A performance covenant is a contractual clause that sets specific standards or benchmarks a party must meet to fulfill their obligations. This legally binding provision ensures accountability and protects stakeholders by outlining measurable criteria for success or failure. Explore the article to understand how performance covenants impact your agreements and business relationships.
Table of Comparison
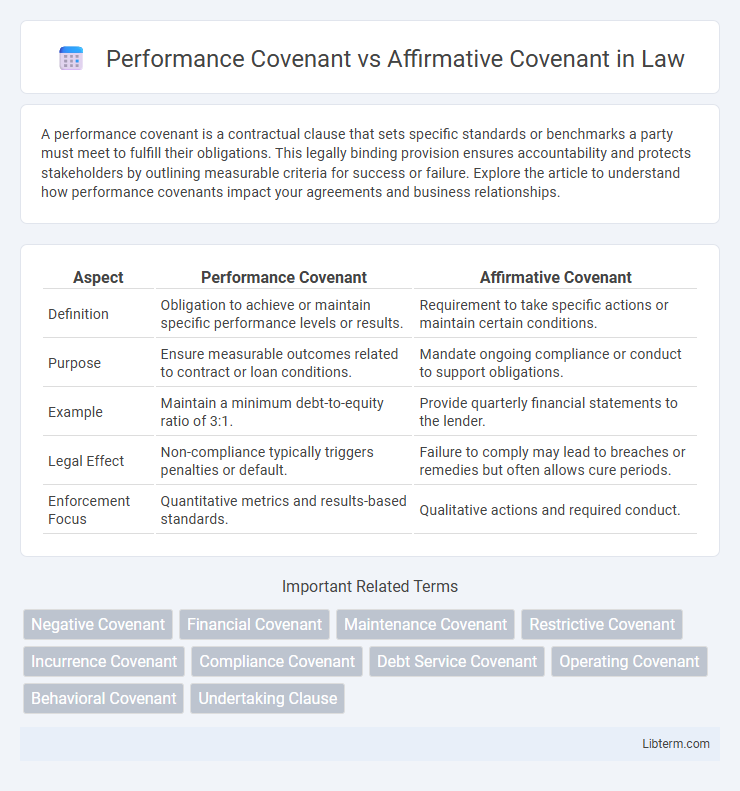
| Aspect | Performance Covenant | Affirmative Covenant |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Obligation to achieve or maintain specific performance levels or results. | Requirement to take specific actions or maintain certain conditions. |
| Purpose | Ensure measurable outcomes related to contract or loan conditions. | Mandate ongoing compliance or conduct to support obligations. |
| Example | Maintain a minimum debt-to-equity ratio of 3:1. | Provide quarterly financial statements to the lender. |
| Legal Effect | Non-compliance typically triggers penalties or default. | Failure to comply may lead to breaches or remedies but often allows cure periods. |
| Enforcement Focus | Quantitative metrics and results-based standards. | Qualitative actions and required conduct. |
Introduction to Performance Covenant and Affirmative Covenant
Performance covenants set specific financial or operational targets that a borrower must meet, ensuring ongoing compliance with key performance metrics. Affirmative covenants require the borrower to take certain actions, such as maintaining insurance or providing regular financial reports, to uphold the loan agreement. Both covenants play crucial roles in risk management and lender protection within financing arrangements.
Defining Performance Covenant
A Performance Covenant is a contractual agreement in which a party commits to achieving specific financial or operational benchmarks, such as maintaining certain revenue levels or profitability ratios, to ensure ongoing compliance. Unlike an Affirmative Covenant, which requires the party to undertake specific actions or maintain certain practices, a Performance Covenant focuses on measurable outcomes and performance standards. These covenants are commonly used in loan agreements to protect lenders by monitoring the borrower's financial health through defined metrics like debt-to-equity ratios or EBITDA thresholds.
Defining Affirmative Covenant
An affirmative covenant is a contractual obligation requiring a party to take specific actions or maintain certain conditions, such as maintaining insurance or timely financial reporting. Performance covenants, by contrast, focus on outcomes or financial ratios the borrower must achieve, like minimum debt service coverage ratios. Defining affirmative covenants highlights proactive duties, ensuring operational compliance and risk management within loan agreements.
Key Differences Between Performance and Affirmative Covenants
Performance covenants specify actions or results that a borrower must achieve or maintain, such as maintaining certain financial ratios or meeting deadlines. Affirmative covenants require the borrower to take specific actions or uphold particular standards, like providing financial statements or maintaining insurance coverage. The key difference lies in performance covenants emphasizing measurable outcomes, while affirmative covenants focus on ongoing obligations or behaviors.
Legal Importance of Each Covenant Type
Performance covenants legally bind parties to achieve specific outcomes, ensuring measurable compliance and providing clear remedies for breaches, which safeguards contract objectives and mitigates risks. Affirmative covenants impose obligations to perform certain actions, maintaining operational standards and preserving contractual relationships crucial for legal enforceability. Both covenant types are essential in contract law, with performance covenants emphasizing results and affirmative covenants focusing on ongoing duties, collectively strengthening the legal framework of agreements.
Common Examples in Contractual Agreements
Performance covenants in contractual agreements commonly include requirements such as achieving specific financial ratios, maintaining minimum cash flow levels, or meeting project milestones within set deadlines. Affirmative covenants typically involve obligations like providing regular financial reports, maintaining insurance coverage, or adhering to environmental regulations. These covenants ensure contractual compliance by defining measurable actions for performance and mandatory duties, respectively.
Impact on Parties’ Obligations
Performance covenants impose specific operational or financial targets that a party must meet, directly affecting ongoing obligations and triggering potential penalties or remedies if unmet. Affirmative covenants require a party to take certain actions, ensuring continuous compliance with contractual duties and maintaining the agreement's integrity. Both types of covenants shape the risk allocation and commitment levels between parties by clearly defining required behaviors and measurable outcomes.
Enforceability and Legal Remedies
Performance covenants require parties to meet specific obligations or achieve certain results, with enforceability often dependent on clear, measurable standards to avoid disputes. Affirmative covenants mandate ongoing actions or behaviors, typically easier to enforce as violations are based on failure to act or comply with agreed terms. Legal remedies for breaches of performance covenants often include damages or specific performance, while affirmative covenant breaches usually result in injunctions or remedial actions to ensure compliance.
Considerations in Drafting Either Covenant
Performance covenants require specific financial or operational targets be met, emphasizing measurable benchmarks like debt-to-equity ratios or EBITDA levels to protect lenders' interests. Affirmative covenants mandate ongoing actions, such as maintaining insurance or providing regular financial reports, ensuring consistent compliance and operational stability. Drafting either covenant demands clear definitions, enforceable metrics, and alignment with the borrower's capabilities and the lender's risk tolerance to balance flexibility with protective oversight.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Covenant for Your Agreement
Performance covenants focus on specific actions or thresholds a borrower must meet, such as maintaining financial ratios, while affirmative covenants require the borrower to take certain positive steps, like providing regular financial reports. Selecting the appropriate covenant depends on the lender's risk tolerance and the nature of the borrower's business, with performance covenants offering stricter control over financial health and affirmative covenants supporting transparency and compliance. A tailored combination of both covenants often provides balanced monitoring and protection in loan agreements.
Performance Covenant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com