Effective medical management focuses on accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and continuous monitoring to optimize patient outcomes. Integrating advanced therapies and evidence-based practices ensures better control of symptoms and prevention of complications. Explore the full article to understand how these strategies can improve your healthcare experience.
Table of Comparison
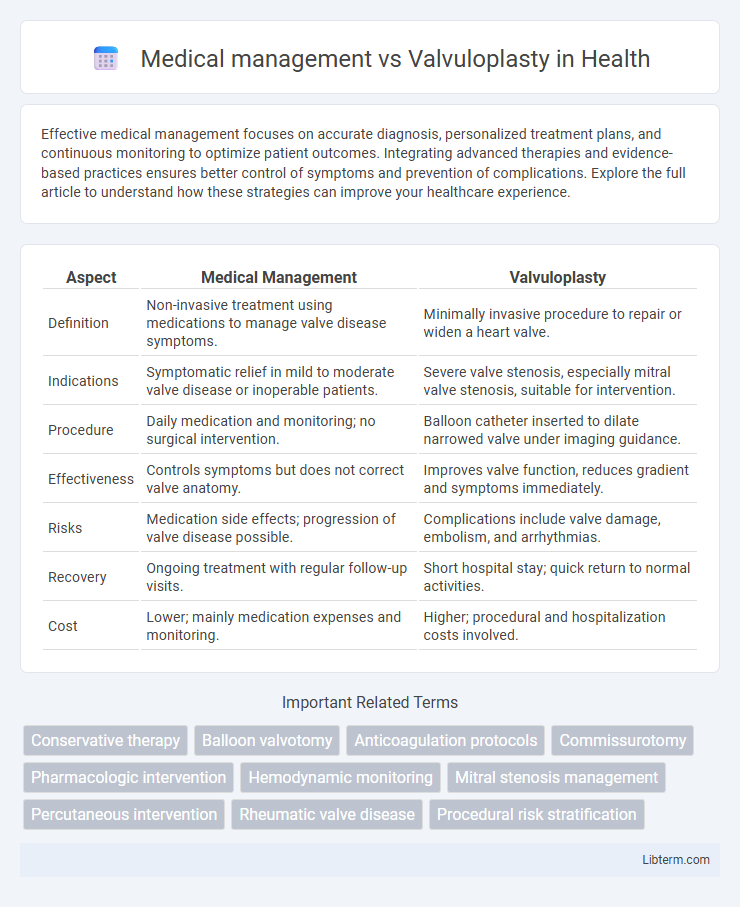
| Aspect | Medical Management | Valvuloplasty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-invasive treatment using medications to manage valve disease symptoms. | Minimally invasive procedure to repair or widen a heart valve. |
| Indications | Symptomatic relief in mild to moderate valve disease or inoperable patients. | Severe valve stenosis, especially mitral valve stenosis, suitable for intervention. |
| Procedure | Daily medication and monitoring; no surgical intervention. | Balloon catheter inserted to dilate narrowed valve under imaging guidance. |
| Effectiveness | Controls symptoms but does not correct valve anatomy. | Improves valve function, reduces gradient and symptoms immediately. |
| Risks | Medication side effects; progression of valve disease possible. | Complications include valve damage, embolism, and arrhythmias. |
| Recovery | Ongoing treatment with regular follow-up visits. | Short hospital stay; quick return to normal activities. |
| Cost | Lower; mainly medication expenses and monitoring. | Higher; procedural and hospitalization costs involved. |
Introduction to Valvular Heart Disease
Valvular heart disease involves damage to or dysfunction of one or more of the heart valves, affecting blood flow through the heart. Medical management typically includes pharmacologic treatments such as diuretics, beta-blockers, and anticoagulants to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Valvuloplasty offers a minimally invasive procedure to repair stenotic valves, particularly in conditions like mitral or aortic stenosis, providing mechanical improvement where medical therapy alone is insufficient.
Overview of Medical Management
Medical management of valvular heart disease primarily involves pharmacologic therapies aimed at symptom control and prevention of disease progression, including diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and anticoagulants depending on valve pathology. This approach is often preferred in asymptomatic patients or those with high surgical risk, focusing on optimizing heart function and managing comorbidities. Regular monitoring through echocardiography and clinical evaluation guides the timing of intervention when medical therapy alone becomes insufficient.
