Hyperandrogenism is a medical condition characterized by excessive levels of androgens, or male hormones, in the body, often resulting in symptoms like severe acne, hair loss, or excessive hair growth. This hormonal imbalance can affect both men and women, leading to complications such as infertility, metabolic issues, or changes in physical appearance that may impact your quality of life. Explore the rest of this article to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for managing hyperandrogenism effectively.
Table of Comparison
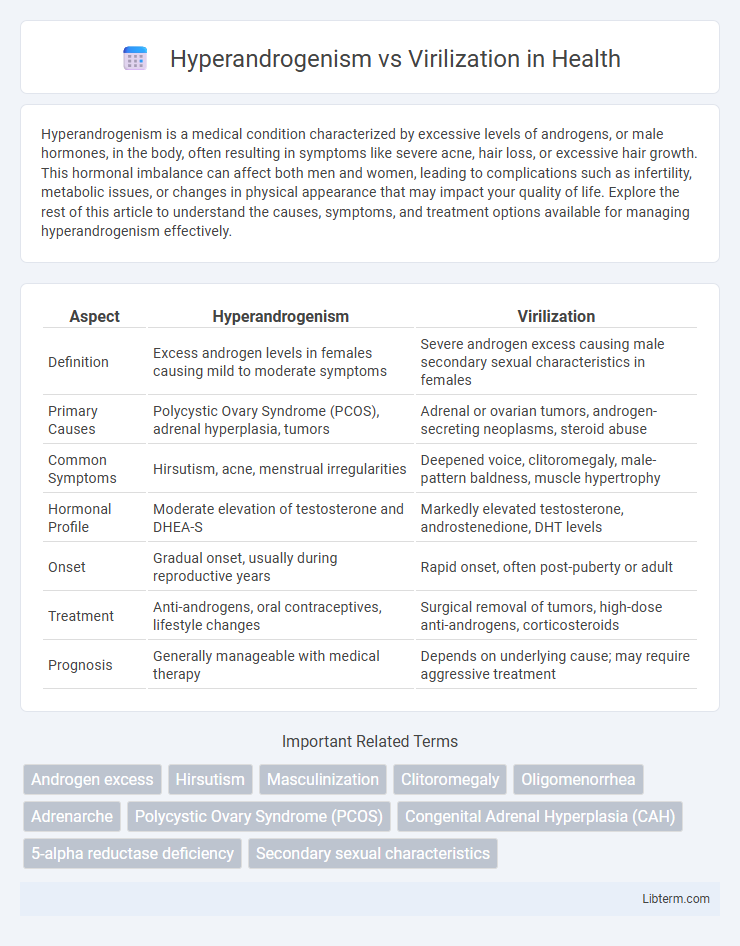
| Aspect | Hyperandrogenism | Virilization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excess androgen levels in females causing mild to moderate symptoms | Severe androgen excess causing male secondary sexual characteristics in females |
| Primary Causes | Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), adrenal hyperplasia, tumors | Adrenal or ovarian tumors, androgen-secreting neoplasms, steroid abuse |
| Common Symptoms | Hirsutism, acne, menstrual irregularities | Deepened voice, clitoromegaly, male-pattern baldness, muscle hypertrophy |
| Hormonal Profile | Moderate elevation of testosterone and DHEA-S | Markedly elevated testosterone, androstenedione, DHT levels |
| Onset | Gradual onset, usually during reproductive years | Rapid onset, often post-puberty or adult |
| Treatment | Anti-androgens, oral contraceptives, lifestyle changes | Surgical removal of tumors, high-dose anti-androgens, corticosteroids |
| Prognosis | Generally manageable with medical therapy | Depends on underlying cause; may require aggressive treatment |
Understanding Hyperandrogenism: Definition and Causes
Hyperandrogenism is a hormonal imbalance characterized by excessive levels of androgens, primarily testosterone, in the female body, leading to symptoms such as hirsutism, acne, and irregular menstruation. It commonly results from polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), adrenal hyperplasia, or androgen-secreting tumors. While hyperandrogenism indicates elevated androgen levels, virilization refers to the development of male secondary sexual characteristics like deepening voice or male pattern baldness, which occur in more severe cases of androgen excess.
