An indictment is a formal charge or accusation of a serious crime issued by a grand jury based on evidence presented by a prosecutor. It initiates the criminal prosecution process, ensuring the accused is informed of the charges against them. Discover how an indictment impacts your legal rights and the steps that follow.
Table of Comparison
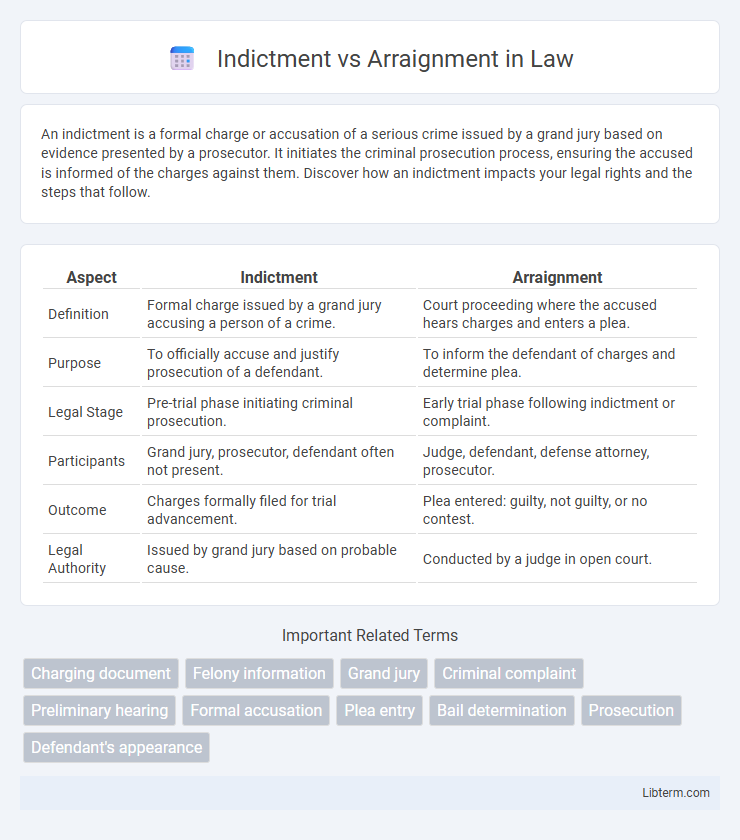
| Aspect | Indictment | Arraignment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal charge issued by a grand jury accusing a person of a crime. | Court proceeding where the accused hears charges and enters a plea. |
| Purpose | To officially accuse and justify prosecution of a defendant. | To inform the defendant of charges and determine plea. |
| Legal Stage | Pre-trial phase initiating criminal prosecution. | Early trial phase following indictment or complaint. |
| Participants | Grand jury, prosecutor, defendant often not present. | Judge, defendant, defense attorney, prosecutor. |
| Outcome | Charges formally filed for trial advancement. | Plea entered: guilty, not guilty, or no contest. |
| Legal Authority | Issued by grand jury based on probable cause. | Conducted by a judge in open court. |
Understanding Indictment: Legal Definition
An indictment is a formal legal accusation issued by a grand jury indicating there is sufficient evidence to charge an individual with a serious crime, typically a felony. It serves as a crucial step in the criminal justice process, ensuring the defendant is officially informed of the charges before trial. The indictment establishes probable cause and initiates the transition from investigation to prosecution.
What Is an Arraignment?
An arraignment is a formal court proceeding where a defendant is officially charged with a crime and asked to enter a plea, such as guilty, not guilty, or no contest. This process ensures the defendant is informed of the charges and their legal rights, including the right to counsel. Unlike an indictment, which is a formal accusation issued by a grand jury, an arraignment initiates the defendant's court involvement and sets the stage for subsequent trial proceedings.
Key Differences Between Indictment and Arraignment
An indictment is a formal charge issued by a grand jury accusing a suspect of a crime, serving as the foundation for criminal prosecution. An arraignment is a court proceeding where the accused is formally read the charges, enters a plea, and bail is considered. The key differences lie in their purpose and timing: indictments establish probable cause for prosecution, while arraignments address the defendant's response to the charges and set the stage for trial.
The Indictment Process Explained
The indictment process involves a grand jury reviewing evidence presented by the prosecutor to determine whether probable cause exists to formally charge a defendant with a crime. This process ensures that charges are supported by sufficient evidence before proceeding to trial, protecting individuals from unwarranted prosecution. Once an indictment is issued, the defendant is formally notified of the charges during the arraignment, marking the transition from investigation to the judicial phase.
Steps Involved in an Arraignment
An arraignment involves several key steps starting with the reading of the formal charges against the defendant in court. The defendant then enters a plea, such as guilty, not guilty, or no contest. The judge may also address issues like bail, legal representation, and set future court dates during the arraignment process.
Who Issues an Indictment?
An indictment is issued by a grand jury after reviewing evidence presented by a prosecutor, determining whether there is probable cause to charge a suspect with a felony. The grand jury's role is to protect individuals from unwarranted prosecution by requiring sufficient evidence before formal charges are brought. In contrast, an arraignment is a court proceeding where the accused is formally charged and enters a plea, conducted by a judge rather than a jury.
Defendant’s Rights During Arraignment
During arraignment, defendants have the critical right to be informed of the charges brought against them, ensuring transparency in the judicial process. They also possess the right to legal counsel, either retained or appointed, to navigate the complexities of criminal law effectively. Furthermore, defendants can enter a plea--guilty, not guilty, or no contest--setting the stage for subsequent legal proceedings and safeguarding their procedural rights.
Indictment and Arraignment in Federal vs. State Courts
Indictments in federal courts are typically issued by a grand jury after reviewing evidence presented by prosecutors, serving as a formal charge that initiates a criminal case, whereas state courts may use either a grand jury indictment or a prosecutor's information depending on jurisdiction. Arraignment occurs shortly after an indictment or information filing, where the defendant is formally read the charges and enters a plea; federal arraignments often follow strict procedural timelines under the Federal Rules of Criminal Procedure, while state court arraignment procedures vary widely by state law. Understanding the differences in indictment and arraignment processes between federal and state courts is critical for navigating the criminal justice system, as procedural protections and timelines directly impact case progression.
Common Misconceptions About Indictment and Arraignment
Indictment and arraignment are often confused as the same legal process, but an indictment is a formal charge issued by a grand jury, while arraignment is a court proceeding where the defendant hears the charges and enters a plea. A common misconception is that an indictment always leads directly to a trial, whereas arraignment is actually the initial step where the court ensures the defendant understands the charges and requests a plea. Many people mistakenly believe arraignment confirms guilt, but it solely serves to inform the accused of the charges and establish legal representation.
Importance of Legal Representation During Indictment and Arraignment
Legal representation during indictment and arraignment is crucial for protecting defendants' rights and ensuring the proper handling of charges. Experienced attorneys help navigate complex legal procedures, challenge unlawful evidence, and negotiate bail or plea terms effectively. Early legal counsel can significantly impact case outcomes by preventing self-incrimination and preserving defense strategies from the outset.
Indictment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com