Discovery unlocks new possibilities and drives innovation across various fields by revealing hidden insights and untapped potential. Understanding its impact can transform your approach to problem-solving and creativity. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge of discovery's significance and practical applications.
Table of Comparison
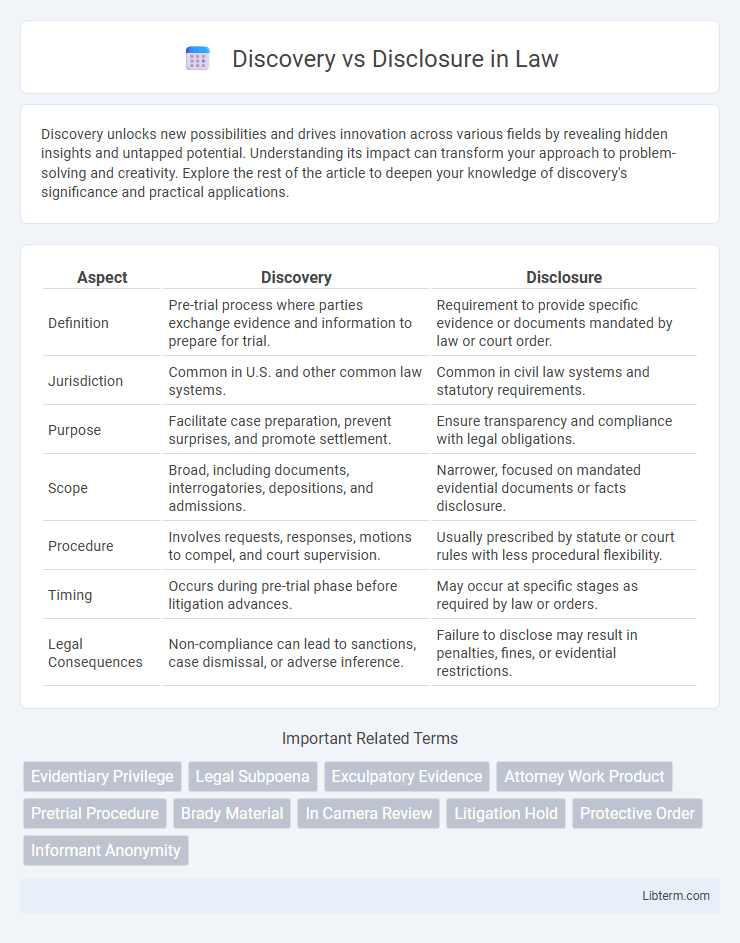
| Aspect | Discovery | Disclosure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-trial process where parties exchange evidence and information to prepare for trial. | Requirement to provide specific evidence or documents mandated by law or court order. |
| Jurisdiction | Common in U.S. and other common law systems. | Common in civil law systems and statutory requirements. |
| Purpose | Facilitate case preparation, prevent surprises, and promote settlement. | Ensure transparency and compliance with legal obligations. |
| Scope | Broad, including documents, interrogatories, depositions, and admissions. | Narrower, focused on mandated evidential documents or facts disclosure. |
| Procedure | Involves requests, responses, motions to compel, and court supervision. | Usually prescribed by statute or court rules with less procedural flexibility. |
| Timing | Occurs during pre-trial phase before litigation advances. | May occur at specific stages as required by law or orders. |
| Legal Consequences | Non-compliance can lead to sanctions, case dismissal, or adverse inference. | Failure to disclose may result in penalties, fines, or evidential restrictions. |
Understanding Discovery and Disclosure
Understanding discovery involves the systematic process of gathering evidence and information relevant to a legal case, enabling parties to prepare their arguments effectively. Disclosure refers to the formal obligation to reveal pertinent documents and facts to the opposing party, ensuring transparency and fairness in legal proceedings. Mastery of both discovery and disclosure enhances case strategy by promoting comprehensive evidence exchange and legal compliance.
Key Differences Between Discovery and Disclosure
Discovery involves the pre-trial process where parties exchange information through methods such as interrogatories, depositions, and requests for production, enabling thorough evidence gathering. Disclosure specifically refers to the mandatory revelation of certain documents and information as required by law or court rules, often without the need for formal requests. Key differences include discovery's broader scope and interactive nature versus disclosure's obligatory and limited nature focused on predefined categories of evidence.
Legal Contexts: Discovery vs Disclosure
In legal contexts, discovery refers to the pre-trial process where parties exchange relevant information and evidence to prepare for litigation, governed by procedural rules such as the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure. Disclosure, on the other hand, mandates the formal presentation of certain documents or evidence to the opposing party or court, often required by statutory or regulatory frameworks. Effective management of discovery and disclosure procedures ensures compliance, prevents surprises at trial, and protects parties' rights to a fair legal process.
Historical Evolution of Discovery and Disclosure
The historical evolution of discovery and disclosure reflects shifting legal priorities from rigid, party-controlled evidence gathering to broader transparency and fairness in litigation. Discovery emerged in the 19th century as a procedural reform to prevent trial by ambush, allowing parties to obtain evidence before trial through interrogatories, depositions, and document requests. Disclosure evolved from this foundation, emphasizing mandatory revelation of certain information to promote judicial efficiency and reduce unnecessary disputes.
Importance in Litigation Processes
Discovery is a crucial phase in litigation, enabling parties to obtain relevant evidence, which ensures informed decision-making and fair trial outcomes. Disclosure mandates the timely sharing of pertinent documents and information, preventing surprises and promoting transparency between litigants. Effective management of both discovery and disclosure processes significantly reduces the risk of delays, sanctions, and unfair advantages in court proceedings.
Procedural Steps in Discovery
Procedural steps in discovery include the initial submission of written interrogatories and requests for production of documents, allowing parties to obtain relevant evidence before trial. Depositions serve as a vital part of discovery, where witnesses provide sworn testimony under oath, enabling attorneys to assess credibility and gather detailed information. This process contrasts with disclosure, which typically involves mandatory, automatic exchange of predefined information without formal requests, streamlining early case evaluation.
Procedural Steps in Disclosure
Disclosure procedures in legal cases typically involve a series of specific steps designed to ensure all relevant evidence is shared between parties. Initially, parties must prepare and exchange lists of documents, followed by requesting and providing copies of these materials according to agreed deadlines. Compliance with court rules mandates timely and thorough documentation, emphasizing accuracy and completeness to facilitate fair trial preparation and avoid sanctions.
Challenges and Controversies
Discovery processes often face challenges related to the scope and relevance of information, leading to disputes over what must be disclosed in legal and corporate settings. Controversies arise when parties withhold or manipulate evidence, complicating transparency and fairness. Ethical concerns and regulatory compliance add layers of complexity, demanding rigorous scrutiny to balance confidentiality with the necessity of disclosure.
Best Practices for Managing Information
Effective management of information requires distinguishing between discovery, the process of uncovering relevant data, and disclosure, the formal release of that information. Implementing secure protocols, thorough documentation, and clear legal guidelines minimizes risks of data breaches and ensures compliance with regulatory standards. Regular training on information governance and utilizing advanced data classification tools optimize control over sensitive content during both discovery and disclosure phases.
Future Trends in Discovery and Disclosure
Future trends in discovery and disclosure emphasize advanced AI-driven data analytics and automated document review, significantly accelerating the identification of relevant information in litigation. Blockchain technology is increasingly integrated to ensure secure, transparent records, enhancing the reliability of disclosed evidence. Regulatory frameworks are evolving to address privacy concerns and cross-border data sharing, shaping more efficient and compliant discovery processes.
Discovery Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com