Substantive justice focuses on the fairness of the outcomes in legal decisions, ensuring that laws are applied in a manner that respects the rights and needs of individuals. This concept emphasizes equitable treatment and the moral correctness of verdicts beyond procedural accuracy. Explore the rest of the article to understand how substantive justice impacts your legal rights and societal fairness.
Table of Comparison
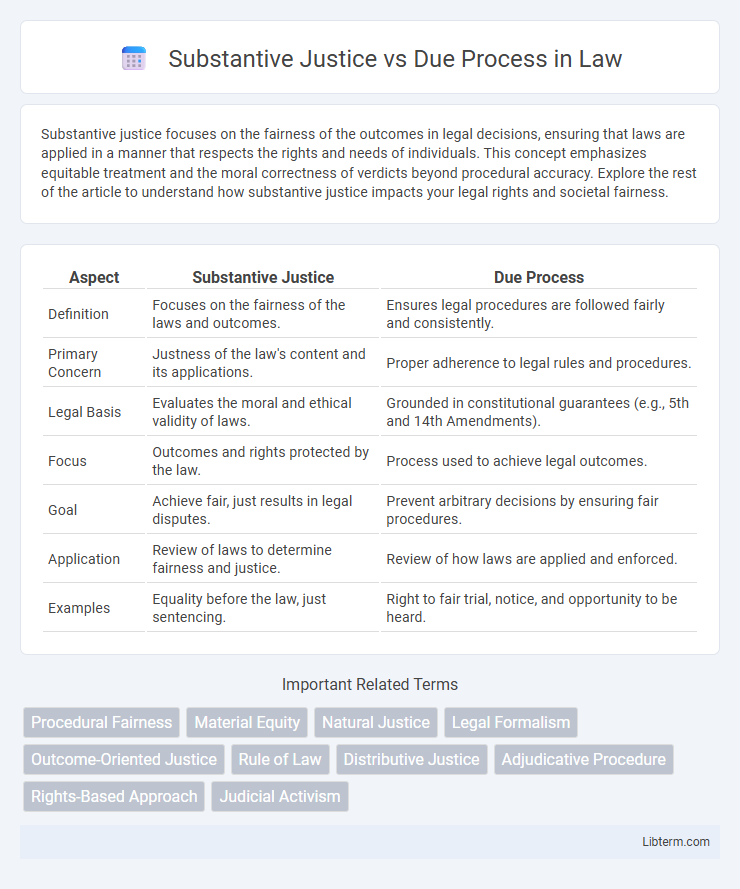
| Aspect | Substantive Justice | Due Process |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on the fairness of the laws and outcomes. | Ensures legal procedures are followed fairly and consistently. |
| Primary Concern | Justness of the law's content and its applications. | Proper adherence to legal rules and procedures. |
| Legal Basis | Evaluates the moral and ethical validity of laws. | Grounded in constitutional guarantees (e.g., 5th and 14th Amendments). |
| Focus | Outcomes and rights protected by the law. | Process used to achieve legal outcomes. |
| Goal | Achieve fair, just results in legal disputes. | Prevent arbitrary decisions by ensuring fair procedures. |
| Application | Review of laws to determine fairness and justice. | Review of how laws are applied and enforced. |
| Examples | Equality before the law, just sentencing. | Right to fair trial, notice, and opportunity to be heard. |
Introduction to Substantive Justice and Due Process
Substantive justice emphasizes the fairness of the actual laws and their outcomes, ensuring that legal rules promote equitable and morally just results. Due process centers on the procedural safeguards and legal steps required to protect individual rights during the enforcement of laws, guaranteeing fair treatment through the judicial system. Together, these concepts form the foundation of a balanced legal framework that upholds both just outcomes and fair procedures.
Defining Substantive Justice
Substantive justice refers to the fundamental fairness in the content and outcomes of legal decisions, emphasizing the protection of individual rights and the achievement of equitable results. It requires that laws and policies themselves be just, ensuring penalties and remedies are appropriate and proportionate to the circumstances. Unlike due process, which focuses on the fairness of the procedures used, substantive justice examines the intrinsic fairness and moral correctness of the law's application.
Understanding Due Process
Due process guarantees fair treatment through established legal procedures, ensuring individuals receive notice and an opportunity to be heard before any deprivation of life, liberty, or property. It serves as a procedural safeguard that upholds the rights enshrined in the Constitution, preventing arbitrary government actions. Understanding due process involves recognizing its role in maintaining legal integrity by requiring transparency, impartiality, and consistency in judicial and administrative processes.
Historical Development of Both Concepts
Substantive justice and due process have distinct historical trajectories rooted in the evolution of legal systems. Substantive justice emphasizes fairness in the content and outcomes of laws, tracing back to ancient legal codes like Hammurabi's Code and Roman law where moral principles guided judgments. Due process originated from English common law, particularly the Magna Carta of 1215, establishing procedural safeguards to protect individuals from arbitrary state actions, eventually influencing constitutional rights in modern democracies.
Key Differences Between Substantive Justice and Due Process
Substantive justice centers on the fairness and correctness of the laws themselves, ensuring that legal outcomes are just based on moral and ethical standards. Due process emphasizes the procedures and methods by which laws are applied, guaranteeing that individuals receive fair treatment through established legal processes. The key difference lies in substantive justice addressing the content of laws while due process focuses on the fairness of legal procedures.
The Role of Substantive Justice in Legal Systems
Substantive justice ensures that legal outcomes are fair and equitable by focusing on the actual rights and wrongs within a case, rather than solely on procedural correctness. It prioritizes the protection of fundamental rights and the moral fairness of laws, playing a crucial role in shaping just laws and remedies. Legal systems that emphasize substantive justice seek to achieve fair results by addressing the underlying truths and ethical principles inherent in disputes.
Due Process Protections in Practice
Due process protections in practice ensure fair treatment through legal procedures that guard against arbitrary deprivation of life, liberty, or property, emphasizing notice and the opportunity to be heard. This procedural safeguard mandates impartial hearings, representation, and the right to appeal, reinforcing the legitimacy of judicial decisions. Courts consistently enforce due process rights to maintain trust in the legal system and prevent abuses of power.
The Interplay Between Substantive Justice and Due Process
The interplay between substantive justice and due process ensures that legal outcomes not only adhere to fair procedural standards but also achieve morally and ethically just results, safeguarding individual rights and promoting equitable treatment. Substantive justice addresses the fairness of the laws themselves and their application, while due process emphasizes the fairness of the legal procedures that enforce those laws. Balancing these elements is crucial for maintaining public trust in the legal system and preventing miscarriages of justice.
Criticisms and Challenges
Substantive justice faces criticism for its subjective interpretation of fairness, which can lead to inconsistent application of laws and potential judicial overreach. Due process is challenged for its procedural rigidity, often causing delays and technical barriers that may obstruct equitable outcomes. Balancing substantive justice with due process remains complex, as excessive focus on one can undermine the other's effectiveness in delivering fair and lawful judgments.
Conclusion: Balancing Justice and Procedure
Substantive justice ensures fairness by emphasizing the just outcome of a case, while due process prioritizes safeguarding legal procedures and individual rights. Achieving an effective legal system requires harmonizing these concepts to uphold both equitable results and procedural integrity. Balancing substantive justice with due process protects against arbitrary rulings and guarantees fairness in judicial decision-making.
Substantive Justice Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com