An emblem represents a symbolic design that conveys identity, values, or affiliations through imagery and style. It often appears on flags, logos, or badges to create instant recognition and convey specific messages. Discover how understanding emblems can enhance Your grasp of cultural and organizational symbolism by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
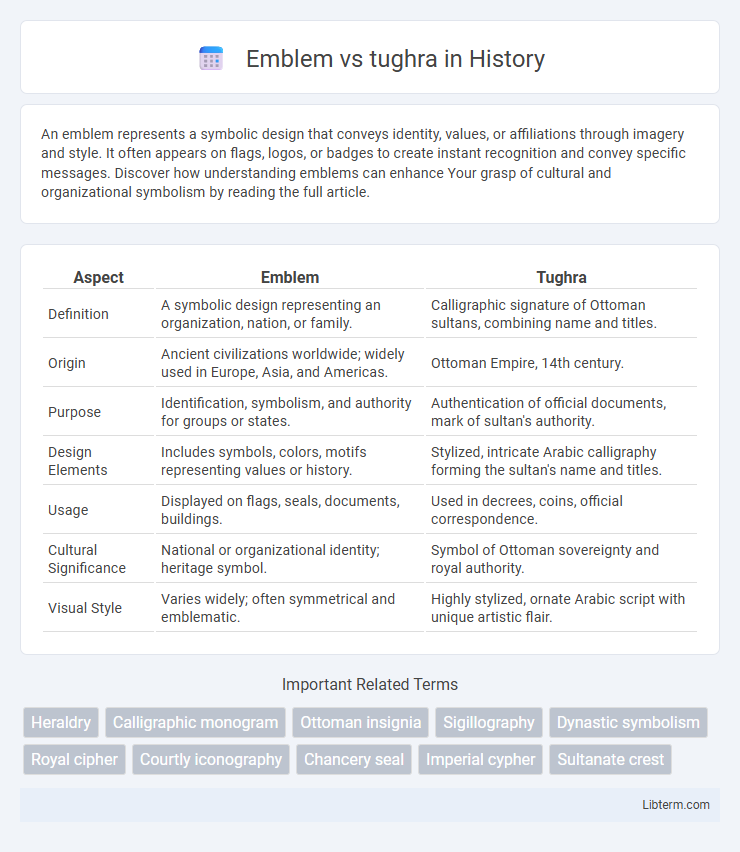
| Aspect | Emblem | Tughra |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A symbolic design representing an organization, nation, or family. | Calligraphic signature of Ottoman sultans, combining name and titles. |
| Origin | Ancient civilizations worldwide; widely used in Europe, Asia, and Americas. | Ottoman Empire, 14th century. |
| Purpose | Identification, symbolism, and authority for groups or states. | Authentication of official documents, mark of sultan's authority. |
| Design Elements | Includes symbols, colors, motifs representing values or history. | Stylized, intricate Arabic calligraphy forming the sultan's name and titles. |
| Usage | Displayed on flags, seals, documents, buildings. | Used in decrees, coins, official correspondence. |
| Cultural Significance | National or organizational identity; heritage symbol. | Symbol of Ottoman sovereignty and royal authority. |
| Visual Style | Varies widely; often symmetrical and emblematic. | Highly stylized, ornate Arabic script with unique artistic flair. |
Understanding Emblems: Definition and Origins
Emblems are symbolic representations that convey specific meanings, often associated with organizations, nations, or families, originating from ancient heraldry and artistic traditions. They serve as visual identifiers that combine imagery, colors, and motifs to express values or authority. The historical use of emblems dates back to medieval Europe, where they functioned as badges of distinction and lineage.
The Historical Significance of the Tughra
The tughra, a calligraphic monogram or signature of Ottoman sultans, embodies centuries of imperial authority and artistic tradition, distinguished by its intricate design symbolizing power and governance. Unlike generic emblems, the tughra served as an official seal on decrees, coins, and documents, reinforcing the sultan's legitimacy and presence throughout the empire. Its historical significance lies in its dual function as both a work of art and a political tool, uniquely reflecting Ottoman identity and sovereignty.
