The Legatus and Quaestor were key officials in the Roman Republic, each with distinct roles in governance and administration. The Legatus acted as a high-ranking military officer or deputy to a commander, while the Quaestor managed financial affairs and public funds. Explore this article to understand how these positions shaped Roman political and military structure.
Table of Comparison
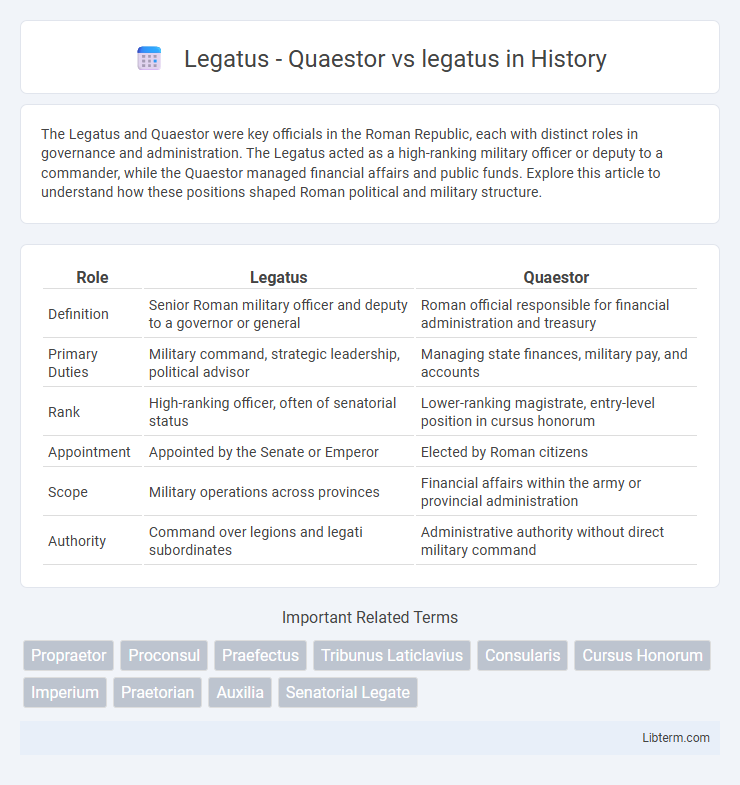
| Role | Legatus | Quaestor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Senior Roman military officer and deputy to a governor or general | Roman official responsible for financial administration and treasury |
| Primary Duties | Military command, strategic leadership, political advisor | Managing state finances, military pay, and accounts |
| Rank | High-ranking officer, often of senatorial status | Lower-ranking magistrate, entry-level position in cursus honorum |
| Appointment | Appointed by the Senate or Emperor | Elected by Roman citizens |
| Scope | Military operations across provinces | Financial affairs within the army or provincial administration |
| Authority | Command over legions and legati subordinates | Administrative authority without direct military command |
Introduction to Roman Military Ranks
Legatus was a senior officer in the Roman army, typically commanding a legion and acting as the governor's deputy, while a Quaestor primarily managed financial and administrative duties rather than military command. The legatus held significant authority, often appointed by the emperor or senate, overseeing tactical operations and strategic decisions on the battlefield. In contrast, the Quaestor's role was crucial for logistical support, ensuring funds and supplies were properly allocated to sustain military campaigns.
Defining the Role of the Legatus
The legatus served as a high-ranking military officer appointed by the Roman Senate or emperor, often commanding legions and overseeing provincial administrations. Unlike the quaestor, who primarily managed financial affairs and treasury functions within a province or legion, the legatus held broader leadership responsibilities, including strategic decision-making and diplomatic duties. As the emperor's representative, the legatus wielded considerable authority, embodying both military command and imperial governance.
Understanding the Quaestor Position
The Quaestor in Roman administration served as a key financial official responsible for managing public funds, overseeing treasury operations, and assisting higher magistrates with fiscal duties. Compared to the broader role of a legatus, who acted as a military commander or diplomatic envoy under a governor or general, the Quaestor's position was primarily administrative and financial within the Roman Republic and early Empire. Understanding the Quaestor's responsibilities highlights the importance of financial control in maintaining the stability and efficiency of Roman provincial governance.
Legatus: Authority and Responsibilities
Legatus was a senior Roman military officer appointed by the emperor, wielding significant authority over legion commanders and provincial administration. Tasked with commanding entire legions, Legati held responsibilities including strategic planning, troop discipline, and liaising directly with imperial authority. Unlike a quaestor, who managed financial affairs and fiscal administration, the Legatus exercised broad military and political power critical to the operational success and governance within Roman provinces.
Quaestor: Duties and Financial Management
The quaestor in Ancient Rome served as the chief financial officer responsible for managing the state treasury, overseeing public revenues, and auditing accounts. Unlike the legatus, who acted as a military commander or provincial governor, the quaestor's duties centered on fiscal administration, including the disbursement of funds for military and civil expenses. This role was crucial in ensuring proper financial control and resource allocation within the Roman government and military campaigns.
Hierarchical Placement: Legatus vs. Quaestor
The Legatus held a higher hierarchical position compared to the Quaestor, serving as a senior officer or deputy to a Roman general or provincial governor with broad administrative and military authority. In contrast, the Quaestor was primarily responsible for financial and administrative duties, managing the treasury and supplies under the command of higher-ranking officials. The Legatus exercised command over military units and provincial governance, while the Quaestor's role was more specialized and subordinate within the Roman administrative hierarchy.
Differences in Power and Influence
Legatus and quaestor held distinct roles in the Roman administrative hierarchy, with legatus serving as a senior military commander or provincial governor wielding substantial power and autonomy over troops and territorial governance. In contrast, quaestor functioned as a financial official responsible for treasury management and fiscal duties, possessing limited authority and influence compared to the legatus. The legatus's influence extended across both military and political spheres, while the quaestor primarily operated within administrative and financial domains.
Collaboration and Interactions in the Legion
The Legatus and Quaestor held distinct but complementary roles within the Roman legion, with the Legatus serving as the legion's commanding officer responsible for strategic decisions and military leadership. The Quaestor managed the financial affairs, including the proper allocation of funds, supplies, and equipment essential for sustaining the legion's operational effectiveness. Their collaboration ensured efficient resource management and operational command, fostering seamless interaction between administrative logistics and battlefield strategy.
Historical Significance of Both Positions
The Legatus and Quaestor held distinct yet pivotal roles in the Roman Republic and Empire, with the Legatus serving as a senior military commander or provincial governor, often appointed by the emperor or Senate to lead legions and administer provinces. The Quaestor functioned primarily as a financial administrator or assistant to higher magistrates, responsible for managing public funds and the treasury, marking the entry point to a political career. Historically, Legati exercised substantial military and administrative authority impacting imperial expansion and governance, while Quaestors provided the essential fiscal foundation supporting Rome's complex bureaucracy and military endeavors.
Conclusion: Comparing Legatus and Quaestor
Legatus and Quaestor represent distinct ranks within the Roman military and administrative hierarchy, with the Legatus serving as a senior commander overseeing legions and the Quaestor managing financial and administrative duties. The Legatus held significant military authority and strategic responsibilities, while the Quaestor ensured fiscal accountability and logistical support for Roman provinces or armies. Comparing these roles highlights the complementary nature of military leadership and financial administration in maintaining Roman imperial efficiency and control.
Legatus - Quaestor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com