized by sudden, severe inflammation and intense pain in the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe, often accompanied by redness and swelling. It represents a specific manifestation of gout caused by the deposition of monosodium urate crystals due to hyperuricemia. Recognizing podagra is crucial for diagnosing gout and differentiating it from other types of arthritis or joint disorders.
Symptoms: Gout vs Podagra Comparison
Gout presents with sudden, intense joint pain, swelling, redness, and warmth, commonly affecting the big toe, knees, or ankles. Podagra specifically refers to gout affecting the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe, characterized by severe pain and inflammation localized to this area. Both conditions involve urate crystal deposition, but podagra is a subset of gout with symptoms focused exclusively on the big toe joint.
Causes and Triggers of Gout Attacks
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by hyperuricemia, leading to the accumulation of monosodium urate crystals in joints, while podagra specifically refers to gout affecting the big toe. Causes of gout attacks include excessive purine intake from red meat, seafood, and alcohol consumption, as well as dehydration and genetic predisposition affecting uric acid metabolism. Triggers for gout attacks often involve sudden increases in uric acid levels due to stress, illness, certain medications like diuretics, and rapid weight changes.
Why the Big Toe? Exploring Podagra Localization
Podagra refers specifically to gout affecting the big toe, a condition caused by the deposition of monosodium urate crystals in the metatarsophalangeal joint. The big toe's susceptibility is linked to lower temperature and reduced blood flow, which promote crystal formation in this distal joint. This localization results in intense pain and swelling, distinguishing podagra as a common initial manifestation of gout.
Diagnosis: Identifying Gout and Podagra
Diagnosis of gout and podagra involves clinical evaluation and laboratory testing to detect elevated serum uric acid levels and urate crystal deposition. Joint aspiration and synovial fluid analysis under polarized light microscopy confirm monosodium urate crystals, crucial for differentiating gout from other arthritis types. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound and dual-energy CT scans support visualization of tophi and urate crystal deposits in affected joints, aiding precise identification of gout and podagra manifestations.
Treatment Options: Managing Gout and Podagra
Treatment options for gout and podagra primarily focus on reducing inflammation and lowering uric acid levels to prevent flare-ups. Anti-inflammatory medications such as NSAIDs, colchicine, and corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to manage acute attacks, while long-term management includes urate-lowering therapies like allopurinol and febuxostat. Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes, weight management, and limiting alcohol intake, are essential components in controlling both gout and podagra symptoms.
Prevention Strategies for Gout and Podagra
Effective prevention strategies for gout and podagra emphasize maintaining a low-purine diet, reducing alcohol consumption, and staying well-hydrated to minimize uric acid buildup. Regular physical activity and weight management play crucial roles in lowering the risk of gout attacks, while medications such as allopurinol or febuxostat may be prescribed to control serum uric acid levels. Monitoring and managing comorbid conditions like hypertension and diabetes further support long-term prevention of gout and podagra flare-ups.
Frequently Asked Questions: Gout vs Podagra
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in joints, often affecting various parts of the body, while podagra specifically refers to gout affecting the big toe. Common questions include differences between gout and podagra symptoms, treatment methods, and risk factors. Effective management typically involves lifestyle changes, medications to lower uric acid, and targeted therapy for acute podagra attacks.
Gout Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com