Myths shape cultural beliefs and explain natural phenomena through storytelling passed down generations. They often blend historical facts with symbolic meanings, influencing social values and traditions around the world. Discover the truth behind popular myths and how they impact your understanding by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
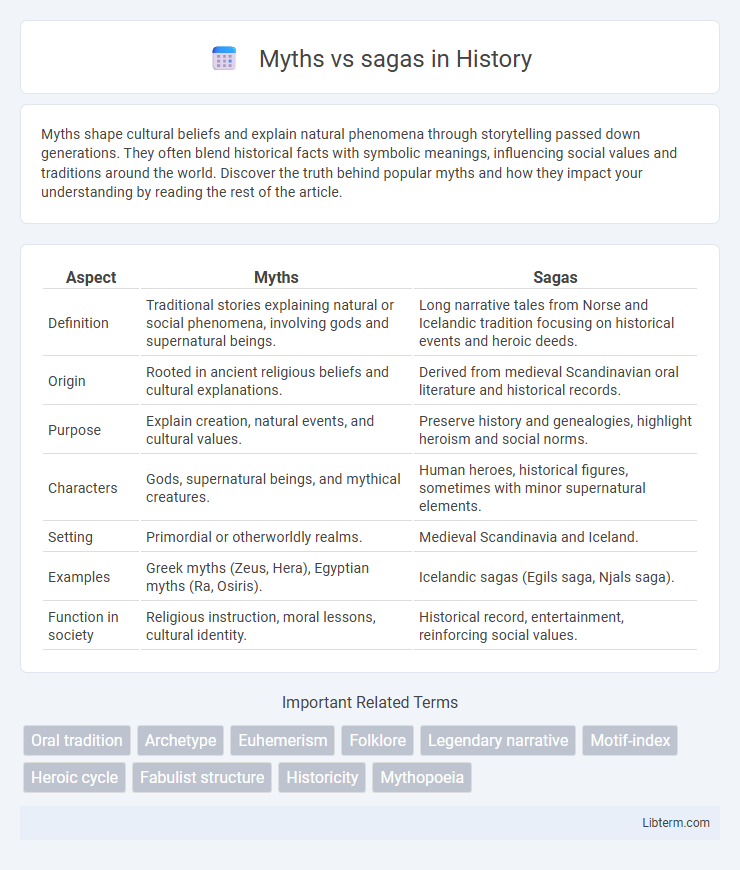
| Aspect | Myths | Sagas |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional stories explaining natural or social phenomena, involving gods and supernatural beings. | Long narrative tales from Norse and Icelandic tradition focusing on historical events and heroic deeds. |
| Origin | Rooted in ancient religious beliefs and cultural explanations. | Derived from medieval Scandinavian oral literature and historical records. |
| Purpose | Explain creation, natural events, and cultural values. | Preserve history and genealogies, highlight heroism and social norms. |
| Characters | Gods, supernatural beings, and mythical creatures. | Human heroes, historical figures, sometimes with minor supernatural elements. |
| Setting | Primordial or otherworldly realms. | Medieval Scandinavia and Iceland. |
| Examples | Greek myths (Zeus, Hera), Egyptian myths (Ra, Osiris). | Icelandic sagas (Egils saga, Njals saga). |
| Function in society | Religious instruction, moral lessons, cultural identity. | Historical record, entertainment, reinforcing social values. |
Understanding Myths and Sagas: Definitions
Myths are traditional stories that explain natural phenomena, origins, and cultural beliefs, often involving gods and supernatural events. Sagas are long, narrative tales rooted in historical events, usually centered on heroes and family histories within Norse and Icelandic cultures. Understanding myths involves recognizing their role in conveying moral lessons and cosmology, while sagas provide detailed accounts blending fact with legend to preserve cultural heritage.
Origins and Historical Contexts
Myths often originate from ancient religious beliefs and serve to explain natural phenomena or cosmic origins, deeply rooted in a culture's spiritual practices. Sagas emerge from the medieval Norse and Icelandic traditions, reflecting historical events and heroic deeds with a strong narrative emphasis on lineage and social values. Both forms provide insights into the worldview of their respective societies, with myths leaning toward symbolic meaning and sagas offering more detailed historical context.
Key Differences Between Myths and Sagas
Myths primarily explain natural phenomena, gods, and origins of the world, often involving supernatural beings and divine intervention. Sagas are lengthy narratives focusing on historical events and heroic deeds, typically rooted in Norse or Icelandic culture without overt mythological explanations. While myths serve a religious or explanatory purpose, sagas emphasize human characters and realistic storytelling within a cultural context.
Common Themes in Myths
Common themes in myths include creation, heroism, and the battle between good and evil, reflecting the values and beliefs of ancient cultures. These narratives often explain natural phenomena, human origins, and societal laws through symbolic stories involving gods, supernatural beings, and legendary heroes. Myths serve to provide moral lessons, cultural identity, and a framework for understanding the world.
Typical Narratives in Sagas
Typical narratives in sagas often center on heroic exploits, familial loyalty, and complex social relationships, emphasizing realistic human experiences grounded in history and cultural identity. These narratives include detailed descriptions of feuds, voyages, and moral dilemmas, reflecting the values and societal norms of Norse and Icelandic communities. Unlike myths, which involve gods and supernatural beings, sagas focus on human characters whose bravery, honor, and struggles shape the collective memory of their people.
Famous Examples of Myths Around the World
Myths such as the Greek tale of Zeus and Prometheus shape the foundation of Western storytelling, while the Norse myths featuring Odin and Thor reveal ancient Scandinavian beliefs. In Hinduism, the epic Ramayana narrates the heroic journey of Rama, reflecting profound moral values. Across cultures, these myths serve as timeless narratives that explain natural phenomena, human behavior, and cultural traditions.
Legendary Sagas and Their Impact
Legendary sagas, a vital subset of Old Norse literature, blend mythological elements with historical events to shape cultural identity and collective memory. These narratives often emphasize heroic feats, dynastic origins, and moral lessons, influencing medieval Scandinavian literature and modern interpretations of Viking history. Their enduring impact is evident in contemporary storytelling, where legendary sagas inform popular culture, literature, and historical understanding.
Cultural Significance: Myths vs. Sagas
Myths often serve as foundational narratives that explain natural phenomena, cultural origins, and religious beliefs, profoundly shaping societal values and worldviews. Sagas, primarily historical or heroic epics, preserve cultural identity by recounting the deeds of ancestors, reflecting social norms and collective memory. Both forms of storytelling reinforce communal bonds and cultural continuity, but myths emphasize cosmology and moral lessons, while sagas emphasize heritage and historical legacy.
Influence on Literature and Storytelling
Myths and sagas have profoundly shaped literature and storytelling by providing foundational narratives that explore human nature, morality, and the supernatural. Myths often convey archetypal themes and cultural values, influencing genres like fantasy and epic poetry through timeless motifs. Sagas, with their detailed historical and genealogical focus, contribute to the development of realistic narrative techniques and character complexity in modern storytelling.
Modern Interpretations and Adaptations
Modern interpretations of myths and sagas emphasize their enduring cultural relevance by exploring timeless themes like heroism, morality, and human nature. Adaptations often reimagine these ancient narratives through contemporary mediums such as film, literature, and digital storytelling, enhancing accessibility and engagement. This ongoing reinterpretation enriches the global cultural landscape, bridging historical tradition with modern values.
Myths Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com