Understanding Valvuloplasty
Valvuloplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat valvular heart disease by repairing a narrowed or stenotic heart valve, primarily through balloon dilation to improve valve function and blood flow. Compared to medical management, which relies on medications to control symptoms and slow disease progression, valvuloplasty directly addresses the mechanical obstruction of the valve, offering symptomatic relief and potential delay of valve replacement surgery. Understanding valvuloplasty involves recognizing patient selection criteria, procedural risks, and the benefits of improved hemodynamics and quality of life in conditions like mitral or aortic stenosis.
Indications for Medical Management
Medical management is primarily indicated for patients with mild to moderate valvular heart disease who are asymptomatic or exhibit stable symptoms, aiming to control underlying conditions such as hypertension, heart failure, or atrial fibrillation. It involves the use of medications like diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and anticoagulants to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and reduce the risk of disease progression. Regular monitoring through echocardiography and clinical evaluation is essential to identify any deterioration that may necessitate interventional procedures like valvuloplasty.
Indications for Valvuloplasty
Valvuloplasty is indicated primarily for patients with symptomatic valvular stenosis, such as mitral or aortic stenosis, who are poor surgical candidates or require urgent intervention. It is preferred when there is favorable valve anatomy without significant calcification or regurgitation, allowing for optimal valve dilation and improved hemodynamics. Medical management remains supportive, focusing on symptom control and delaying progression but is insufficient for severe stenosis or significant valve obstruction.
Comparative Efficacy: Medical vs Valvuloplasty
Medical management of valvular heart disease primarily focuses on symptom control and slowing disease progression through pharmacological treatments such as diuretics, beta-blockers, and anticoagulants. Valvuloplasty, a minimally invasive catheter-based procedure, offers more immediate symptomatic relief by mechanically improving valve function, especially in stenotic lesions like mitral or aortic stenosis. Comparative studies show valvuloplasty provides superior hemodynamic improvement and quality of life benefits, whereas medical management is preferred for patients with contraindications to intervention or less severe disease.
Risks and Benefits of Each Approach
Medical management for valvular heart disease primarily involves pharmacological treatment to control symptoms and prevent complications, with lower immediate procedural risks but limited efficacy in severe cases. Valvuloplasty offers a minimally invasive option to improve valve function and reduce symptoms, with benefits including symptomatic relief and potential delay of surgery, but carries risks such as restenosis, embolism, and vascular complications. Careful patient selection is essential, as medical management suits those with mild symptoms or high surgical risk, while valvuloplasty is preferable for patients with moderate to severe stenosis who are poor surgical candidates.
Patient Selection Criteria
Patient selection criteria for medical management versus valvuloplasty primarily depend on the severity and type of valvular heart disease, with medical management favored for patients with mild to moderate symptoms or contraindications to invasive procedures. Valvuloplasty is typically indicated in patients with symptomatic severe valvular stenosis, particularly mitral stenosis, who have favorable valve anatomy such as pliable leaflets and minimal calcification. Evaluation using echocardiographic parameters, including valve area, gradient, and presence of regurgitation, alongside functional status and comorbidities, guides optimal treatment strategy.
Long-Term Outcomes and Prognosis
Long-term outcomes of medical management for valvular heart disease often show limited symptom control and a higher risk of progressive valve deterioration compared to interventional procedures. Valvuloplasty, particularly balloon valvuloplasty, offers improved valve function and symptomatic relief, leading to better prognosis and reduced incidence of heart failure and repeated hospitalizations. However, durability varies with valve type and patient factors, necessitating regular follow-up for optimal long-term prognosis.
Future Trends in Valvular Heart Disease Treatment
Future trends in valvular heart disease treatment emphasize minimally invasive valvuloplasty techniques, leveraging advances in catheter-based interventions and imaging technology to enhance precision and patient outcomes. Emerging medical management strategies focus on targeted pharmacotherapy to delay disease progression and reduce the need for surgical intervention. Integration of artificial intelligence in diagnostics and personalized treatment plans predicts improved long-term management and prognostication of valvular disorders.
Medical management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com