Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) allows a judge to overrule a jury's decision when the evidence overwhelmingly contradicts the verdict. This legal motion ensures that miscarriages of justice are corrected even after a jury's findings. Explore the details of JNOV to understand how it might impact your case outcomes.
Table of Comparison
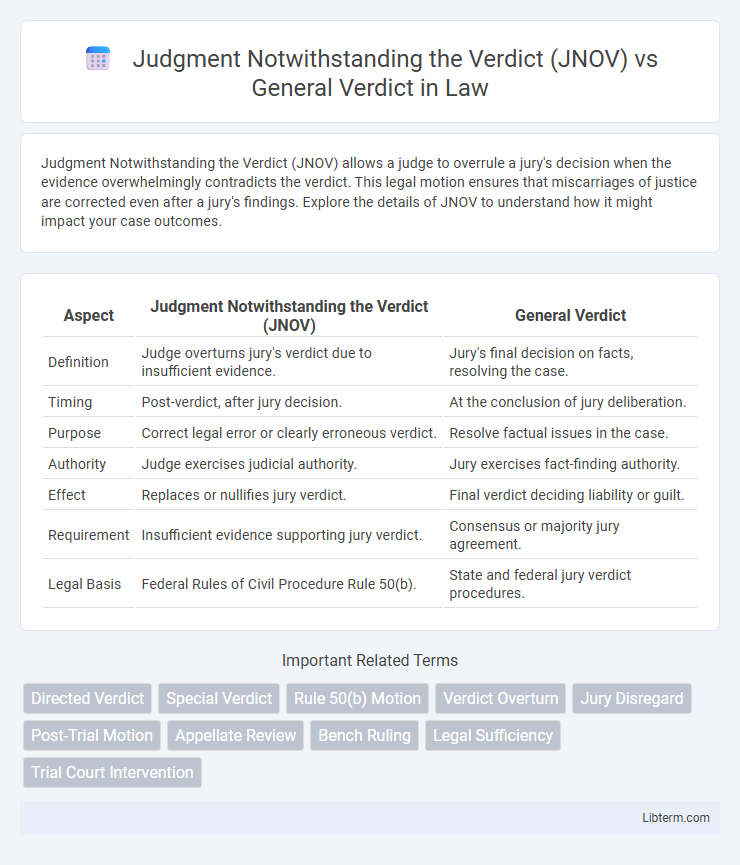
| Aspect | Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) | General Verdict |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judge overturns jury's verdict due to insufficient evidence. | Jury's final decision on facts, resolving the case. |
| Timing | Post-verdict, after jury decision. | At the conclusion of jury deliberation. |
| Purpose | Correct legal error or clearly erroneous verdict. | Resolve factual issues in the case. |
| Authority | Judge exercises judicial authority. | Jury exercises fact-finding authority. |
| Effect | Replaces or nullifies jury verdict. | Final verdict deciding liability or guilt. |
| Requirement | Insufficient evidence supporting jury verdict. | Consensus or majority jury agreement. |
| Legal Basis | Federal Rules of Civil Procedure Rule 50(b). | State and federal jury verdict procedures. |
Introduction to JNOV and General Verdict
Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) is a post-trial motion allowing a judge to overturn the jury's general verdict if the jury's findings lack sufficient legal basis or evidence. A General Verdict represents the jury's final decision on all issues in a case, indicating which party prevails, without specifying factual determinations for each issue. JNOV serves as a critical check on general verdicts by ensuring judicial oversight to prevent legally unsupported outcomes.
Legal Definitions: JNOV vs General Verdict
Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) is a legal motion requesting the court to overturn the jury's verdict on the grounds that the evidence does not reasonably support it, effectively substituting the court's judgment for that of the jury. A General Verdict, on the other hand, is the jury's overall decision in a case, determining the outcome based on the facts and law presented without specifying detailed findings. The key distinction lies in JNOV being a post-trial motion challenging the sufficiency of evidence, whereas a General Verdict represents the jury's final and unqualified determination of liability or guilt.
