Symposion refers to an ancient Greek social gathering centered around drinking, intellectual conversation, and entertainment, often held by elite men. These events fostered philosophical debates, poetry recitals, and musical performances, shaping the cultural and intellectual life of classical Greece. Discover how symposia influenced modern social and philosophical traditions by reading on.
Table of Comparison
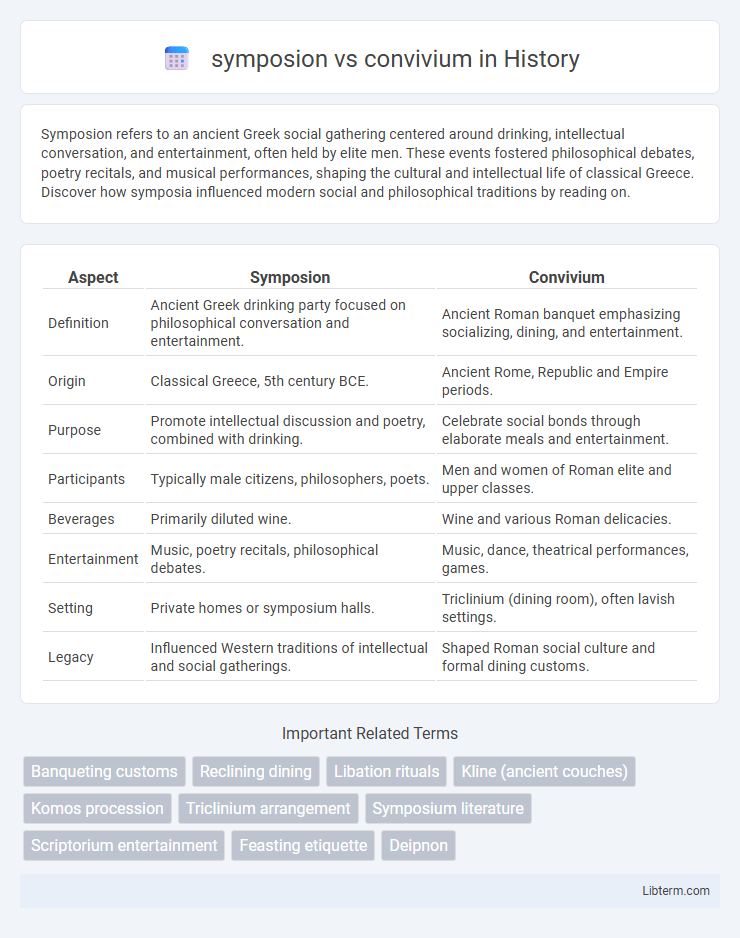
| Aspect | Symposion | Convivium |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ancient Greek drinking party focused on philosophical conversation and entertainment. | Ancient Roman banquet emphasizing socializing, dining, and entertainment. |
| Origin | Classical Greece, 5th century BCE. | Ancient Rome, Republic and Empire periods. |
| Purpose | Promote intellectual discussion and poetry, combined with drinking. | Celebrate social bonds through elaborate meals and entertainment. |
| Participants | Typically male citizens, philosophers, poets. | Men and women of Roman elite and upper classes. |
| Beverages | Primarily diluted wine. | Wine and various Roman delicacies. |
| Entertainment | Music, poetry recitals, philosophical debates. | Music, dance, theatrical performances, games. |
| Setting | Private homes or symposium halls. | Triclinium (dining room), often lavish settings. |
| Legacy | Influenced Western traditions of intellectual and social gatherings. | Shaped Roman social culture and formal dining customs. |
Introduction to Symposion and Convivium
Symposion and convivium are ancient social gatherings with distinct cultural roles; symposion primarily refers to a Greek drinking party combined with philosophical discussion, while convivium is a Roman feast emphasizing formal dining and social hierarchy. The symposion encouraged intellectual exchange, music, and entertainment among elite male participants, often featuring ritualistic drinking and symposium games. In contrast, the convivium centered on feasting and rituals, showcasing wealth and status through elaborate meals and structured seating arrangements.
