A petition for habeas corpus challenges unlawful detention by requesting a court order to review the legality of a prisoner's imprisonment. This legal tool safeguards individual freedom by ensuring that no one is held without just cause. Explore the article to understand the process and importance of filing a petition for habeas corpus.
Table of Comparison
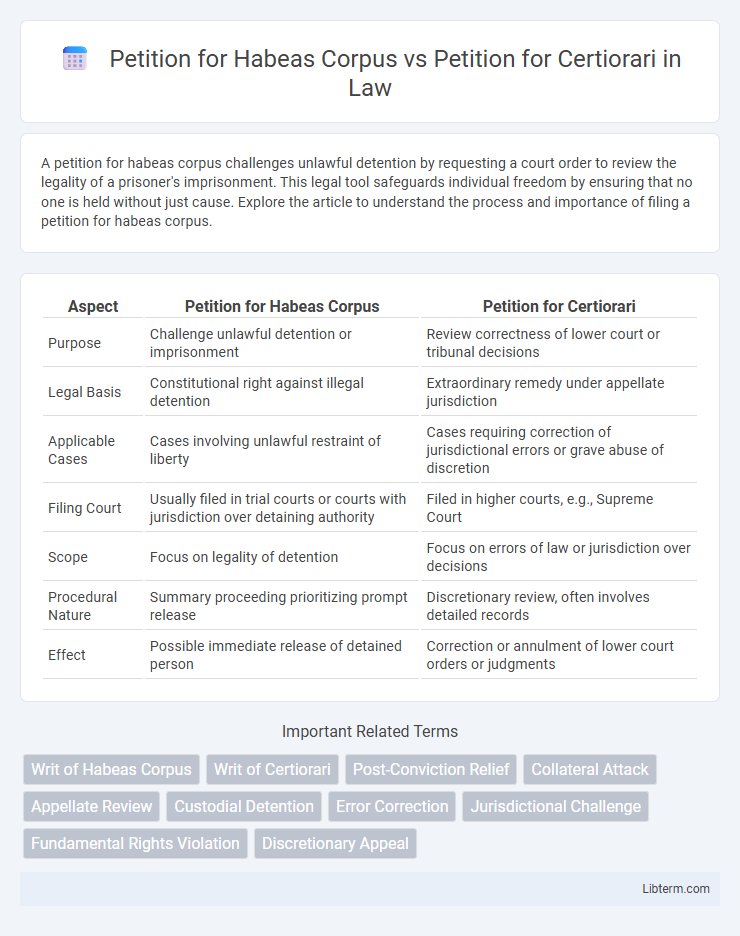
| Aspect | Petition for Habeas Corpus | Petition for Certiorari |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Challenge unlawful detention or imprisonment | Review correctness of lower court or tribunal decisions |
| Legal Basis | Constitutional right against illegal detention | Extraordinary remedy under appellate jurisdiction |
| Applicable Cases | Cases involving unlawful restraint of liberty | Cases requiring correction of jurisdictional errors or grave abuse of discretion |
| Filing Court | Usually filed in trial courts or courts with jurisdiction over detaining authority | Filed in higher courts, e.g., Supreme Court |
| Scope | Focus on legality of detention | Focus on errors of law or jurisdiction over decisions |
| Procedural Nature | Summary proceeding prioritizing prompt release | Discretionary review, often involves detailed records |
| Effect | Possible immediate release of detained person | Correction or annulment of lower court orders or judgments |
Introduction to Habeas Corpus and Certiorari
A Petition for Habeas Corpus challenges unlawful detention or imprisonment, asserting a person's right to liberty under constitutional law. In contrast, a Petition for Certiorari seeks judicial review by a higher court to examine errors in lower court decisions or public authority actions. Habeas Corpus serves as a fundamental safeguard of individual freedom, while Certiorari functions as a discretionary tool for correcting legal errors and ensuring justice.
Legal Basis: Constitutional and Statutory Foundations
Petition for Habeas Corpus is grounded in constitutional law, primarily under Article 8, Section 1 of the 1987 Philippine Constitution, which safeguards individual liberty against unlawful detention. Petition for Certiorari is based on statutory provisions, notably Rule 65 of the Rules of Court, allowing courts to review acts of government officials or entities that exceed jurisdiction or unlawfully exercise discretion. Both remedies serve as checks on government power, but Habeas Corpus is a direct protection of personal liberty, while Certiorari addresses legal errors or abuses in administrative or judicial decisions.
