Negotiated clauses allow parties to tailor contract terms to better suit their specific needs and objectives, ensuring mutual agreement and clarity. Carefully crafted clauses reduce the risk of disputes and strengthen the enforceability of the contract under applicable laws. Explore the rest of this article to understand how you can effectively negotiate clauses that protect your interests.
Table of Comparison
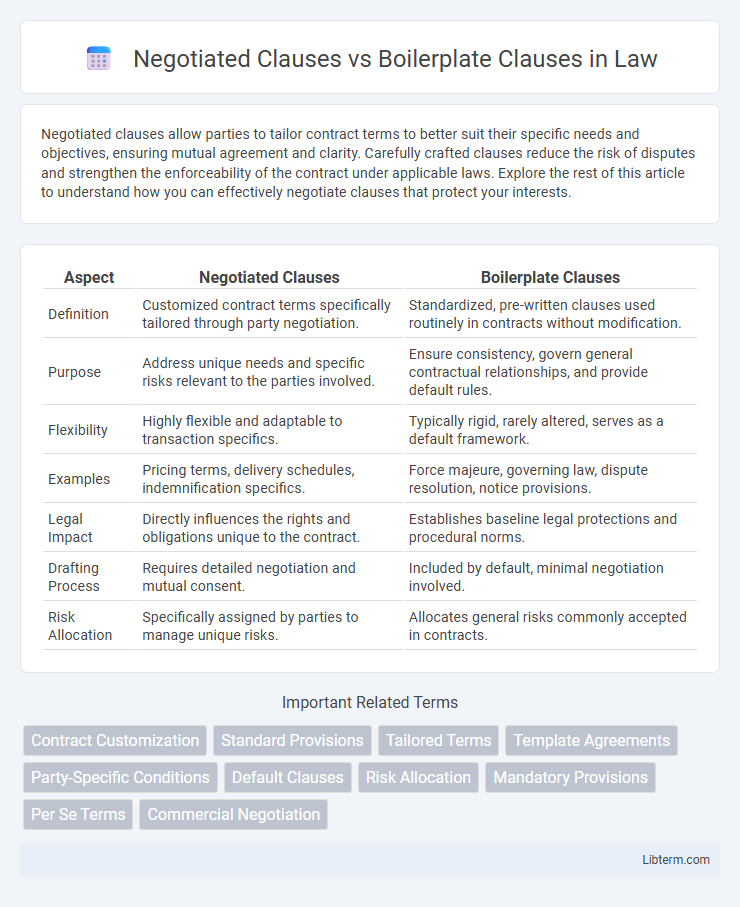
| Aspect | Negotiated Clauses | Boilerplate Clauses |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Customized contract terms specifically tailored through party negotiation. | Standardized, pre-written clauses used routinely in contracts without modification. |
| Purpose | Address unique needs and specific risks relevant to the parties involved. | Ensure consistency, govern general contractual relationships, and provide default rules. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and adaptable to transaction specifics. | Typically rigid, rarely altered, serves as a default framework. |
| Examples | Pricing terms, delivery schedules, indemnification specifics. | Force majeure, governing law, dispute resolution, notice provisions. |
| Legal Impact | Directly influences the rights and obligations unique to the contract. | Establishes baseline legal protections and procedural norms. |
| Drafting Process | Requires detailed negotiation and mutual consent. | Included by default, minimal negotiation involved. |
| Risk Allocation | Specifically assigned by parties to manage unique risks. | Allocates general risks commonly accepted in contracts. |
Introduction to Contract Clauses
Negotiated clauses in contracts are tailored provisions directly discussed and agreed upon by the parties to address specific terms and conditions unique to their agreement. Boilerplate clauses consist of standard, pre-drafted provisions that provide consistency and legal stability across various contracts, covering general aspects such as jurisdiction, confidentiality, and dispute resolution. Understanding the distinction between negotiated and boilerplate clauses is crucial for effective contract drafting and risk management.
Defining Negotiated Clauses
Negotiated clauses are contract provisions specifically tailored and modified through direct discussions between parties to address unique aspects of a deal or relationship, ensuring mutual agreement on key terms. These clauses contrast with boilerplate clauses, which are standardized, pre-drafted sections commonly inserted to manage routine contractual obligations like governing law or dispute resolution. Defining negotiated clauses highlights their role in customizing agreements by reflecting the parties' distinct needs and risk allocations rather than relying on default, uniform language.