What Is Virilization? Key Signs and Mechanisms
Virilization refers to the development of male secondary sexual characteristics in females due to excessive androgen exposure, often caused by conditions like congenital adrenal hyperplasia or androgen-secreting tumors. Key signs include deepening of the voice, increased facial and body hair (hirsutism), clitoromegaly, and male-pattern baldness. The underlying mechanism involves hyperactivation of androgen receptors and overproduction of testosterone or dihydrotestosterone, leading to the masculinization of tissues.
Hormonal Imbalances: Differentiating Hyperandrogenism and Virilization
Hyperandrogenism is characterized by elevated androgen levels, such as testosterone and androstenedione, causing symptoms like acne, hirsutism, and menstrual irregularities. Virilization represents a more severe form of androgen excess, leading to male secondary sexual characteristics, including deepening voice, clitoromegaly, and increased muscle mass. Differentiating these conditions relies on quantifying serum androgen levels and assessing clinical manifestations to guide appropriate endocrine evaluation and treatment.
Clinical Presentation: Symptoms That Set Them Apart
Hyperandrogenism primarily manifests with symptoms such as hirsutism, acne, and menstrual irregularities due to elevated androgen levels, whereas virilization presents more severe clinical features including clitoromegaly, deepening of the voice, and increased muscle mass. Hyperandrogenism often leads to mild to moderate androgenic signs, while virilization indicates a more profound androgen excess resulting in irreversible physical changes. Distinguishing between these conditions is critical for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies in disorders like polycystic ovary syndrome and androgen-secreting tumors.
Common Conditions Associated With Hyperandrogenism
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most prevalent condition associated with hyperandrogenism, characterized by elevated androgen levels leading to symptoms such as hirsutism, acne, and menstrual irregularities. Other common causes include congenital adrenal hyperplasia, adrenal tumors, and androgen-secreting ovarian tumors, which can contribute to excessive androgen production. Hyperandrogenism manifests along a spectrum, where virilization represents more severe androgen effects, including deepening of the voice, clitoromegaly, and increased muscle mass.
Underlying Causes of Virilization in Females
Virilization in females is primarily caused by excessive androgen production or exposure, often linked to conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), androgen-secreting tumors of the ovaries or adrenal glands, and exogenous androgen intake. These underlying causes disrupt normal hormonal balance, leading to male secondary sexual characteristics like hirsutism, deepening voice, and clitoromegaly. Accurate diagnosis involves biochemical assays measuring serum testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS), and imaging studies to pinpoint tumor sources or adrenal hyperplasia.
Diagnostic Approaches: Evaluating Androgen Excess and Virilization
Diagnostic approaches for hyperandrogenism and virilization focus on quantifying androgen excess through serum measurements of total and free testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS), and androstenedione. Imaging studies such as pelvic ultrasound and adrenal CT scans are critical for identifying underlying ovarian or adrenal tumors contributing to virilization. Dynamic endocrine tests, including dexamethasone suppression and ACTH stimulation, aid in differentiating adrenal sources from ovarian causes of androgen excess.
Treatment Strategies for Hyperandrogenism vs Virilization
Treatment strategies for hyperandrogenism primarily involve anti-androgen medications such as spironolactone and oral contraceptives to reduce androgen levels and alleviate symptoms like hirsutism and acne. In contrast, virilization, which indicates more severe androgen excess with features like deepening voice and clitoromegaly, often requires a more aggressive approach including the identification and management of underlying causes such as adrenal or ovarian tumors, sometimes necessitating surgical intervention. Both conditions benefit from individualized treatment plans based on hormone levels, symptom severity, and underlying etiology to optimize patient outcomes.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes
Hyperandrogenism presents a variable prognosis depending on the underlying cause, with many cases responding well to treatment and leading to improved metabolic and reproductive functions. Virilization, characterized by severe androgen excess causing male secondary sexual characteristics, often indicates more advanced or untreated hyperandrogenism and may result in irreversible physical changes if not addressed promptly. Long-term outcomes emphasize early diagnosis and management to prevent progression, optimize fertility, and reduce risks of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular complications.
Frequently Asked Questions: Myths and Facts
Hyperandrogenism involves elevated androgen levels causing symptoms like acne, hirsutism, and menstrual irregularities, while virilization denotes more severe masculinization such as deepening voice, male-pattern baldness, and clitoromegaly. A common myth is that all women with hyperandrogenism experience virilization, but only high androgen levels over time typically lead to virilization symptoms. Factually, hyperandrogenism requires medical evaluation to distinguish between benign causes like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and serious conditions such as adrenal tumors that may cause virilization.
Hyperandrogenism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com