Senators play a crucial role in shaping national legislation and representing their constituents' interests at the highest level of government. Understanding the responsibilities and influence of a senator can help you appreciate the legislative process and how policies impact your community. Dive into the full article to explore the vital functions and significance of senators in modern governance.
Table of Comparison
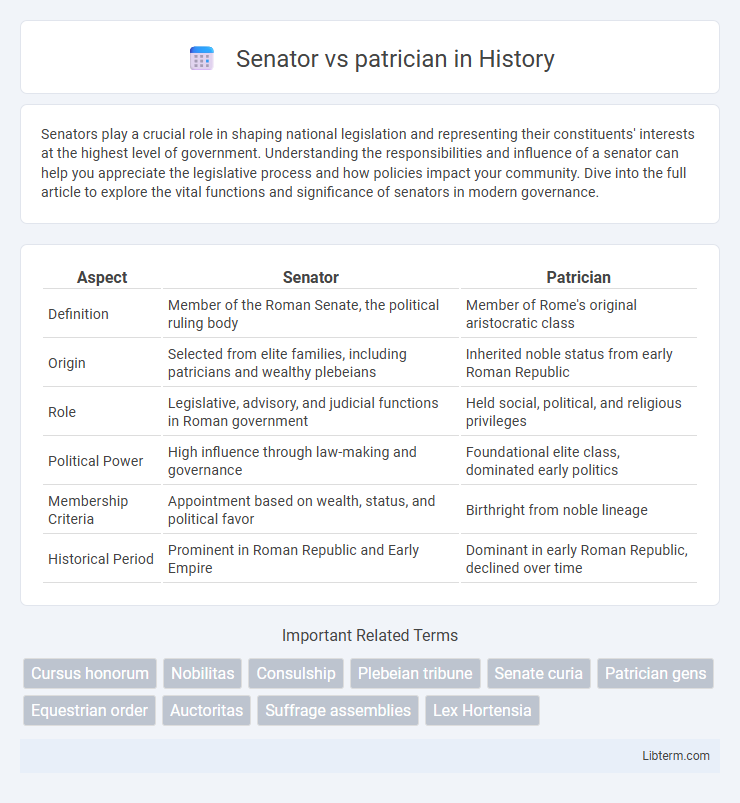
| Aspect | Senator | Patrician |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Member of the Roman Senate, the political ruling body | Member of Rome's original aristocratic class |
| Origin | Selected from elite families, including patricians and wealthy plebeians | Inherited noble status from early Roman Republic |
| Role | Legislative, advisory, and judicial functions in Roman government | Held social, political, and religious privileges |
| Political Power | High influence through law-making and governance | Foundational elite class, dominated early politics |
| Membership Criteria | Appointment based on wealth, status, and political favor | Birthright from noble lineage |
| Historical Period | Prominent in Roman Republic and Early Empire | Dominant in early Roman Republic, declined over time |
Introduction: Defining Senators and Patricians
Senators were members of the legislative body in ancient Rome, responsible for making laws and advising magistrates, originating mainly from the patrician class. Patricians comprised the aristocratic elite, holding hereditary privileges, land ownership, and early political power, often dominating the Senate's composition. The distinction lies in senators representing a political office, while patricians signify a hereditary social class rooted in Rome's early history.
Historical Origins of Senators
Senators originated in ancient Rome as members of the Senate, a political institution established during the Roman Kingdom around the 6th century BCE, composed initially of patricians--aristocratic families who held hereditary status. Over time, the Senate evolved to include wealthy plebeians, cementing its role as a governing body that advised monarchs and later republic leaders. The patrician class maintained political dominance through Senate membership, shaping Roman legislative, financial, and foreign policies throughout the Republic period.
Historical Origins of Patricians
Patricians originated as the elite ruling class in ancient Rome, tracing their lineage to the city's founding families who held exclusive political and religious privileges. This hereditary aristocracy controlled the Senate, shaping early Roman governance and law during the Republic era. The distinction between patricians and plebeians defined social and political dynamics, with patricians maintaining dominance through birthright and landownership.
Social Status: Senatorial vs Patrician Class
Senators belonged to the senatorial class, a political elite distinguished by wealth, landownership, and eligibility for governing roles in ancient Rome. Patricians were members of the original aristocratic families, holding hereditary privileges and social prestige but not necessarily occupying political office. While all senators had to be Roman citizens of high status, not all patricians were senators, reflecting a distinction between hereditary nobility and political authority.
Roles and Responsibilities in Government
Senators in ancient Rome primarily served as advisers and decision-makers in the Senate, shaping legislation, foreign policy, and financial matters through deliberation and voting. Patricians, as the elite hereditary class, initially monopolized key government roles, including priesthoods, magistracies, and Senate membership, wielding significant influence over political and religious affairs. While senators executed governance and policy, patricians maintained their dominance by controlling access to powerful offices and guiding the Republic's aristocratic framework.
Pathways to Power: How Senators and Patricians Rose
Senators primarily rose to power through formal political careers, often beginning with roles in local magistracies and advancing via the cursus honorum, a structured sequence of public offices in the Roman Republic. Patricians gained influence through hereditary status within Rome's aristocratic families, leveraging ancestral prestige and exclusive religious and social privileges. Both groups solidified authority by controlling land, wealth, and key military commands, ensuring their dominance in political and social hierarchies.
Influence on Roman Politics and Society
Senators, as members of Rome's ruling aristocracy, wielded considerable influence over legislative decisions, military command, and financial policies, shaping the Republic's political landscape. Patricians, the hereditary elite class, initially monopolized political offices and religious roles, reinforcing social hierarchies and consolidating power through ancestral lineage. Over time, the gradual inclusion of plebeians into the Senate diluted patrician dominance, altering Rome's societal structure and political dynamics.
Legal Privileges and Restrictions
Senators in ancient Rome held extensive legal privileges, including immunity from certain forms of prosecution and exclusive access to specific political offices, which reinforced their influence over legislative processes. Patricians, as members of the aristocratic class, enjoyed hereditary privileges such as exclusive rights to hold high religious and political positions, though their legal status was increasingly challenged by plebeian rights reforms. Both groups experienced evolving restrictions over time, with legal reforms gradually diminishing patrician monopolies while senators maintained distinct privileges tied to their political roles.
Notable Senators and Patricians in History
Notable senators like Cicero, renowned for his oratory skills and political influence in the late Roman Republic, shaped legislative decisions and legal frameworks. Prominent patricians such as Julius Caesar, a member of the aristocratic class, wielded significant power through both military conquests and political reforms. The distinction between senators and patricians in ancient Rome underscores the intersection of legislative authority and hereditary nobility in shaping the Republic's governance.
Lasting Legacy: Senators and Patricians in Modern Context
Senators of ancient Rome, primarily drawn from the patrician class, established a political legacy that shaped modern legislative institutions emphasizing governance, civic duty, and aristocratic influence. Patricians represented a hereditary elite whose social and political dominance influenced contemporary concepts of nobility, privilege, and class stratification. The intertwining of senatorial authority with patrician status laid foundational principles for republic governance and aristocratic political participation evident in modern democratic systems.
Senator Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com