Understanding Boilerplate Clauses
Boilerplate clauses are standardized contract provisions that define the basic legal framework, such as jurisdiction, confidentiality, and dispute resolution, applied uniformly across agreements to ensure consistency and reduce risk. Unlike negotiated clauses, which are customized to address specific deal terms or parties' interests, boilerplate clauses often remain unchanged and serve as the contractual foundation. A clear understanding of boilerplate clauses is essential because their default terms can significantly impact enforceability and the relationship between contracting parties.
Key Differences Between Negotiated and Boilerplate Clauses
Negotiated clauses are tailored provisions actively discussed and modified by parties to address specific transaction risks and obligations, ensuring customized legal protection. Boilerplate clauses consist of standardized, pre-drafted language commonly found in contracts, providing consistency and predictable legal interpretation. Key differences lie in flexibility, customization, and the role each plays: negotiated clauses adapt to unique deal terms, while boilerplate clauses establish fundamental, generic contract frameworks.
Importance of Negotiated Clauses in Contracts
Negotiated clauses in contracts are crucial as they allow parties to tailor terms specific to their business needs, risk tolerance, and regulatory requirements, enhancing clarity and reducing potential disputes. Unlike boilerplate clauses, which are standardized and often generic, negotiated clauses address unique conditions such as pricing, delivery timelines, and liability, providing legal protection and operational flexibility. This customization fosters stronger contractual relationships by ensuring that all parties' interests are explicitly represented and enforceable.
Common Boilerplate Clauses and Their Purposes
Common boilerplate clauses in contracts include jurisdiction, force majeure, confidentiality, and indemnity provisions, each serving specific legal functions to manage risks and clarify responsibilities. Jurisdiction clauses determine the legal venue for dispute resolution, while force majeure clauses excuse performance delays due to unforeseen events. Confidentiality clauses protect sensitive information, and indemnity provisions allocate liability between parties, ensuring contract stability and predictability.
Risks of Relying Solely on Boilerplate Clauses
Relying solely on boilerplate clauses introduces significant legal and operational risks, as these standard provisions may not account for specific transactional nuances or evolving regulatory requirements. Such generic clauses can lead to ambiguities, enforceability issues, and unforeseen liabilities that expose parties to disputes and financial losses. Customizing negotiated clauses ensures alignment with the parties' intentions, risk tolerance, and jurisdiction-specific legal standards, thereby mitigating potential contractual vulnerabilities.
Customization Strategies for Negotiated Clauses
Negotiated clauses offer customizable provisions tailored to the specific needs and risks of contracting parties, enabling precise alignment with business goals and regulatory requirements. Customization strategies for negotiated clauses include iterative drafting, collaborative review sessions, and incorporating jurisdiction-specific legal nuances to enhance enforceability and clarity. This contrasts with boilerplate clauses, which serve as standardized, less flexible terms designed to provide general contract stability without adaptation to unique transaction contexts.
Best Practices for Drafting Balanced Clauses
Negotiated clauses are tailored through mutual agreement to address specific needs and risks, ensuring clarity and fairness between parties, while boilerplate clauses provide standardized legal language that governs general contractual terms. Best practices for drafting balanced clauses include clearly defining obligations, incorporating flexibility for unforeseen circumstances, and aligning language with the overall contract purpose to minimize disputes. Effective contract drafting requires blending negotiated specificity with the reliability of boilerplate provisions to achieve equitable and enforceable agreements.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Clause Approach
Selecting between negotiated clauses and boilerplate clauses depends on the complexity and specificity of the contract; negotiated clauses offer tailored solutions aligned with unique business needs, while boilerplate clauses provide standardized, risk-mitigated language for efficiency. Contracts involving distinctive terms or high-stakes arrangements benefit from customization through negotiated clauses to address nuanced legal and operational requirements. Conversely, boilerplate clauses ensure consistency and reduce negotiation time in routine agreements, supporting enforceability and legal certainty across standard transactions.
Negotiated Clauses Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com