The term "tribune" refers to an elected official in ancient Rome who represented the interests of the plebeians, or common people. Serving as a vital political figure, tribunes had the power to veto decisions by magistrates to protect plebeian rights. Discover how the roles of the tribune and plebeians shaped Roman history and governance in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
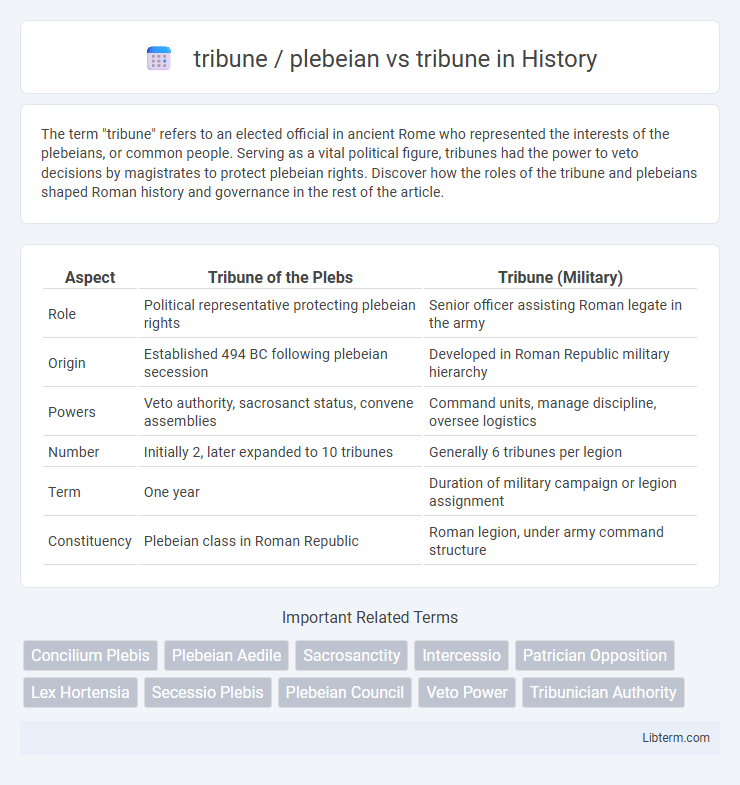
| Aspect | Tribune of the Plebs | Tribune (Military) |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Political representative protecting plebeian rights | Senior officer assisting Roman legate in the army |
| Origin | Established 494 BC following plebeian secession | Developed in Roman Republic military hierarchy |
| Powers | Veto authority, sacrosanct status, convene assemblies | Command units, manage discipline, oversee logistics |
| Number | Initially 2, later expanded to 10 tribunes | Generally 6 tribunes per legion |
| Term | One year | Duration of military campaign or legion assignment |
| Constituency | Plebeian class in Roman Republic | Roman legion, under army command structure |
Understanding the Role of the Tribune in Ancient Rome
The Tribune in Ancient Rome served as a critical protector of plebeian interests, possessing the authority to veto actions by magistrates and the Senate that threatened the common people. Distinct from ordinary plebeians, tribunes held a unique political office established to safeguard the rights and privileges of Rome's lower class against patrician dominance. Their role was instrumental in balancing power within the Roman Republic, ensuring plebeian voices influenced legislation and governance.
The Origins and Evolution of the Tribune
The tribune originated in ancient Rome as officials elected by the plebeians to protect their rights against patrician magistrates. Over time, the office of the plebeian tribune evolved from a purely defensive role to one wielding significant political power, including veto authority over senate actions. This evolution marked a critical shift in Roman governance, institutionalizing plebeian influence and balancing aristocratic control.
Plebeians: The Common People of Rome
Plebeians were the common people of ancient Rome, comprising the majority of the population and initially excluded from political power held by Patricians. The Tribune of the Plebs was an official elected by Plebeians to protect their interests and veto harmful legislation, embodying the political empowerment of the lower class. This office became a cornerstone of Roman Republic social dynamics, balancing elite dominance and plebeian rights through legally enforced protections and representation.
Tribune of the Plebs: Defender of Plebeian Rights
The Tribune of the Plebs was a powerful official in ancient Rome elected to protect the interests and rights of the plebeian class against patrician dominance. Holding sacrosanct status, tribunes had the authority to veto legislation, intervene in legal matters, and convene the Plebeian Council, ensuring that plebeian concerns were represented in the political arena. This role was crucial in balancing social inequalities and advancing plebeian influence within the Roman Republic's governance structure.
Patricians vs Plebeians: Social Divide and Political Struggle
Tribunes were elected representatives of the plebeians, tasked with protecting their interests against the patrician-dominated Senate in ancient Rome. The social divide pitted wealthy patricians, who held political power and land, against the plebeians, who sought legal rights and political inclusion through the tribunate. Tribunes wielded the power to veto patrician decisions, enabling plebeians to challenge aristocratic authority and gradually achieve political reforms.
Tribune’s Powers and Limitations
Tribunes of the plebs wielded significant powers including the ability to veto actions by magistrates and the Senate, propose legislation, and protect plebeians from unjust treatment. Their sacrosanct status provided legal immunity, preventing harm or obstruction by other officials during their term. However, their authority was limited geographically to Rome, could be overruled by collective plebeian assembly decisions, and lacked the power to enforce laws without broader political support.
How Tribunes Represented Plebeian Interests
Tribunes of the plebs exercised significant political power by safeguarding plebeian rights against patrician dominance in Ancient Rome through their veto authority over Senate decisions and magistrates' actions. They convened the Plebeian Council, proposing laws that directly addressed commoners' grievances, including land reforms and debt relief, reinforcing social equity. Their sacrosanct status protected them from harm, enabling effective advocacy for the plebeian class within the Roman Republic's political structure.
Key Historical Tribunes and Their Impact
Key historical tribunes such as Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus significantly shaped Roman political reform by championing plebeian rights and land redistribution, challenging the patrician elite's dominance. The plebeian tribunes held sacrosanct powers, including veto authority, which they leveraged to protect commoners from legislative injustices and to promote social equity during the Roman Republic. Their impact laid the groundwork for future political representation methods, influencing democratic principles and the balance of power between social classes.
Plebeian vs Tribune: Misconceptions and Clarifications
The plebeians were the commoner class in ancient Rome, while tribunes were elected officials representing plebeian interests. A common misconception is that all plebeians were tribunes, but only a select few were granted this political role to protect plebeian rights against patrician dominance. The tribunate was a powerful institution designed to give plebeians political influence, distinct from the broader plebeian populace.
Legacy of the Tribune System in Modern Governance
The tribune system, rooted in ancient Rome, established a precedent for protecting the rights of ordinary citizens against elite power, influencing modern concepts of representative democracy and checks and balances. Tribunes, originally plebeian officials with the power to veto unjust laws and actions, embody the principle of citizen advocacy that persists in contemporary legislative bodies and ombudsman roles worldwide. The legacy of the tribune system is reflected in institutional mechanisms designed to ensure accountability, prevent abuses of authority, and amplify marginalized voices within modern governance structures.
tribune / plebeian Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com