Historical Origins of Symposion
The symposion originated in ancient Greece as a structured social gathering centered around drinking, intellectual conversation, and philosophical debate, often following a formal banquet. Rooted in Homeric traditions, symposia served as venues for elite men to engage in music, poetry, and political discussion, reinforcing social hierarchies and cultural values. Unlike the convivium of ancient Rome, which emphasized communal dining and feasting, the symposion prioritized dialogue and performance within a ritualized drinking context.
Historical Roots of Convivium
The convivium traces its roots to Roman dining traditions where social and intellectual interaction flourished during elaborate feasts centered on communal meals. Unlike the Greek symposion, which emphasized drinking and philosophical discourse, the convivium encompassed a broader cultural and religious experience with food as a central element. This practice highlighted hospitality and social hierarchy, showcasing the intertwining of sustenance, celebration, and social order in ancient Roman society.
Cultural Contexts: Greece vs Rome
Symposion in ancient Greece was a key social institution centered around intellectual conversation, music, and drinking, primarily involving elite male participants within private homes, reflecting Greek values of philosophy and civic discourse. In contrast, the Roman convivium served as a more diverse social gathering that emphasized lavish feasting and entertainment, often including a broader range of social classes and sometimes slaves or women, illustrating Rome's emphasis on social hierarchy and display of wealth. These differing cultural contexts highlight the symposion as a space for philosophical exchange in Greece, while the convivium functioned as a means of reinforcing social status and fostering political alliances in Rome.
Rituals and Customs of the Symposion
The symposion was an ancient Greek ritual gathering centered on communal drinking, intellectual discussion, and entertainment, characterized by specific customs such as reclining on couches, reciting poetry, and participating in drinking games like kottabos. Symposion participants followed strict protocols involving libations to the gods, especially Dionysus, and the use of specialized vessels such as kylixes and kraters for wine mixing. This structured ritual emphasized social bonding, philosophical debate, and the reinforcement of cultural values, distinguishing the symposion from the more egalitarian and celebratory Roman convivium.
Structure and Format of the Convivium
The convivium featured a highly structured format centered around communal dining with a sequence of courses, accompanied by poetry, music, and philosophical discussions. Unlike the symposion's emphasis on drinking and competitive recitations, the convivium prioritized a balanced integration of food, conversation, and cultural performances within a formalized schedule. The convivium's design fostered social cohesion and intellectual exchange, often including ritualized toasts and designated speakers to guide the event.
Social Roles and Participants
Symposion in ancient Greece primarily involved male aristocrats engaging in intellectual discussions, wine-drinking, and philosophical debates, emphasizing hierarchical social roles and exclusivity. Convivium, rooted in Roman culture, included a broader social spectrum, incorporating both men and women, often slaves and freedpersons, reflecting more diverse and interactive social participation. The symposion's structured roles, such as the *symposiarch* who controlled drinking, contrasted with the convivium's fluid seating and social exchange, highlighting differing cultural norms in social organization.
Food, Drink, and Entertainment
Symposion in ancient Greece featured reclining diners enjoying wine diluted with water, accompanied by musical performances, poetry recitations, and intellectual discussions, creating a sophisticated entertainment environment. Convivium in Roman culture emphasized lavish, multi-course meals served while reclining on couches, paired with rich wines and often followed by theatrical performances or dancing to enhance the festive atmosphere. Both events centered around communal indulgence in food and drink but differed in the style and cultural significance of their entertainment forms.
Philosophical and Intellectual Aspects
Symposion and convivium both represent ancient gatherings centered on intellectual discourse, yet the symposion specifically emphasizes philosophical dialogue intertwined with ritualistic drinking and poetry, fostering dialectical reasoning among participants. Convivium, while also a social banquet, places greater focus on conviviality and cultural exchange, allowing philosophical ideas to emerge more informally alongside culinary enjoyment. The symposion served as a critical setting for the development of classical Greek philosophy, notably in the works of Plato, highlighting its role in shaping dialectical methods and epistemological inquiry.
Lasting Influence on Modern Gatherings
Symposia, originating in ancient Greece, emphasize intellectual discourse and philosophical debate, shaping modern academic conferences and panel discussions. Convivium, rooted in Roman tradition, centers on communal dining and social bonding, influencing contemporary dinner parties and celebratory feasts. The enduring legacy of both fosters environments where ideas and relationships flourish in diverse modern gatherings.
symposion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com