Historical Background and Evolution
Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) emerged in common law as a judicial mechanism allowing courts to override jury verdicts deemed unreasonable based on the evidence, solidifying its role by the mid-20th century. The historical evolution of JNOV reflects a balance between respecting jury decisions and ensuring legal correctness, with significant developments influenced by landmark rulings such as Baltimore & Carolina Line, Inc. v. Redman. In contrast, the General Verdict has deep roots dating back to early English legal traditions, serving as the standard jury decision format before innovations like JNOV introduced judicial checks on verdicts.
Procedural Differences Between JNOV and General Verdict
Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) allows a court to overturn a jury's general verdict when the evidence insufficiently supports the decision, typically after a motion for directed verdict has been denied. The procedural process for JNOV requires a timely post-verdict motion within a specified period, often governed by rules like Federal Rule of Civil Procedure 50(b), whereas a general verdict is the initial decision rendered by the jury without detailed findings on specific issues. Unlike a general verdict, which concludes the fact-finding phase, the JNOV procedure involves judicial review to ensure legal sufficiency before final judgment is entered.
Grounds for Seeking JNOV
Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) is sought when a party believes the jury's general verdict lacks sufficient legal basis or is unsupported by the evidence presented during the trial. Grounds for seeking JNOV include errors in applying the law, absence of legally sufficient evidence to support the jury's findings, or when the verdict is contrary to the manifest weight of the evidence. Unlike a general verdict, which reflects the jury's final decision on the facts, JNOV challenges the legal validity of that decision, requesting the court to override the jury's verdict.
Role of the Judge Versus Jury
Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) occurs when a judge overturns the jury's general verdict due to insufficient legal basis or lack of evidence supporting the jury's decision. The jury's role is to assess facts and render a general verdict based on evidence, while the judge ensures legal standards are applied correctly and may intervene through JNOV to prevent unjust outcomes. This distinction emphasizes the judge's authority to review the jury's findings and enforce legal correctness in the final judgment.
Impact on Appeals and Future Litigation
Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) allows the trial court to overturn a jury's general verdict if the evidence does not legally support it, significantly affecting appeals by narrowing grounds for appellate review to questions of law rather than factual disputes. This procedural tool can streamline future litigation by eliminating the need for new trials when verdicts lack legal sufficiency, thereby promoting judicial efficiency and finality. In contrast, general verdicts upheld on appeal often prolong litigation through potential retrials, as appellate courts typically defer to jury findings on factual issues unless clearly erroneous.
Notable Case Law Illustrating Both Concepts
In *Baltimore & Ohio Railroad Co. v. National Traffic Service, Inc.*, 409 F.2d 990 (D.C. Cir. 1969), the court clarified the scope of Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) by emphasizing that it applies only when no reasonable jury could have reached the given verdict. The case of *Beck v. City of Upland*, 527 F.3d 853 (9th Cir. 2008), exemplifies the general verdict, where the jury's decision was based on an overall assessment of liability without special interrogatories. These landmark rulings underscore how JNOV can overturn a general verdict when the evidence legally fails to support it.
Advantages and Disadvantages for Litigants
Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) allows litigants to challenge a jury's decision when the evidence legally cannot support the verdict, providing a crucial safeguard against erroneous outcomes but potentially prolonging litigation and increasing costs. A General Verdict offers finality and efficiency by reflecting the jury's collective judgment; however, it may disadvantage a party if the verdict is based on unclear or insufficient evidence. Litigants must weigh JNOV's protective benefits against the risk of extended legal battles, while accepting the General Verdict's swiftness but potential for injustice.
Conclusion: Choosing Between JNOV and General Verdict
Selecting between Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) and a General Verdict hinges on the sufficiency of evidentiary support and legal standards. JNOV serves as a judicial remedy when the jury's findings lack reasonable support, allowing the judge to override the verdict to correct errors of law or fact. A General Verdict reflects the jury's comprehensive decision on all issues, best suited when evidence is legally adequate and findings are clear.
Judgment Notwithstanding the Verdict (JNOV) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com