Definition and Purpose of Habeas Corpus
A Petition for Habeas Corpus is a legal request challenging unlawful detention or imprisonment, aiming to protect individual freedom by requiring the custodian to justify the legality of the detention. It serves as a fundamental safeguard against arbitrary deprivation of liberty under constitutional and statutory rights. In contrast, a Petition for Certiorari primarily seeks appellate review of lower court decisions to correct errors of law or jurisdiction.
Definition and Purpose of Certiorari
Petition for Habeas Corpus is a legal request challenging unlawful detention or imprisonment, seeking immediate release of the detainee. Petition for Certiorari, on the other hand, is a supervisory writ filed before a higher court to review and correct errors of jurisdiction or grave abuse of discretion by a lower court or tribunal. The primary purpose of Certiorari is to ensure that the lower court or tribunal acted within its authority and followed due process, thereby safeguarding the integrity of judicial proceedings.
Key Differences Between Habeas Corpus and Certiorari
Petition for Habeas Corpus challenges unlawful detention or imprisonment, seeking immediate release by arguing constitutional or legal violations, while Petition for Certiorari requests a higher court to review and correct lower court rulings on legal errors. Habeas Corpus primarily safeguards individual liberty under the Constitution, often in criminal cases, whereas Certiorari serves as a discretionary appellate mechanism to ensure consistent judicial interpretation. The procedural grounds differ: Habeas Corpus addresses custody legality, while Certiorari addresses legal questions or jurisdictional issues raised in judicial proceedings.
Grounds for Filing Each Petition
A Petition for Habeas Corpus is filed primarily to challenge unlawful detention or imprisonment, focusing on violations of constitutional rights such as due process or illegal confinement. In contrast, a Petition for Certiorari is filed to review decisions of lower courts on questions of law, seeking correction of grave abuse of discretion or errors affecting jurisdiction. Habeas Corpus centers on personal liberty issues, whereas Certiorari addresses judicial errors in legal rulings.
Jurisdiction: Which Courts Handle Each Petition
Petitions for Habeas Corpus are typically handled by federal district courts or state trial courts, depending on where the custody is challenged, as these courts have original jurisdiction to examine unlawful detention. Petitions for Certiorari are reviewed exclusively by the U.S. Supreme Court, which exercises discretionary appellate jurisdiction to decide whether to hear cases from lower federal courts or state supreme courts. Habeas Corpus focuses on constitutional claims related to unlawful imprisonment, while Certiorari serves as a gatekeeper mechanism for Supreme Court review of significant legal questions or conflicts among lower courts.
Procedural Requirements and Filing Process
Petitions for Habeas Corpus require the petitioner to demonstrate unlawful detention and must be filed in the court with jurisdiction over the custodian, adhering to strict timelines and including a verified complaint or affidavit. In contrast, Petitions for Certiorari challenge the decisions of lower courts or quasi-judicial bodies, necessitating that the petitioner first exhaust all available remedies, file within 60 days from notice of the questioned order, and raise questions of grave abuse of discretion. Both petitions demand precise compliance with procedural rules, verified pleadings, and proper service to ensure judicial review.
Common Scenarios and Case Examples
Petition for Habeas Corpus is commonly filed to challenge unlawful detention or imprisonment, such as in wrongful arrest or denial of bail cases, exemplified by prisoners contesting illegal incarceration without due process. Petition for Certiorari typically arises when a higher court reviews a lower court's decision to correct errors of jurisdiction or legal interpretation, often seen in appeals against dismissal of cases or decisions exceeding authority. Habeas corpus addresses personal liberty issues, whereas certiorari focuses on legal oversight and justice administration in judicial proceedings.
Conclusion: Choosing the Appropriate Remedy
Petition for Habeas Corpus serves as the primary remedy to challenge unlawful detention or imprisonment, focusing on the violation of personal liberty under constitutional or statutory grounds. Petition for Certiorari targets errors of jurisdiction or grave abuse of discretion by lower courts or arbiters, providing a mechanism for judicial review of administrative or quasi-judicial decisions. Selecting the appropriate remedy depends on whether the issue concerns personal liberty restriction, which warrants habeas corpus, or errors in legal procedures or jurisdiction, which calls for certiorari.
Petition for Habeas Corpus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com