A bail hearing determines whether a defendant can be released from custody before trial, based on factors like flight risk and community safety. Judges consider evidence and arguments to set bail conditions that protect your rights while ensuring public security. Explore the full article to understand what to expect and how to prepare effectively for a bail hearing.
Table of Comparison
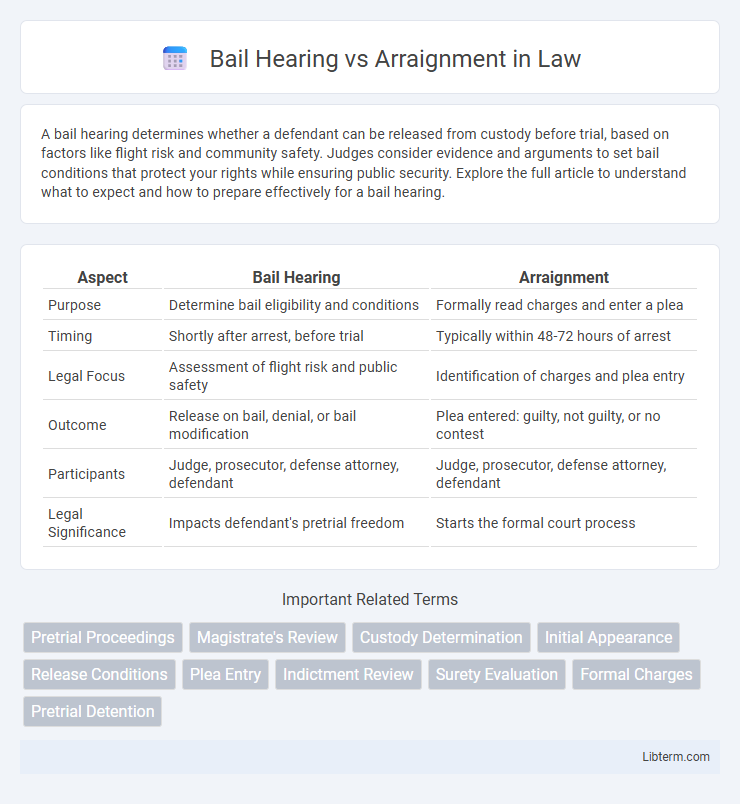
| Aspect | Bail Hearing | Arraignment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Determine bail eligibility and conditions | Formally read charges and enter a plea |
| Timing | Shortly after arrest, before trial | Typically within 48-72 hours of arrest |
| Legal Focus | Assessment of flight risk and public safety | Identification of charges and plea entry |
| Outcome | Release on bail, denial, or bail modification | Plea entered: guilty, not guilty, or no contest |
| Participants | Judge, prosecutor, defense attorney, defendant | Judge, prosecutor, defense attorney, defendant |
| Legal Significance | Impacts defendant's pretrial freedom | Starts the formal court process |
Understanding Bail Hearings: Definition and Purpose
Bail hearings determine if a defendant is eligible for release before trial and set the bail amount based on factors like flight risk and public safety. The purpose of a bail hearing is to balance the presumption of innocence with ensuring the defendant's appearance at future court dates. This process is distinct from arraignment, where formal charges are read and the defendant enters a plea.
What is an Arraignment? Key Elements Explained
An arraignment is a court proceeding where the accused is formally presented with criminal charges and asked to enter a plea, such as guilty, not guilty, or no contest. Key elements include reading of charges, informing the defendant of their rights, and setting bail or release conditions. This step ensures the defendant understands the accusations and initiates the pre-trial process.
Differences Between Bail Hearings and Arraignments
Bail hearings determine whether a defendant is released before trial and under what conditions, focusing on flight risk and public safety, whereas arraignments involve formally reading charges and entering pleas. Bail hearings occur immediately after arrest to address pretrial release, while arraignments take place once charges are officially filed. The outcomes of bail hearings influence detention status, whereas arraignments establish the defendant's initial plea and schedule subsequent court dates.
Legal Procedures: Bail Hearing vs. Arraignment
A bail hearing determines whether a defendant can be released from custody before trial and sets the bail amount based on factors like flight risk and public safety. An arraignment formally reads the charges to the defendant, informs them of their rights, and allows them to enter a plea. Both legal procedures serve distinct roles: the bail hearing addresses pretrial release, while the arraignment initiates the formal court process.
Rights of the Accused During Bail Hearings
During bail hearings, the accused holds crucial rights designed to protect their liberty and ensure a fair legal process, such as the right to be informed of the charges, the right to legal representation, and the opportunity to present evidence or argue against excessive bail. Courts consider factors like flight risk, public safety, and the nature of the offense when determining bail amounts or conditions, ensuring the accused is not subjected to arbitrary detention. Unlike arraignments, which focus on formally reading charges and entering pleas, bail hearings specifically address pretrial release conditions, safeguarding due process rights before trial proceedings commence.
Defendant’s Rights at Arraignment
During an arraignment, the defendant's rights include the right to be informed of the charges, to enter a plea, and to have legal counsel present. The arraignment sets the foundation for the defendant's case by ensuring that they understand the accusations and the subsequent legal process. Unlike a bail hearing, which primarily determines pretrial release conditions, the arraignment emphasizes the defendant's procedural protections and the initiation of formal court proceedings.
Outcomes of Bail Hearings
Bail hearings determine whether a defendant is released pretrial, influencing their freedom and ability to prepare a defense outside jail. Outcomes often include setting bail amount, imposing release conditions, or detention without bail, impacting case strategy and court appearance compliance. Courts weigh factors like flight risk, criminal history, and public safety to decide appropriate bail outcomes.
Typical Outcomes of Arraignments
Arraignments typically result in the formal reading of charges, the entry of a plea--usually guilty, not guilty, or no contest--and the setting of future court dates, including trial or pretrial motions. Unlike bail hearings that primarily determine pretrial release conditions, arraignments establish the defendant's legal stance and initiate the trial process. Court decisions during arraignments influence case timelines and defense strategies by defining the legal framework moving forward.
Role of Legal Representation in Both Proceedings
Legal representation plays a crucial role in both bail hearings and arraignments by ensuring the defendant's rights are protected throughout the judicial process. During a bail hearing, attorneys present arguments for reasonable bail or release conditions based on the defendant's flight risk and community ties, influencing the court's decision on pretrial detention. At the arraignment, counsel advises on the charges, enters pleas, and begins building the defense strategy, directly impacting the defendant's legal posture and case trajectory.
Frequently Asked Questions: Bail Hearings vs. Arraignments
Bail hearings determine whether a defendant can be released from custody before trial and set bail amounts, while arraignments involve formally reading charges and entering a plea. Frequently asked questions highlight the timing differences, as bail hearings occur soon after arrest, typically within 48 hours, whereas arraignments follow shortly after bail decisions. Clarifying the distinct roles of each ensures defendants understand their legal rights and next steps in the criminal justice process.
Bail Hearing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com