A sliding scale fee adjusts the cost of services based on your income or financial situation, making essential services more accessible and affordable. This flexible pricing model is commonly used in healthcare, counseling, and legal assistance to ensure equitable access. Explore the rest of the article to understand how sliding scale fees can benefit you and learn where to find them.
Table of Comparison
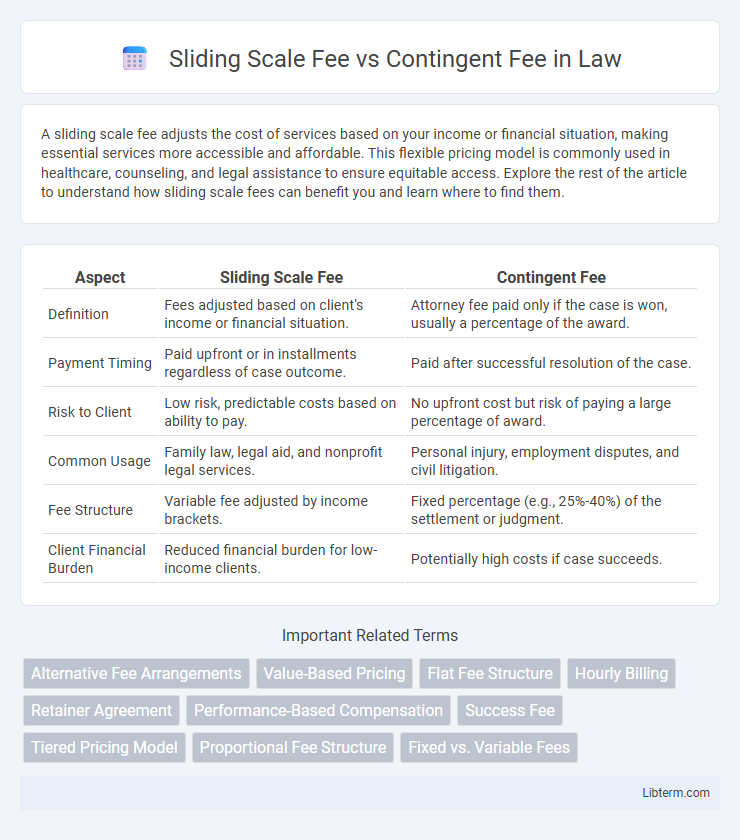
| Aspect | Sliding Scale Fee | Contingent Fee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fees adjusted based on client's income or financial situation. | Attorney fee paid only if the case is won, usually a percentage of the award. |
| Payment Timing | Paid upfront or in installments regardless of case outcome. | Paid after successful resolution of the case. |
| Risk to Client | Low risk, predictable costs based on ability to pay. | No upfront cost but risk of paying a large percentage of award. |
| Common Usage | Family law, legal aid, and nonprofit legal services. | Personal injury, employment disputes, and civil litigation. |
| Fee Structure | Variable fee adjusted by income brackets. | Fixed percentage (e.g., 25%-40%) of the settlement or judgment. |
| Client Financial Burden | Reduced financial burden for low-income clients. | Potentially high costs if case succeeds. |
Introduction to Legal Fee Structures
Sliding scale fees adjust legal costs based on a client's income or financial situation, ensuring access to legal services for those with limited resources. Contingent fees require payment only if the lawyer successfully recovers money for the client, typically as a percentage of the settlement or judgment. Both fee structures aim to accommodate different client needs while providing flexibility in legal billing.
What Is a Sliding Scale Fee?
A sliding scale fee is a payment model where the cost of services varies based on an individual's income or financial situation, making essential services more accessible to low-income clients. This fee structure is commonly used in healthcare, legal aid, and counseling to ensure affordability while still covering basic provider costs. Unlike contingent fees that depend on case outcomes, sliding scale fees are predetermined and adjusted according to a client's ability to pay.
What Is a Contingent Fee?
A contingent fee is a payment arrangement where a lawyer receives a percentage of the client's financial recovery only if the case is won, commonly used in personal injury and civil litigation cases. Unlike sliding scale fees that adjust based on the client's income, contingent fees align the attorney's compensation with the success of the claim. This structure incentivizes lawyers to maximize the client's award, making legal representation accessible without upfront fees.
Key Differences Between Sliding Scale and Contingent Fees
Sliding scale fees adjust legal service costs based on a client's income or financial situation, ensuring affordability and access to justice for low-income individuals. Contingent fees involve payment only if the lawyer wins the case, typically as a percentage of the settlement or judgment, aligning the lawyer's incentives with the client's success. The key difference lies in payment structure: sliding scale fees depend on ability to pay upfront, while contingent fees depend on case outcome and are risk-based for the attorney.
Advantages of Sliding Scale Fee Arrangements
Sliding scale fee arrangements offer increased accessibility by adjusting costs based on clients' income, making legal and healthcare services more affordable for low-income individuals. This model fosters client trust and long-term relationships by demonstrating flexibility and empathy, which can lead to higher retention and positive referrals. Sliding scale fees also promote social equity by reducing financial barriers and enabling service providers to support diverse populations effectively.
Benefits of Contingent Fee Agreements
Contingent fee agreements offer significant benefits by allowing clients to pursue legal claims without upfront costs, reducing financial barriers to justice. Lawyers are motivated to achieve favorable outcomes since their payment depends on winning the case, aligning their interests with clients' success. This arrangement also provides clients with financial predictability, as legal fees are proportional to the settlement or award received.
Potential Drawbacks of Each Fee Model
Sliding scale fees may limit provider income and reduce access to high-quality services due to lower payment rates, potentially causing financial strain for professionals. Contingent fees create uncertainty in payment timing and amounts, often delaying compensation until case resolution and risking total non-payment if the case is lost. Both models can lead to conflicts over fee fairness and may influence service delivery priorities, impacting client outcomes and provider satisfaction.
Selecting the Right Fee Structure for Your Case
Selecting the right fee structure for your case depends on factors such as your financial situation and the likelihood of winning. Sliding scale fees adjust based on your ability to pay, offering flexibility for clients with limited income. Contingent fees require no upfront payment but involve paying a percentage of any settlement or judgment, making them ideal for cases with strong chances of success.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Sliding scale fees in legal services adjust charges based on a client's income, promoting access to justice while maintaining ethical standards of fairness and non-discrimination. Contingent fees, where lawyers receive a percentage of the settlement or judgment, align financial incentives with case outcomes but require careful adherence to ethical rules to avoid conflicts of interest and ensure transparency. Both fee arrangements demand compliance with state bar regulations to uphold professional responsibility and protect client interests.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Sliding Scale and Contingent Fees
Selecting between sliding scale fees and contingent fees depends largely on the client's financial situation and the type of legal service required. Sliding scale fees offer flexibility by adjusting costs based on income, making legal services more accessible to low-income clients. Contingent fees align attorney payment with case success, often preferred in personal injury or litigation cases where clients may have limited upfront resources but potential for significant compensation.
Sliding Scale Fee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com