Discover the hidden stories beneath the earth's surface through archaeology, a discipline dedicated to uncovering past civilizations and cultures. Excavations reveal artifacts and structures that help reconstruct human history and understand societal evolution. Dive deeper into how archaeology connects you to ancient worlds by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
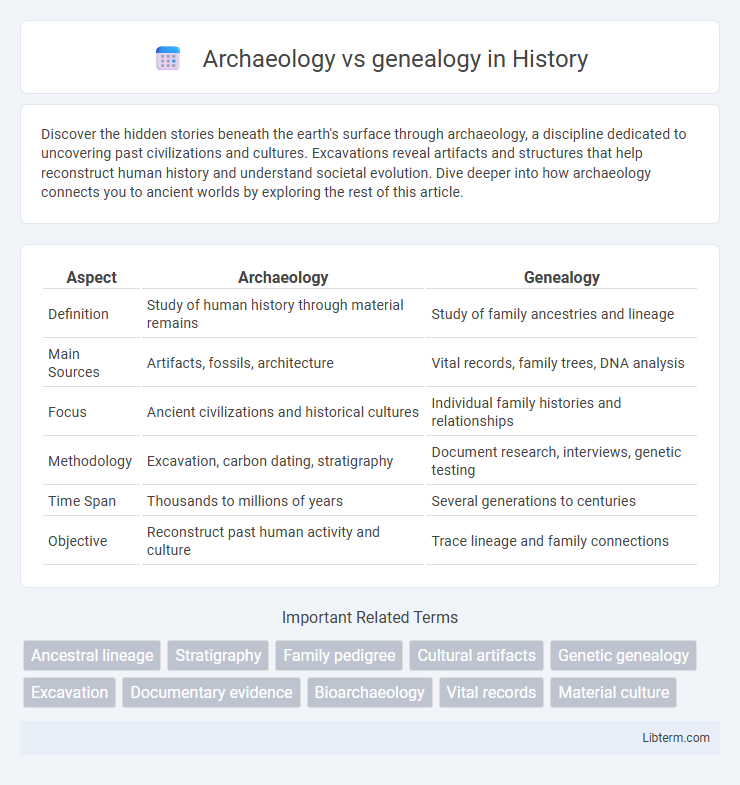
| Aspect | Archaeology | Genealogy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of human history through material remains | Study of family ancestries and lineage |
| Main Sources | Artifacts, fossils, architecture | Vital records, family trees, DNA analysis |
| Focus | Ancient civilizations and historical cultures | Individual family histories and relationships |
| Methodology | Excavation, carbon dating, stratigraphy | Document research, interviews, genetic testing |
| Time Span | Thousands to millions of years | Several generations to centuries |
| Objective | Reconstruct past human activity and culture | Trace lineage and family connections |
Introduction to Archaeology and Genealogy
Archaeology explores human history through the excavation and analysis of artifacts, structures, and other physical remains, providing insights into ancient cultures and societies. Genealogy traces family lineages and ancestry using historical records, vital documents, and genetic testing to construct family trees and understand heritage. Both disciplines offer complementary perspectives on human history, with archaeology emphasizing material culture and genealogy focusing on personal and familial connections.
Defining Archaeology: Uncovering the Past
Archaeology involves the scientific study and excavation of physical artifacts, structures, and landscapes to uncover human history and cultural evolution. Through meticulous analysis of material remains such as pottery, tools, and ancient settlements, archaeology reconstructs past societies and their behaviors. This discipline provides tangible evidence that shapes our understanding of historical events and prehistoric civilizations.
Genealogy Explained: Tracing Family Roots
Genealogy involves systematically tracing family roots through historical documents like birth certificates, census records, and marriage licenses to construct an accurate family tree. Unlike archaeology, which studies ancient cultures through material artifacts, genealogy emphasizes living memory and recorded evidence to connect generations and understand lineage. Modern genealogical research often incorporates DNA testing to verify relationships and uncover ancestral origins.
Key Methodologies in Archaeology
Key methodologies in archaeology include excavation, which involves systematically uncovering artifacts and features from historical sites to understand past human activity; remote sensing techniques like ground-penetrating radar that identify subsurface remains without disturbing the site; and stratigraphy, the analysis of soil layers to date and contextualize findings. Archaeologists also use radiocarbon dating to determine the age of organic materials, providing a chronological framework for interpreting ancient cultures. These methods contrast with genealogy's focus on historical records, vital statistics, and DNA analysis to trace familial lineages rather than material culture.
Genealogical Research Techniques
Genealogical research techniques involve analyzing historical documents such as birth, marriage, and death records, census data, and immigration logs to construct family trees and trace lineage. DNA testing and genetic analysis have become increasingly valuable in confirming relationships and uncovering ancestral origins. Unlike archaeology, which studies artifacts and cultural remains, genealogy focuses on personal and familial histories through detailed record examination and oral history collection.
Types of Evidence Used in Both Fields
Archaeology relies on physical artifacts such as tools, pottery, and architectural remains to reconstruct past human activities and cultural patterns. Genealogy uses historical records including birth certificates, census data, and family trees to trace lineage and heritage across generations. Both fields analyze evidence to understand human history, but archaeology emphasizes material culture while genealogy prioritizes documented ancestry.
Technology’s Impact on Archaeology and Genealogy
Advancements in technology have revolutionized archaeology and genealogy by enabling more precise data collection and analysis methods, such as LiDAR scanning and DNA sequencing. Archaeologists utilize remote sensing and 3D modeling to uncover and reconstruct ancient sites with minimal disturbance, while genealogists benefit from genetic genealogy databases and digital archives to trace lineage and ancestral connections more accurately. These innovations have significantly enhanced the accuracy, efficiency, and scope of research in both fields, bridging historical gaps through scientific tools.
Differences in Purpose and Scope
Archaeology focuses on studying ancient civilizations and cultures through material remains like artifacts, structures, and fossils, aiming to reconstruct past human behavior and societal development. Genealogy centers on tracing individual family histories and lineages using documents such as birth, marriage, and death records to establish ancestry and heritage. While archaeology examines broad historical contexts over millennia, genealogy targets specific familial connections often within a few generations.
Intersections and Collaborations Between Disciplines
Archaeology and genealogy intersect in their shared objective of uncovering human history, where archaeological findings provide physical context for genealogical records, enriching family histories with cultural and material evidence. Collaborations between archaeologists and genealogists often involve integrating DNA analysis, artifact examination, and archival research to create comprehensive narratives of ancestral lineages and past civilizations. These interdisciplinary approaches enhance the accuracy of historical reconstructions and deepen understanding of human migration, social structures, and heritage preservation.
Choosing the Right Path: Which Field is For You?
Archaeology uncovers human history through excavations and artifact analysis, ideal for those passionate about ancient cultures and scientific methods. Genealogy traces family lineages using historical records, DNA, and oral histories, suited for individuals interested in personal heritage and historical connections. Choosing the right path depends on whether you prefer uncovering broad historical contexts or exploring intimate ancestral stories.
Archaeology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com