Emblem vs Tughra: Key Differences
Emblem and tughra differ fundamentally in design and purpose; an emblem is a symbolic image representing an organization, nation, or concept, often incorporating multiple elements like shields, animals, or mottos, while a tughra is a highly stylized, calligraphic signature used by Ottoman sultans to authenticate documents. Emblems emphasize visual complexity and symbolic representation, whereas tughras prioritize elegant, flowing Arabic script conveying authority and identity in a minimalistic form. The key distinction lies in the emblem's role as a broader identity symbol versus the tughra's specific function as a personalized royal signature.
Symbolism in Emblems and Tughra
Emblems symbolize identity and authority through distinct visual elements, often representing organizations, nations, or ideals with specific icons or motifs that convey historical and cultural significance. Tughras, intricate calligraphic signatures of Ottoman sultans, serve as personalized symbols of sovereignty, power, and legitimacy, combining artistic elegance with political authority. Both utilize symbolism to communicate status and governance, with emblems emphasizing collective representation and tughras highlighting individual rulership.
Artistic Styles: Emblematic vs Calligraphic
Emblems often feature geometric shapes, symbols, and icons crafted with distinct lines and balanced symmetry to convey identity or authority succinctly. Tughras exemplify intricate calligraphic art, merging elaborate Arabic script with ornamental flourishes that represent a sultan's signature and convey both authority and aesthetic elegance. The emblematic style emphasizes visual symbolism and clarity, while the calligraphic style prioritizes fluidity, personalization, and intricate detailing.
Emblems and Tughras in Islamic Culture
Emblems and tughras both hold significant cultural and religious symbolism in Islamic heritage, with emblems often representing institutions, nations, or families through intricate geometric and calligraphic designs. Tughras, specifically, are highly stylized signatures or monograms of Ottoman sultans, combining elegant Arabic calligraphy with ornate floral and abstract motifs to assert authority and authenticity. These artistic forms showcase the profound importance of calligraphy in Islamic art, where figural representation is limited, making emblems and tughras key elements in visual identity and spiritual expression.
Political Powers and Royal Identity
Emblems and tughras serve as distinct symbols of political power and royal identity, with emblems often representing state authority and institutional legitimacy through codified imagery, while tughras function as intricate calligraphic signatures symbolizing the personal authority and sovereignty of Ottoman sultans. The emblem encapsulates collective governance and national ideology, frequently appearing on official documents, flags, and seals to unify a political entity under a shared identity. Tughras reinforce royal identity by intertwining artistic expression with the sultan's name and titles, asserting dynastic legitimacy and imperial command in a visually elaborate manner.
Usage in Modern Times: Evolution and Influence
Emblems often serve as official symbols for nations, organizations, or brands, commonly used in logos, flags, and official documents to convey identity and authority in modern governance and corporate branding. Tughra, historically an ornate Ottoman sultan's signature, has evolved into a cultural symbol featured in contemporary art, luxury design, and branding, reflecting heritage and artistic influence in Middle Eastern and Islamic contexts. Both forms show significant influence in modern times by merging traditional aesthetics with contemporary visual communication strategies, enhancing cultural identity and brand recognition globally.
Emblems and Tughras in Visual Communication
Emblems function as symbolic representations often combining text and imagery to convey identity, authority, or brand recognition effectively in visual communication. Tughras, traditional Ottoman calligraphic signatures, emphasize intricate, stylized design elements that communicate power and authenticity through artistic form. Both emblems and tughras serve as potent visual devices, leveraging cultural and historical contexts to enhance recognition and convey complex messages succinctly.
Collecting and Preserving Historic Emblems and Tughras
Collecting and preserving historic emblems and tughras involves understanding their cultural and artistic significance, as tughras are intricate calligraphic signatures of Ottoman sultans, while emblems often symbolize broader national or organizational identities. Specialists use advanced archival techniques and climate-controlled environments to maintain the integrity of delicate materials, such as parchment, ink, and textiles used in these artifacts. Digitization projects and detailed provenance research enhance accessibility and historical context, ensuring these symbols endure for scholarly study and cultural appreciation.
Emblem Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com